INFORMATION:
Artificial intelligence enables smart control and fair sharing of resources in energy communities
2021-06-01
(Press-News.org) Energy communities will play a key role in building the more decentralised, less carbon intensive, and fairer energy systems of the future. Such communities enable local prosumers (consumers with own generation and storage) to generate, store and trade energy with each other -- using locally owned assets, such as wind turbines, rooftop solar panels and batteries. In turn, this enables the community to use more locally generated renewable generation, and shifts the market power from large utility companies to individual prosumers.
Energy community projects often involve jointly-owned assets such as community-owned wind turbines or shared battery storage. Yet, this raises the question of how these assets should be controlled - often in real time, and how the energy outputs jointly-owned assets should be shared fairly among community members, given not all members have the same size, energy needs or demand profiles.
It turns out that we can use Artificial Intelligence not only to use more renewable energy and protect the lifetime of expensive assets (such as batteries), but also to devise fairer ways to divide joint gains.
A paper recently published in Applied Energy: doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116575 by researchers from the Smart Systems Group (SSG) at Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland (UK), has shown that tools from distributed AI (specifically multi-agent systems) and cooperative game theory can be efficiently used to answer these questions.
Their work develops new algorithms for smart control of community energy assets (such as local wind turbines and batteries), both to use more locally generated electricity, and to extend the lifetime of energy assets. They compare the case when individual households invest in their own home battery vs. investing in a larger community energy storage unit, and show the benefits of a pooled storage approach. Next, they propose several practically applicable and computationally efficient mechanism to share the outputs of these assets between homes in a fair way. Their works makes use of the key concept of marginal value - borrowed from coalitional game theory and distributed AI, looking at what each member contributes to (and costs) the local community.
The authors were motivated in their work by real case studies from communities in the Responsive Flexibility (ReFLEX) project - the UK's largest smart energy demonstration project running on Orkney Islands in Scotland. In ongoing work, they also aim to explore the use of their methods for energy communities in India, in the framework of the CEDRI project (Community Energy Demand Reduction in India), a project led by researchers Heriot-Watt University in Scotland and the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) in New Delhi, India.
Sonam Norbu, the PhD student leading the work from the SSG group said: "This work is the first, to the best of our knowledge, to integrate a battery depreciation model in community energy optimization modelling. Data-driven monitoring of battery state of health is crucial for economically viable integration of local renewable generation, and the community energy model provides a very attractive application. Moreover, for researchers interested in cooperative game theory application in energy (which is a growing research area), the proposed model is one of the first to use such concepts in a community energy setting. Specifically, we propose a redistribution model for benefits in a community based on marginal value, a key concept in cooperative game theory."
Dr. Valentin Robu, Co-Director of the Smart Systems Group added: "This work, led by our PhD student Sonam Norbu, who joined us from Bhutan 3 years ago, demonstrates an excellent mix of top-level scientific impact and practical contribution. The contribution of the Responsive Flexibility project on Orkney Islands, one of the largest smart energy demonstration and "living lab" projects in the UK. I was delighted that Sonam's work was recently recognised by a nomination for the Young Professional Green Energy Academic Award, awarded yearly by Scottish Renewables, to top industry body for the renewable energy industry in Scotland."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
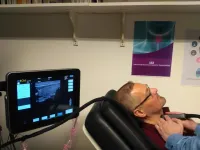
The LUCA device proves its readiness for a better thyroid cancer screening
2021-06-01
Thyroid nodules are a common pathology having a prevalence of 19-76% when screened with ultrasound, with higher frequencies in women. Current medical methods used to assess the malignancy of a nodule consist in performing an ultrasound, followed by a Doppler ultrasound, and then a biopsy. However, unfortunately, these methods present both low specificity and low sensitivity. This insufficient effectiveness in accurately being able to diagnose thyroid tumors leads to many unclear or unnoticed cases as well as many others that undergo unnecessary surgeries (false positives) and increase the cost ...
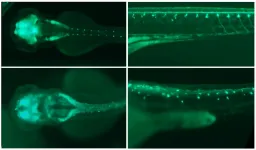
Gene plays major role in brain development
2021-06-01
When the Augustinian monk Gregor Mendel crossed white-flowering with purple-flowering pea plants in the mid-19th century, he made an interesting discovery: The offspring were all purple. He therefore called this trait dominant, while the white blossom color was recessive. The reason for this phenomenon: In peas, each gene occurs twice. One version comes from the maternal plant and the other from the paternal plant. If a pea has inherited the gene for purple flower color from one parent, but the gene for white flower color from the other, purple wins. Only when two genes for white flowers come together in the offspring plant is it white.
Humans also have genes that are inherited either dominantly or recessively. However, the case is not so clear for the mutations investigated ...
The secret lives of Canada lynx
2021-06-01
Using a Fitbit and a spy mic, scientists have discovered new insight into the behaviour of the elusive Canada lynx. A new study by researchers from McGill University, University of Alberta, and Trent University provides a first look at how miniaturized technology can open the door to remote wildlife monitoring.
"Working on one of the boreal forest's top predators, the Canada lynx, we found that two different technologies, accelerometers and audio recording devices, can be used to remotely monitor the hunting behaviour of predators, even documenting the killing of small prey," says lead author Emily Studd, a Postdoctoral Fellow under the supervision of Murray Humphries at McGill University and Stan Boutin at University ...
Survey shows weak trust in Canadian courts on energy projects, climate policy disputes
2021-06-01
The University of Ottawa's Positive Energy program released new survey results showing that a large segment of the Canadian public does not trust the courts to settle disputes over energy projects or climate policy. The survey was conducted by Positive Energy's official pollster, Nanos Research.
Canadians were asked: On a scale of 0 to 10, where 0 means do not trust at all and 10 means trust completely, how much do you trust the courts to settle disputes over government decisions on energy projects? They were asked the same question for climate policy. The results are very similar. Only one in three Canadians trust the courts to settle disputes over energy projects or climate policy (answering between 7 and 10: 31% for energy, 30% for ...
Trust the machine -- it knows what it is doing
2021-06-01
Machine learning, when used in climate science builds an actual understanding of the climate system, according to a study published in the journal Chaos by Manuel Santos Gutiérrez and Valerio Lucarini, University of Reading, UK, Mickäel Chekroun, the Weizmann Institute, Israel and Michael Ghil, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France. This means we can trust machine learning and further its applications in climate science, say the authors. The study is part of the European Horizon 2020 TiPES project on tipping points in the Earth system. TiPES is administered from the University of Copenhagen, Denmark.
Man or ...
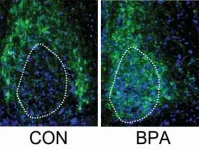
UCalgary study shows BPA exposure below regulatory levels can impact brain development
2021-06-01
Humans are exposed to a bath of chemicals every day. They are in the beds where we sleep, the cars that we drive and the kitchens we use to feed our families. With thousands of chemicals floating around in our environment, exposure to any number is practically unavoidable. Through the work of researchers like Dr. Deborah Kurrasch, PhD, the implications of many of these chemicals are being thoroughly explored.
"Manufacturers follow standards set by regulatory bodies, it's not up to the manufacturers to prove the chemicals in consumer products are safe," says Kurrasch, a researcher in the University of Calgary's Hotchkiss Brain ...
Right-wing rhetoric and the trivialization of pandemic casualties
2021-06-01
Right-wing voices set out powerful but misleading arguments to justify inaction by the Trump administration during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study of the rhetoric used by high-level government officials and influential commentators in the US during the first half of 2020.
In a study published in the DeGruyter journal Open Anthropological Research, Professor Martha Lincoln of San Francisco State University examined how public officials openly pushed for people to accept widespread illness and death from the virus by adopting a tone that suggested premature death was normal and the scale of death acceptable in the grander ...
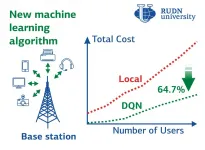
RUDN mathematician found a way to boost computations for IoT devices by three times
2021-06-01
RUDN mathematician and his colleagues from China, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, United Kingdom, and Qatar have developed an algorithm allowing the distribution of computing tasks between the IoT devices and the cloud in an optimal way. As a result, the power and time costs are reduced by about three times. The study was published in the Big Data.
With the development of technologies and devices, Internet of Things (IoT) applications require more and more computing power. The amount of data that the IoT devices need to process can be so large that it is reasonable to migrate computing to the cloud. Cloud computing provides flexible data processing and storage capabilities. But Computation offloading, meaning transferring of the resource-intensive processes ...
A new soft electronic material for human-machine-interfacing
2021-06-01
A DTU research team consisting of Malgorzata Gosia Pierchala, Firoz Babu Kadumundi, and Mehdi Mehrali from #TeamBioEngine headed by Alireza Dolatshahi-Pirouz, have developed a new material - CareGum - that among other things has potential for monitoring motor impairment associated with neurological disorders such as Parkinson's.
A green material with many properties
The CareGum property portfolio is incredibly broad with feats such as skin-like softness, it is stretchable up to 30,000 % and has self-healing capacities reminiscent of that of natural tissues. It is printable, moldable, and electrically conductive. Notably, the electrical conductivity enables the material to respond to external stimuli ...
Oncotarget: STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
2021-06-01
Oncotarget published "STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells" which reported that what induces GLI1 expression in GLI1-unmutated CLL cells is unknown.
Because signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is constitutively activated in CLL cells and sequence analysis detected putative STAT3-binding sites in the GLI1 gene promoter, the authors hypothesized that STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1.
Western immunoblotting detected GLI1 in CLL cells from 7 of 7 patients, flow cytometry analysis confirmed that CD19 /CD5 CLL cells co-express GLI1 and confocal microscopy showed co-localization of GLI1 and phosphorylated STAT3. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed ...