Geostationary Earth Orbit Hyperspectral Infrared Radiance data improve local severe storm forecasts proofed by using a new Hybrid OSSE method
2021-06-04
(Press-News.org) Since the era of meteorological satellites began in the 1950s, continuous remote sensing instrument improvements have elevated Earth science and have significantly increased available atmospheric observations. Likewise, scientists have made considerable advancements in understanding Earth's atmosphere, climate, and environment. Furthering growth of atmospheric science within the last 20 years, satellite-based infrared (IR) sounders onboard low Earth orbiting (LEO) satellites have provided high spectral (or hyperspectral) IR radiances. These sounders can determine small differences in reflected IR wavelengths, which help identify different targets of the atmosphere. These data have significantly improved global numerical weather prediction (NWP) modelling and forecasting.
Despite global coverage, each LEO sounder provides observations only twice per day for a given location. However, the hyperspectral IR sounders from geostationary Earth orbiting (GEO) satellites can provide higher resolution 4-D temperature (including time), moisture, and dynamic motion information needed to initialize, or start a model simulation. To accurately reflect atmospheric changes throughout an entire 24-hour period, LEO satellites can provide more frequent data updates for NWP models to use.
Scientists are developing data assimilation methods for NWP models that will increase the quality of initialization data from satellites. The Observing System Simulation Experiment (OSSE) is designed to use data assimilation to investigate the potential impact of future atmospheric observing systems. Traditional OSSE processes require significant effort to compute, simulate, and calibrate information, then assimilate the data to produce a forecast. Therefore, model meteorologists are working to make this process more efficient.
"We studied the added-value from a GEO-hyperspectral IR sounder using the hybrid OSSE method." said Prof. Jun Li, a distinguished scientist with the University of Wisconsin-Madison Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies.
Compared to the traditional OSSE, in a hybrid OSSE, most of the data are real observations, except for observations from new sensors, which are simulated frequently through small grid, high resolution global atmospheric analysis or reanalysis. A detailed proposal of hybrid OSSE applications is included in a new paper published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, which is also part of a special issue on Fengyun Meteorological Satellites: Data, Application and Assessment
Before they assessed the impact of the new method, Prof. Li and his team had to validate simulated radiances from the new GEO hyperspectral IR sensor to verify that simulating new sensor data would work in the hybrid OSSE system. They used two local severe storms cases from 2018 and 2019 in the Great Plains and Midwestern United States to evaluate the value-added impacts from the GEO hyperspectral IR data.
"We are glad to find improved atmospheric temperature, moisture, and precipitation forecasts, along with some improvements in the wind forecasts." commented Prof. Li regarding the research results.
Overall, the team's impact study presents added value, resulting in a 5% Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) reduction when GEO hyperspectral IR data are used in lieu of LEO data. This indicates potential applications of a GEO hyperspectral IR sounder that may improve local severe storm forecasts.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-04
The first evidence of a genetic link explaining why some people who catch Covid-19 don't become sick has been discovered
A scientific and medical team led by Newcastle University, UK, has demonstrated that the gene, HLA-DRB1*04:01, is found three times as often in people who are asymptomatic. This suggests that people with this gene have some level of protection from severe Covid.
The study, funded by Innovate UK, the UK's innovation agency, compared asymptomatic people to patients from the same community who developed severe Covid but had no underlying illnesses, and is published in the HLA journal.
The study team believe this is the first clear evidence of genetic ...
2021-06-04
They recently published their findings in the renowned journal "Advanced Materials". Cells are not only our biological building blocks, but also highly dynamic, active systems. The research group led by Professor Käs has succeeded in significantly reducing these dynamics with heavy water, without damaging the cells.
"Generally, a lot of people know heavy water for its important technical use in nuclear power plants. We took a different approach here and were able to show that for cells, time - or, more specifically, their dynamics - can be significantly slowed down in the presence of heavy ...
2021-06-04
Graphene may be among the most exciting scientific discoveries of the last century. While it is strikingly familiar to us--graphene is considered an allotrope of carbon, meaning that it essentially the same substance as graphite but in a different atomic structure--graphene also opened up a new world of possibilities for designing and building new technologies.
The material is two-dimensional, meaning that each "sheet" of graphene is only 1 atom thick, but its bonds make it as strong as some of the world's hardest metal alloys while remaining lightweight and flexible. This valuable, unique mix of properties have piqued the interest of scientists from a wide range of fields, leading to research in using graphene for next-generation ...
2021-06-04
Engaged listening techniques such as eye contact, nodding and using key words to praise openness helps teenagers when they admit bad behaviour and share hurt feelings with their parents, a new study has shown.
University of Reading and Haifa researchers asked 1001 13 to 16-year-olds to watch a staged conversation between a parent and teenager about a difficult situation, with the parent adopting different body language and listening behaviour in different versions.
The participants who watched the versions where the parent was visibly attentive stated that they would have felt better about themselves as the teenager and would be more likely to open up about their ...
2021-06-04
Water is weird - and yet so important. In fact, it is one of the most unusual molecules on Earth. It boils at a temperature it shouldn't. It expands and floats when it is in the solid-state. Its surface tension is higher than it should be. Now, new research published in the journal Nature has added one other equally strange property to water's list of oddities. The implications of this new revelation could have a remarkable impact on all water-related processes from water purification to drug manufacturing.
Stephen Cronin, professor of electrical and computer engineering at USC Viterbi School of Engineering, ...
2021-06-04
Cancer researchers say they have established a new, life-extending treatment option for men with prostate cancer that has spread and become resistant to hormone therapy. The injected treatment combines a targeting compound with a radioactive isotope to irradiate and kill cancer cells.
An international clinical trial sponsored by Endocyte, Inc., a Novartis company tested the targeted radioligand therapy in study participants with advanced prostate cancer. All subjects had cancers that had spread to other organs and continued to progress after previous treatment with two kinds of drugs, androgen axis inhibitors and taxanes. The experimental treatment significantly extended survival, delayed ...
2021-06-04
Leesburg, VA, June 4, 2021--According to a pilot study published in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), the flexed elbow valgus external rotation (FEVER) view can improve MRI evaluation of the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) in Major League Baseball (MLB) pitchers.
"The increased joint space width confirms elbow valgus stress with FEVER view," wrote corresponding author Thomas Knoblauch at the University of Nevada Las Vegas. "Diagnostic confidence increased, and additional UCLs were identified as abnormal."
Due to repetitive extreme valgus stress during overhead throwing maneuvers, UCL injuries remain common in throwing athletes. Because standard positioning for elbow MRI ...
2021-06-04
DALLAS - June 4, 2021 - Increasing a protein concentrated in brown fat appears to lower blood sugar, promote insulin sensitivity, and protect against fatty liver disease by remodeling white fat to a healthier state, a new study led by UT Southwestern scientists suggests. The END ...
2021-06-04
Fukuoka, Japan--According to the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017, close to nine percent of the global population lives with some form of chronic kidney disease, or CKD. Not only does the condition affect renal function, CKD has long been associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Now, in a new study that could aid the development of therapeutic drugs to reduce these cardiac complications, researchers led by Kyushu University have found an underlying molecular pathway that can explain how chronic kidney disease induces heart failure.
Studying mice, the researchers found that a key driver is the dysfunction of a type of white blood cell called a ...
2021-06-04
Overview:
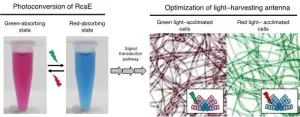
Certain cyanobacteria can change the absorbing light colors for photosynthesis using a green- and red-light sensing photosensor protein. A Japanese research group elucidated the molecular structure of RcaE, a representative member of the photosensors. They revealed the unique conformation of the bilin chromophore and the unique protein structure that potentially functions as a proton transfer route to bilin. They also demonstrated that RcaE undergoes protonation and deprotonation of the bilin chromophore during the green and red photoconversion. These results provide insights into how cyanobacteria evolved photosensors with diverse spectral sensitivities and contribute to the development of new photoswitches of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Geostationary Earth Orbit Hyperspectral Infrared Radiance data improve local severe storm forecasts proofed by using a new Hybrid OSSE method