(Press-News.org) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. NAFLD patients are at higher risk of developing Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which causes severe and chronic liver inflammation, fibrosis and liver damage. A patient with NASH is believed to be at high risk for developing a form of liver cancer called hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Apart from lifestyle interventions, there are currently no approved treatments for NASH. A liver transplant is sometimes the only remedy.
While risk factors for NASH (obesity, type-2 diabetes and gene mutations like PNPLA3) and HCC (Hepatitis B and C infections, alcohol overconsumption and cirrhosis) are well known, the precise mechanism of how simple fatty liver progresses to chronic inflammation, liver fibrosis, NASH and HCC is not known.
A recent study led by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found in a mouse model that when fed a Western diet rich in calories, fat and cholesterol, the mice progressively became obese, diabetic and developed NASH, which progressed to HCC, chronic kidney and cardiovascular disease.
The findings, published in the May 31, 2021 online edition of Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, showed that by simply changing the Western diet in a mouse model to a normal chow diet, where calories are derived from proteins and carbohydrates rather than fats, with no cholesterol, NASH and liver fibrosis were improved; and cancer progression and mortality prevented.
"While the mice that continued on a Western diet developed HCC and had an increased risk of death, 100 percent of the mice that stopped the diet survived the length of the study without developing HCC," said Debanjan Dhar, PhD, co-senior author of the study and assistant professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology at UC San Diego School of Medicine.
"This indicates that NASH and HCC may be a preventable disease and that diet plays a crucial role in the disease outcome."
In mice no longer fed the Western diet, researchers also found a decrease in liver fat and improvement in glucose tolerance -- an indicator of diabetes -- and several genes and cytokines that were affected in NASH returned to normal levels and function. In addition, Dhar and his team found key changes in the gut microbiome that modulate liver disease progression.
"Although NASH is a liver disease, our results show its development and progression is orchestrated by multiple organs."
A surprising finding, said the researchers, was that when they switched the Western diet of the mice with NASH to normal chow, the effect was more pronounced on the liver rather than on whole body weight.
"This could mean that slight changes in the liver might have profound effects on the disease outcome," said David Brenner, MD, co-senior author and vice chancellor of UC San Diego Health Sciences.
Researchers also compared mouse model findings to human patient datasets, indicating that gene expression changes in mouse livers were similar to human counterparts.
"Our animal model provides an important pre-clinical testing platform to study the safety and efficacy of drugs that are currently being developed, as well as to test the repurposing of other drugs that are already FDA approved for other diseases," said Dhar.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include: Souradipta Ganguly, Linshan Shang, Ruoyu Wang, Yanhan Wang, Bernd Schnabl, Rob Knight, Sara Brin Rosenthal, Gibraan Rahman, Anthony Diomino, Tatiana Kisseleva, Mojgan Hosseini and Mojgan Hosseini, all with UC San Diego; German Aleman Muench and Pejman Soorosh with Janssen Research and Development; and Hyeok Choon Kwon with National Medical Center, South Korea.
CHAPEL HILL, North Carolina--Researchers have discovered a gene, OTUD7A, that impacts the development of Ewing sarcoma, a bone cancer that occurs mainly in children. They have also identified a compound that shows potential to block OTUD7A protein activity. The finding, by scientists at the University of North Carolina and the Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, appeared online June 1, 2021, in Advanced Science.
About 250 children and young adults are diagnosed with Ewing sarcoma each year in the U.S. About half of those diagnosed will ultimately succumb to the disease, pointing to the need for better therapies.
"Our primary research focus targeted the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein found in about 85 percent of Ewing sarcoma patients," said UNC Lineberger's ...
"SWOG always brings an impressive portfolio of work to the ASCO annual meeting," said SWOG Chair Charles D. Blanke, MD, "and this year I'm particularly excited about the research our investigators are presenting because it includes results that are likely to be practice-changing."
Investigators will present 12 abstracts from SWOG-led or co-led studies and 11 abstracts from studies led by other groups within the National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN).
Results from S1216 will be presented orally by study chair Neeraj Agarwal, MD, of the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah. S1216 compared androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) combined with TAK-700 to the standard ...
Quantum computing and quantum sensing have the potential to be vastly more powerful than their classical counterparts. Not only could a fully realized quantum computer take just seconds to solve equations that would take a classical computer thousands of years, but it could have incalculable impacts on areas ranging from biomedical imaging to autonomous driving.
However, the technology isn't quite there yet.
In fact, despite widespread theories about the far-reaching impact of quantum technologies, very few researchers have been able to demonstrate, using the technology available now, that quantum methods have an advantage over their classical counterparts.
In a paper published on June 1 in the journal Physical Review X, University of Arizona researchers experimentally ...
Irvine, CA - June 1, 2021 - A new study analyzing the association between an individual's genetics (genotype) and their observable characteristics resulting from the interaction of genetics and the environment (phenotype), contributes new knowledge to the understanding of human complex traits and diseases.
The study titled, "An atlas of alternative polyadenylation quantitative trait loci (3?aQTLs) contributing to complex trait and disease heritability," was recently published in Nature Genetics. Led by University of California, Irvine professor of ...
Over 50% of adults surveyed across six different countries report experiencing weight stigma, and those who engage in self-stigma and self-blame for their weight are more likely to avoid healthcare, obtain less frequent checkups, and perceive less respect from doctors, according to two new studies from the UConn Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity. These studies, which compared experiences of adults in Australia, Canada, France, Germany, the UK, and the US are the first multi-national studies to examine the link between weight stigma and negative ...
Plasmodium vivax malaria is a mosquito-borne illness that causes significant morbidity. However, the household and healthcare provider costs of the disease are unknown. A new study published in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Dr Angela Devine at Menzies School of Health Research in Australia, and colleagues estimate the global economic burden of P. vivax for the first time using country-level data.
Researchers first estimated household and healthcare provider P. vivax costs, then collated and combined these data with national case estimates for 44 endemic countries in 2017. The resulting global cost estimate was US$359 million.
The authors wanted to explore how these cost estimates might change with widespread access to radical cure. Radical ...
Observational studies have suggested that increased vitamin D levels may protect against COVID-19. However, these studies were inconclusive and possibly subject to confounding. A study published in PLOS Medicine by Guillaume Butler-Laporte and Tomoko Nakanishi at McGill University in Quebec, Canada, and colleagues suggests that genetic evidence does not support vitamin D as a protective measure against COVID-19.
The ability of vitamin D to protect against severe COVID-19 illness is of great interest to public health experts, but has limited supporting evidence. To assess the relationship between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 susceptibility ...
A nationwide study in Sweden estimates the elevated risk of advanced or fatal prostate cancer among relatives of men with the disease, providing new data that could help refine guidelines for the age at which screening should begin. Mahdi Fallah and Elham Kharazmi of the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in Heidelberg, Germany, and colleagues present these new findings in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
Clinical guidelines for the age to start prostate cancer screening aim to ensure that the benefits of identifying the disease early ...
The malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax may accumulate in the spleen soon after infection to a greater extent than its better-known relative P. falciparum, according to new research published by John Woodford of the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia and colleagues in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
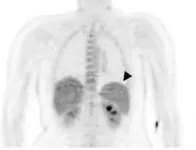
Managing and treating P. vivax and P. falciparum infections calls for investigation of their different pathways of infection, and our limited understanding of disease pathology has generally relied on indirect and imprecise approaches. Woodford and colleagues studied 7 healthy participants who were infected under controlled conditions with either P. vivax or P. falciparum. They underwent a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) ...
Many organisms in need of conservation are still unknown or lumped in with similar species, which potentially interferes with conservation efforts. In a new study published June 1 in the Open Access journal PLOS Biology, Jane Melville of Museums Victoria, and her colleagues present a new "return-on-investment" approach to best direct efforts to identify new species before they are lost.
Humans have had a profoundly destructive impact on global biodiversity. However, this loss of biodiversity may be even greater than scientists have realized, due to the unknown number of undocumented species. Before a species and its habitat can be preserved, though, it must first ...