(Press-News.org) Fukuoka, Japan--According to the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017, close to nine percent of the global population lives with some form of chronic kidney disease, or CKD. Not only does the condition affect renal function, CKD has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Now, in a new study that could aid the development of therapeutic drugs to reduce these cardiac complications, researchers led by Kyushu University have found an underlying molecular pathway that can explain how chronic kidney disease induces heart failure.
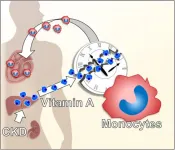
Studying mice, the researchers found that a key driver is the dysfunction of a type of white blood cell called a monocyte. The dysfunction is caused by increased levels of vitamin A and its binding protein--a common symptom of chronic kidney disease--breaking a well-known genetic pathway: the circadian clock.
The circadian clock is one of the most indispensable biological functions in living organisms. Common understanding of the pathway is that it controls our sleep patterns. However, the circadian clock plays a much larger role, affecting blood pressure, metabolic rate, and even hormone levels. In fact, nearly 10% of our genes are directly influenced by the circadian clock.
These properties made it a natural target for Shigehiro Ohdo, professor of Kyushu University's Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, and his team for investigating the causes of chronic kidney disease-induced heart inflammation and fibrosis.
"We found that mice with a mutated Clock gene--one of the main regulators of the circadian clock--have decreased symptoms of heart problems related to chronic kidney disease, despite having high blood pressure," explains Yuya Yoshida, one of the first authors of the study published in the journal Nature Communications.
To search for the underlying cause of this protective effect, the team looked for abnormalities in genes that connect Clock and kidney dysfunction.
"Our investigation led us to find that a protein called 'G protein-coupled receptor 68,' or GPR68, produced in monocytes was playing a key role. GPR68 is known to increase the production of proteins that cause inflammation, and more importantly, it is regulated by the Clock gene," states Naoya Matsunaga, another author of the study.
One sign of kidney dysfunction is elevated levels of vitamin A and its binding protein, two molecules that are usually carefully controlled. The researchers found that this elevation disrupts the normal activity of the circadian clock in monocytes, which in turn over-express GPR68.
These high-GPR68-expressing monocytes then infiltrate the heart and cause inflammation and fibrosis. This explains why mice with defective Clock genes have less severe CKD-induced heart problems: there is no Clock gene to produce GPR68.
"Our study reveals a previously unknown role of monocytic clock genes in CKD-induced heart failure," concludes Ohdo. "The findings will help us develop therapeutic drugs such as ones targeting GPR68. We also can investigate better treatments for abnormal vitamin A accumulation in the blood."
INFORMATION:
For more information about this research, see "Alteration of circadian machinery in monocytes underlies chronic kidney disease-associated cardiac inflammation and fibrosis," Yuya Yoshida, Naoya Matsunaga, Takaharu Nakao, Kengo Hamamura, Hideaki Kondo, Tomomi Ide, Hiroyuki Tsutsui, Akito Tsuruta, Masayuki Kurogi, Michio Nakaya, Hitoshi Kurose, Satoru Koyanagi, and Shigehiro Ohdo, Nature Communications (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23050-x.
Overview:
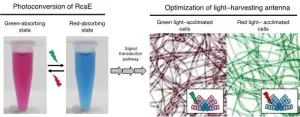
Certain cyanobacteria can change the absorbing light colors for photosynthesis using a green- and red-light sensing photosensor protein. A Japanese research group elucidated the molecular structure of RcaE, a representative member of the photosensors. They revealed the unique conformation of the bilin chromophore and the unique protein structure that potentially functions as a proton transfer route to bilin. They also demonstrated that RcaE undergoes protonation and deprotonation of the bilin chromophore during the green and red photoconversion. These results provide insights into how cyanobacteria evolved photosensors with diverse spectral sensitivities and contribute to the development of new photoswitches of ...
Coral insights into 1,000 years of seasonal changes in the Arabian Sea warn of significant impacts caused by global warming.
Every year, the southwesterly winds of the summer monsoon sweep down the Arabian Peninsula, pushing the surface waters of the Arabian Sea away from the coast and driving an upwelling of deep waters to the surface. This rising seawater is colder and less saline than the surface water and is rich in nutrients, providing energy for the various organisms living in the Arabian Sea and Indian Ocean.
Scientists from Japan, Taiwan and Germany, including coral reef scientist Dr. Tsuyoshi Watanabe of Hokkaido University, have uncovered evidence from corals off the coast of Oman suggesting that global warming is causing changes to the Arabian Sea that could impact the ...
Delicious to some, but a bitter bane to others' taste buds, vegetables like broccoli rabe, bok choy and turnips are a dinner staple ---and picky eater conflict --- around the world.
It all likely started in the mountains near present-day Afghanistan, where humans first domesticated turnips 3,500 to 6,000 years ago, according to a new study recently published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution. University of Wisconsin-Madison Professor of Botany Eve Emshwiller and her former graduate student Alex McAlvay (now an assistant curator assistant ...
HOUSTON-(June 3, 2021) - Results were released this week on a new treatment with the potential to improve the outcomes for patients with hereditary BRCA mutations and high-risk, early-stage breast cancer. These results represent the first time a drug that blocks cancer cells from repairing their DNA (called a PARP inhibitor) has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer returning in high-risk patients following completion of standard chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy.
Titled "Adjuvant Olaparib for Patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 Mutated Breast Cancer," the paper appears in the June 3 issue of the ...
Could an over-the-counter health "shot" help fight COVID-19? George Mason University researchers think it just might. ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A study by Mayo Clinic researchers provides some clarity in the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC), such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, to treat acute venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. The findings were published Wednesday, June 2, in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Among the study's findings:
Rivaroxaban showed no higher risk of bleeding in luminal gastrointestinal cancer and should not be considered contraindicated in this group of patients.
Apixaban showed a higher risk of bleeding in patients with luminal gastrointestinal cancer, and it should be used with great caution to treat this type of cancer until more studies ...
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Plastics are everywhere. From cell phones to pens and cars to medical devices, the modern world is full of plastic-- and plastic waste. New research from scientists at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) END ...
A team led by UC Riverside engineers has developed a catalyst to remove a dangerous chemical from water on Earth that could also make Martian soil safer for agriculture and help produce oxygen for human Mars explorers.
Perchlorate, a negative ion consisting of one chlorine atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, occurs naturally in some soils on Earth, and is especially abundant in Martian soil. As a powerful oxidizer, perchlorate is also manufactured and used in solid rocket fuel, fireworks, munitions, airbag initiators for vehicles, matches and signal flares. It is a byproduct in some disinfectants ...
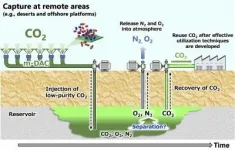
Fukuoka, Japan - The global threat of ongoing climate change has one principal cause: carbon that was buried underground in the form of fossil fuels is being removed and released into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2). One promising approach to addressing this problem is carbon capture and storage: using technology to take CO2 out of the atmosphere to return it underground.
In a new study published in Greenhouse Gases Science and Technology, researchers from Kyushu University and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan, investigated geological storage of low-purity CO2 mixed with nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), produced by direct air capture (DAC) using membrane-based technology.
Many current ...
Climate scientists at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU, Singapore) have extended the known record of Singapore's sea-level to almost 10,000 years ago, providing a more robust dataset to aid future predictions of sea-level rise.
One of the main challenges in researching climate change is to reconstruct its history over thousands of years. To have a better sense of the potential causes and effects of future changes, scientists need to learn from and understand the past.
Extracting ancient sediments from a depth of up to 40 m underground at a site at Singapore's Marina South, an international team led by NTU researchers put the samples through rigorous laboratory ...