Using advanced imaging to study sickle cell disease
Pitt's Tamer Ibrahim uses recently optimized 7-Tesla MRI imaging technology to study SCD's effect on the brain
2021-06-03
(Press-News.org) Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a genetically inherited group of red blood cell disorders. END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers reveal the inner workings of a viral DNA-packaging motor
2021-06-03
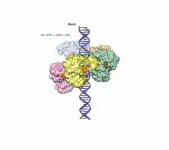
DURHAM, N.C. - A group of researchers have discovered the detailed inner workings of the molecular motor that packages genetic material into double-stranded DNA viruses. The advance provides insight into a critical step in the reproduction cycle of viruses such as pox- herpes- and adeno-viruses. It could also give inspiration to researchers creating microscopic machines based on naturally occurring biomotors.
The research was conducted by scientists from Duke University, the University of Minnesota, the University of Massachusetts and the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB). The results appear online in a trilogy of papers published in Science Advances, ...
Fifty years of progress in women's health
2021-06-03
WHO: JoAnn Manson, MD, DrPH, Physician and Epidemiologist, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; co-author of a new Perspective piece published in The New England Journal of Medicine (pdf attached)
WHAT: Less than 50 years ago, a U.S. Supreme Court decision paved the way for women's use of contraception irrespective of marital status, and a year later, in 1973, the Court ruled in Roe v. Wade that women have a right to legalized abortion. In recent decades, clinical researchers and policymakers alike have made important strides ...
Let's talk about the elephant in the data
2021-06-03
You would not be surprised to see an elephant in the savanna or a plate in your kitchen. Based on your prior experiences and knowledge, you know that is where elephants and plates are often to be found. If you saw a mysterious object in your kitchen, how would you figure out what it was? You would rely on your expectations or prior knowledge. Should a computer approach the problem in the same way? The answer may surprise you. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Partha Mitra described how he views problems like these in a "Perspective" in Nature Machine Intelligence. He hopes his insights will help researchers teach computers how to analyze complex systems more effectively.
Mitra thinks it helps to understand the nature of knowledge. Mathematically speaking, many data scientists ...
Which way does the solar wind blow?
2021-06-03
The surface of the sun churns with energy and frequently ejects masses of highly-magnetized plasma towards Earth. Sometimes these ejections are strong enough to crash through the magnetosphere -- the natural magnetic shield that protects the Earth -- damaging satellites or electrical grids. Such space weather events can be catastrophic.
Astronomers have studied the sun's activity for centuries with greater and greater understanding. Today, computers are central to the quest to understand the sun's behavior and its role in space weather events.
The ...
Polar vortex, winter heat may change bird populations
2021-06-03
MADISON, Wis. -- For birds and other wildlife, winter is a time of resource scarcity. Extreme winter weather events such as a polar vortex can push some species to the edge of survival. Yet winter tends to get short shrift in climate change research, according to UW-Madison forest and wildlife ecology Professor Ben Zuckerberg.
"When we think about the impact of climate change, winter tends to be overlooked as a time of year that could have significant ecological and biological implications," says Zuckerberg. "It makes me, and my colleagues, think quite deeply about the impacts of these extreme events during this time when species are particularly vulnerable."
Zuckerberg, ...
Water droplets become hydrobots by adding magnetic beads
2021-06-03
Using a piece of magnet, researchers have designed a simple system that can control the movement of a small puddle of water, even when it's upside down. The new liquid manipulation strategy, described in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science on June 3, can have a wide range of applications including cleaning hard-to-reach environments or delivering small objects.
Previous attempts to control the movement of fluids often relied on special platforms. For example, on a surface that has one section more hydrophobic than another, water will spontaneously ...
Puppies are born ready to communicate with people, study shows
2021-06-03
Anyone that's ever interacted with a dog knows that they often have an amazing capacity to interact with people. Now researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on June 3 have found that this ability is present in dogs from a very young age and doesn't require much, if any, prior experience or training. But, some of them start off better at it than others based on their genetics.
"We show that puppies will reciprocate human social gaze and successfully use information given by a human in a social context from a very young age and prior to extensive experience with humans," said Emily E. Bray of the University of Arizona, Tucson. "For example, even before puppies have left their littermates to live ...
North Atlantic right whales have gotten smaller since the 1980s
2021-06-03
Whales are largely protected from direct catch, but many populations' numbers still remain far below what they once were. A study published in the journal Current Biology on June 3 suggests that, in addition to smaller population sizes, those whales that survive are struggling. As evidence, they find that right whales living in the North Atlantic today are significantly shorter than those born 30 to 40 years ago.
"On average, a whale born today is expected to reach a total length about a meter shorter than a whale born in 1980," said Joshua Stewart of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in La Jolla, CA. That represents an average decline in length of about 7%. "But that's just the average--there are also some extreme cases where young whales are several ...
Predictive model identifies patients for genetic testing
2021-06-03
Patients who, perhaps unbeknownst to their health care providers, are in need of genetic testing for rare undiagnosed diseases can be identified en masse based on routine information in electronic health records (EHRs), a research team reported today in the journal Nature Medicine.
Findings from the Vanderbilt University Medical Center study suggest that, among the patients of any sizeable health care system, there are hundreds or thousands with undiagnosed rare diseases of the sort where a genetic test could lead to a diagnosis.
"Patients with rare genetic diseases often face ...
Changes in pregnancy, birth rates during COVID-19
2021-06-03
What The Study Did: Changes in pregnancy and birth rates before and after COVID-19 lockdown measures were estimated using electronic medical records.
Authors: Molly J. Stout, M.D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11621)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
[Press-News.org] Using advanced imaging to study sickle cell diseasePitt's Tamer Ibrahim uses recently optimized 7-Tesla MRI imaging technology to study SCD's effect on the brain