How to retard time for cells
Heavy water makes biological clocks tick more slowly
2021-06-04
(Press-News.org) They recently published their findings in the renowned journal "Advanced Materials". Cells are not only our biological building blocks, but also highly dynamic, active systems. The research group led by Professor Käs has succeeded in significantly reducing these dynamics with heavy water, without damaging the cells.
"Generally, a lot of people know heavy water for its important technical use in nuclear power plants. We took a different approach here and were able to show that for cells, time - or, more specifically, their dynamics - can be significantly slowed down in the presence of heavy water," said Käs, who has devoted himself to researching the physical properties of cells and tissue. The research showed on various biological levels that the movement of cells and their dynamics was only taking place in slow motion. "It is very intriguing that cellular dynamics can be slowed down at the same temperature. So far, only the theory of relativity has offered such possibilities in the physical context," explained Käs. He added that the results form the basis of a method to offer cells and organs longer-lasting protection against degeneration.
The researchers confirmed this effect with a variety of complementary methods and attributed the observations to an increased interaction between the structural proteins. "Heavy water also forms hydrogen bonds, but these are stronger than in normal aqueous environments. As a result, structural proteins such as actin seem to interact more strongly with one another and briefly stick together. What is spectacular here is that the effects are reversible, with cells showing their native properties again as soon as they are transferred into a normal aqueous medium," said Dr Jörg Schnauß. "What is even more astonishing is that these changes show the fingerprint of a passive material. However, cells are highly active and far from thermodynamic equilibrium. If they behave like a passive material, they are usually dead," added Käs.
However, as the researchers were able to show, this was not the case in their experiments. They now hope to be able to use the knowledge gained to keep cells or even tissue vital for longer. If this approach is confirmed, heavy water could be used for longer storage times, for example during organ transplants.
INFORMATION:
Original title of the publication in Advanced Materials:
"Cells in Slow Motion: Apparent Undercooling Increases Glassy Behavior at Physiological Temperatures"
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-04
Graphene may be among the most exciting scientific discoveries of the last century. While it is strikingly familiar to us--graphene is considered an allotrope of carbon, meaning that it essentially the same substance as graphite but in a different atomic structure--graphene also opened up a new world of possibilities for designing and building new technologies.
The material is two-dimensional, meaning that each "sheet" of graphene is only 1 atom thick, but its bonds make it as strong as some of the world's hardest metal alloys while remaining lightweight and flexible. This valuable, unique mix of properties have piqued the interest of scientists from a wide range of fields, leading to research in using graphene for next-generation ...
2021-06-04
Engaged listening techniques such as eye contact, nodding and using key words to praise openness helps teenagers when they admit bad behaviour and share hurt feelings with their parents, a new study has shown.
University of Reading and Haifa researchers asked 1001 13 to 16-year-olds to watch a staged conversation between a parent and teenager about a difficult situation, with the parent adopting different body language and listening behaviour in different versions.
The participants who watched the versions where the parent was visibly attentive stated that they would have felt better about themselves as the teenager and would be more likely to open up about their ...
2021-06-04
Water is weird - and yet so important. In fact, it is one of the most unusual molecules on Earth. It boils at a temperature it shouldn't. It expands and floats when it is in the solid-state. Its surface tension is higher than it should be. Now, new research published in the journal Nature has added one other equally strange property to water's list of oddities. The implications of this new revelation could have a remarkable impact on all water-related processes from water purification to drug manufacturing.
Stephen Cronin, professor of electrical and computer engineering at USC Viterbi School of Engineering, ...
2021-06-04
Cancer researchers say they have established a new, life-extending treatment option for men with prostate cancer that has spread and become resistant to hormone therapy. The injected treatment combines a targeting compound with a radioactive isotope to irradiate and kill cancer cells.
An international clinical trial sponsored by Endocyte, Inc., a Novartis company tested the targeted radioligand therapy in study participants with advanced prostate cancer. All subjects had cancers that had spread to other organs and continued to progress after previous treatment with two kinds of drugs, androgen axis inhibitors and taxanes. The experimental treatment significantly extended survival, delayed ...
2021-06-04
Leesburg, VA, June 4, 2021--According to a pilot study published in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), the flexed elbow valgus external rotation (FEVER) view can improve MRI evaluation of the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) in Major League Baseball (MLB) pitchers.
"The increased joint space width confirms elbow valgus stress with FEVER view," wrote corresponding author Thomas Knoblauch at the University of Nevada Las Vegas. "Diagnostic confidence increased, and additional UCLs were identified as abnormal."
Due to repetitive extreme valgus stress during overhead throwing maneuvers, UCL injuries remain common in throwing athletes. Because standard positioning for elbow MRI ...
2021-06-04
DALLAS - June 4, 2021 - Increasing a protein concentrated in brown fat appears to lower blood sugar, promote insulin sensitivity, and protect against fatty liver disease by remodeling white fat to a healthier state, a new study led by UT Southwestern scientists suggests. The END ...
2021-06-04
Fukuoka, Japan--According to the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017, close to nine percent of the global population lives with some form of chronic kidney disease, or CKD. Not only does the condition affect renal function, CKD has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Now, in a new study that could aid the development of therapeutic drugs to reduce these cardiac complications, researchers led by Kyushu University have found an underlying molecular pathway that can explain how chronic kidney disease induces heart failure.
Studying mice, the researchers found that a key driver is the dysfunction of a type of white blood cell called a ...
2021-06-04
Overview:
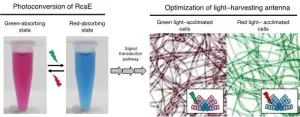
Certain cyanobacteria can change the absorbing light colors for photosynthesis using a green- and red-light sensing photosensor protein. A Japanese research group elucidated the molecular structure of RcaE, a representative member of the photosensors. They revealed the unique conformation of the bilin chromophore and the unique protein structure that potentially functions as a proton transfer route to bilin. They also demonstrated that RcaE undergoes protonation and deprotonation of the bilin chromophore during the green and red photoconversion. These results provide insights into how cyanobacteria evolved photosensors with diverse spectral sensitivities and contribute to the development of new photoswitches of ...
2021-06-04
Coral insights into 1,000 years of seasonal changes in the Arabian Sea warn of significant impacts caused by global warming.
Every year, the southwesterly winds of the summer monsoon sweep down the Arabian Peninsula, pushing the surface waters of the Arabian Sea away from the coast and driving an upwelling of deep waters to the surface. This rising seawater is colder and less saline than the surface water and is rich in nutrients, providing energy for the various organisms living in the Arabian Sea and Indian Ocean.
Scientists from Japan, Taiwan and Germany, including coral reef scientist Dr. Tsuyoshi Watanabe of Hokkaido University, have uncovered evidence from corals off the coast of Oman suggesting that global warming is causing changes to the Arabian Sea that could impact the ...
2021-06-04
Delicious to some, but a bitter bane to others' taste buds, vegetables like broccoli rabe, bok choy and turnips are a dinner staple ---and picky eater conflict --- around the world.
It all likely started in the mountains near present-day Afghanistan, where humans first domesticated turnips 3,500 to 6,000 years ago, according to a new study recently published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution. University of Wisconsin-Madison Professor of Botany Eve Emshwiller and her former graduate student Alex McAlvay (now an assistant curator assistant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How to retard time for cells
Heavy water makes biological clocks tick more slowly