Giving brown fat a boost to fight type 2 diabetes
Increasing a protein concentrated in brown adipose tissue remodels white adipose tissue to lower diabetes risk, study suggests
2021-06-04
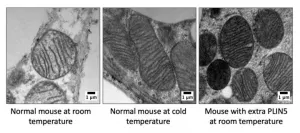
(Press-News.org) DALLAS - June 4, 2021 - Increasing a protein concentrated in brown fat appears to lower blood sugar, promote insulin sensitivity, and protect against fatty liver disease by remodeling white fat to a healthier state, a new study led by UT Southwestern scientists suggests. The END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How do bad kidneys lead to heart disease? Broken cellular clocks provide new clues
2021-06-04
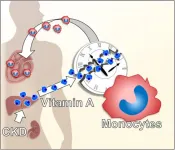
Fukuoka, Japan--According to the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017, close to nine percent of the global population lives with some form of chronic kidney disease, or CKD. Not only does the condition affect renal function, CKD has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Now, in a new study that could aid the development of therapeutic drugs to reduce these cardiac complications, researchers led by Kyushu University have found an underlying molecular pathway that can explain how chronic kidney disease induces heart failure.
Studying mice, the researchers found that a key driver is the dysfunction of a type of white blood cell called a ...
Structural uniqueness of the green- and red-light sensing photosensor in cyanobacteria
2021-06-04
Overview:
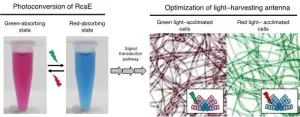
Certain cyanobacteria can change the absorbing light colors for photosynthesis using a green- and red-light sensing photosensor protein. A Japanese research group elucidated the molecular structure of RcaE, a representative member of the photosensors. They revealed the unique conformation of the bilin chromophore and the unique protein structure that potentially functions as a proton transfer route to bilin. They also demonstrated that RcaE undergoes protonation and deprotonation of the bilin chromophore during the green and red photoconversion. These results provide insights into how cyanobacteria evolved photosensors with diverse spectral sensitivities and contribute to the development of new photoswitches of ...
Corals tell Arabian Sea story of global warming
2021-06-04
Coral insights into 1,000 years of seasonal changes in the Arabian Sea warn of significant impacts caused by global warming.
Every year, the southwesterly winds of the summer monsoon sweep down the Arabian Peninsula, pushing the surface waters of the Arabian Sea away from the coast and driving an upwelling of deep waters to the surface. This rising seawater is colder and less saline than the surface water and is rich in nutrients, providing energy for the various organisms living in the Arabian Sea and Indian Ocean.
Scientists from Japan, Taiwan and Germany, including coral reef scientist Dr. Tsuyoshi Watanabe of Hokkaido University, have uncovered evidence from corals off the coast of Oman suggesting that global warming is causing changes to the Arabian Sea that could impact the ...
Don't like your greens? Blame it on Brassica domestication
2021-06-04
Delicious to some, but a bitter bane to others' taste buds, vegetables like broccoli rabe, bok choy and turnips are a dinner staple ---and picky eater conflict --- around the world.
It all likely started in the mountains near present-day Afghanistan, where humans first domesticated turnips 3,500 to 6,000 years ago, according to a new study recently published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution. University of Wisconsin-Madison Professor of Botany Eve Emshwiller and her former graduate student Alex McAlvay (now an assistant curator assistant ...
New findings offer improved therapy of early-stage, BRCA mutation-associated breast cancer
2021-06-04
HOUSTON-(June 3, 2021) - Results were released this week on a new treatment with the potential to improve the outcomes for patients with hereditary BRCA mutations and high-risk, early-stage breast cancer. These results represent the first time a drug that blocks cancer cells from repairing their DNA (called a PARP inhibitor) has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer returning in high-risk patients following completion of standard chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy.
Titled "Adjuvant Olaparib for Patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 Mutated Breast Cancer," the paper appears in the June 3 issue of the ...
Mason scientists explore herbal treatment for COVID-19
2021-06-04
Could an over-the-counter health "shot" help fight COVID-19? George Mason University researchers think it just might. ...
Mayo Clinic study provides clarity on use of anticoagulants in gastrointestinal cancers
2021-06-04
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A study by Mayo Clinic researchers provides some clarity in the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC), such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, to treat acute venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. The findings were published Wednesday, June 2, in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Among the study's findings:
Rivaroxaban showed no higher risk of bleeding in luminal gastrointestinal cancer and should not be considered contraindicated in this group of patients.
Apixaban showed a higher risk of bleeding in patients with luminal gastrointestinal cancer, and it should be used with great caution to treat this type of cancer until more studies ...
Salt marshes trap microplastics in their sediments, creating record of human plastic use
2021-06-04
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Plastics are everywhere. From cell phones to pens and cars to medical devices, the modern world is full of plastic-- and plastic waste. New research from scientists at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) END ...
A new water treatment technology could also help Mars explorers
2021-06-04
A team led by UC Riverside engineers has developed a catalyst to remove a dangerous chemical from water on Earth that could also make Martian soil safer for agriculture and help produce oxygen for human Mars explorers.
Perchlorate, a negative ion consisting of one chlorine atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, occurs naturally in some soils on Earth, and is especially abundant in Martian soil. As a powerful oxidizer, perchlorate is also manufactured and used in solid rocket fuel, fireworks, munitions, airbag initiators for vehicles, matches and signal flares. It is a byproduct in some disinfectants ...
Underground storage of carbon captured directly from air -- green and economical
2021-06-04
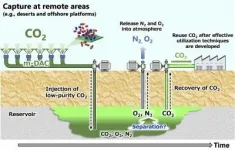
Fukuoka, Japan - The global threat of ongoing climate change has one principal cause: carbon that was buried underground in the form of fossil fuels is being removed and released into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2). One promising approach to addressing this problem is carbon capture and storage: using technology to take CO2 out of the atmosphere to return it underground.
In a new study published in Greenhouse Gases Science and Technology, researchers from Kyushu University and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan, investigated geological storage of low-purity CO2 mixed with nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), produced by direct air capture (DAC) using membrane-based technology.
Many current ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
[Press-News.org] Giving brown fat a boost to fight type 2 diabetesIncreasing a protein concentrated in brown adipose tissue remodels white adipose tissue to lower diabetes risk, study suggests