INFORMATION:
The paper, published in the journal Science Advances, is entitled: "Large historical carbon emissions from cultivated northern peatlands."
Substantial carbon dioxide emissions from northern peatlands drained for crop cultivation
2021-06-04
(Press-News.org) A new study shows that substantial amounts of carbon dioxide were released during the last millennium because of crop cultivation on peatlands in the Northern Hemisphere.
Only about half of the carbon released through the conversion of peat to croplands was compensated by continuous carbon absorption in natural northern peatlands.
Peatlands are a type of wetland which store more organic carbon than any other type of land ecosystem in the world.
Due to waterlogged conditions, dead plant materials do not fully decay and carbon accumulates in peatlands over thousands of years.
Therefore, natural peatlands help to cool the climate by capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and trapping carbon in soils.
However, artificial drainage of peatlands for agriculture aerates the soil and enhances the decay of organic matter, rapidly releasing carbon into the atmosphere.
Peatlands are a missing piece of the carbon cycle puzzle; little is known about how much carbon has been released due to drainage and conversion of peatland to cropland during the historical sprawl of agriculture, and about the role of cultivated peatlands versus natural peatlands.
The new international study, led by INRAE and LSCE, and including the University of Exeter, quantified CO2 fluxes in natural and cultivated peatlands between 850 and 2010.
The study provides the first detailed estimates of historical carbon losses from cultivated northern peatlands.
"We incorporated peatland hydrological and carbon processes into a process-based land surface model," said Chunjing Qiu who developed the model and designed the study, and worked at the Institut National de de recherche pour l'agriculture, l'alimentation et l'environnement (INRAE) and the Laboratory for Sciences of Climate and Environment (LSCE) in France.
"This model is one of the first to simulate natural peatland and the conversion of peatland to cropland and resultant CO2 emissions.
"We also looked at how the carbon emission rates of cultivated peatlands vary with time after conversion.
"High CO2 emissions can occur after the initial drainage of peatland, but then, the emission rates decrease with time because of depletion of labile carbon and increasing recalcitrance of the remaining material."
Professor Angela Gallego-Sala, of Exeter's Global Systems Institute, said: "This study highlights how much carbon is lost if you drain peatlands, as we have done to many peatlands in Europe, but it also reminds us how important it is to make sure we manage peatlands appropriately."
The study shows that cultivated northern peatlands emitted 72 billons tons of carbon over 850-2010, and 40 billons tons over the period 1750-2010.
According to the authors, this indicates that historical CO2 emissions caused by land-use changes are greater than previously estimated.
It also implies an underestimation of historical carbon uptake by terrestrial ecosystems if carbon emissions from cultivated peatlands is ignored.
"Carbon emissions from drainage of peatlands are a source of concern for national greenhouse gas budgets and future emission trajectories," said Philippe Ciais from LSCE, who co-lead the study with Chunjing Qiu.
"However, we have only a very few observations, and peatland drainage and cultivation are not explicitly considered by bookkeeping models and dynamic global vegetation models used to compute the annual carbon budget.
"Emissions from cultivated peatlands are omitted in previous global carbon budget assessments.
"Our study brings new and important implications for a better understanding of the global carbon budget."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newly approved targeted therapy sotorasib prolongs survival in KRAS G12C-mutated lung cancer
2021-06-04
ABSTRACT #9003
HOUSTON - Results from the Phase II cohort of the CodeBreaK 100 study showed that treatment with the KRAS G12C inhibitor sotorasib achieved a 37.1% objective response rate and 12.5 months median overall survival in previously treated patients with KRAS G12C-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The findings were presented today at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting and published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Trial results indicated the targeted therapy was safe and tolerable in a heavily pre-treated patient population. The reported findings make sotorasib the first KRAS G12C inhibitor to demonstrate overall survival benefit in a registrational ...
"Mexican variant" and monitoring actions of SARS-CoV-2 genome
2021-06-04
A research group of the Department of Pharmacy and Biotechnology of the University of Bologna analyzed more than one million SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences. This analysis led to the identification of a new variant that, over the past weeks, has been spreading mostly in Mexico but has also been found in Europe. Their paper published in the Journal of Medical Virology presented the so-called "Mexican variant", whose scientific name is T478K. Like other strains, this presents a mutation in the Spike protein, which allows coronaviruses to attach to and penetrate their targeted cells.
"This variant has been increasingly spreading among people in North America, particularly in Mexico. To date, this variant covers more than 50% of the existing viruses in this area. The ...
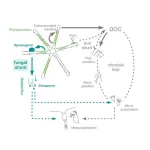
Fungus creates a fast track for carbon
2021-06-04
Tiny algae in Earth's oceans and lakes take in sunlight and carbon dioxide and turn them into sugars that sustain the rest of the aquatic food web, gobbling up about as much carbon as all the world's trees and plants combined.
New research shows a crucial piece has been missing from the conventional explanation for what happens between this first "fixing" of CO2 into phytoplankton and its eventual release to the atmosphere or descent to depths where it no longer contributes to global warming. The missing piece? Fungus.
"Basically, carbon moves up the food chain in aquatic environments differently than we commonly think it does," said Anne Dekas, an assistant professor of Earth system science at Stanford University. Dekas is the senior ...
Why scientists want to solve an underground mystery about where microbes live
2021-06-04
Though it might seem inanimate, the soil under our feet is very much alive. It's filled with countless microorganisms actively breaking down organic matter, like fallen leaves and plants, and performing a host of other functions that maintain the natural balance of carbon and nutrients stored in the ground beneath us.
"Soil is mostly microorganisms, both alive and dead," says END ...
Magnetism drives metals to insulators in new experiment
2021-06-04
Like all metals, silver, copper, and gold are conductors. Electrons flow across them, carrying heat and electricity. While gold is a good conductor under any conditions, some materials have the property of behaving like metal conductors only if temperatures are high enough; at low temperatures, they act like insulators and do not do a good job of carrying electricity. In other words, these unusual materials go from acting like a chunk of gold to acting like a piece of wood as temperatures are lowered. Physicists have developed theories to explain this so-called metal-insulator transition, but the mechanisms behind the transitions are not ...
Beyond synthetic biology, synthetic ecology boosts health by engineering the environment
2021-06-04
There's a lot of interest right now in how different microbiomes--like the one made up of all the bacteria in our guts--could be harnessed to boost human health and cure disease. But Daniel Segrè has set his sights on a much more ambitious vision for how the microbiome could be manipulated for good: "To help sustain our planet, not just our own health."
Segrè, director of the END ...
New drug effective against lung cancers caused by common genetic error
2021-06-04
A new drug reduced tumor size in patients who have lung cancer patients with a specific, disease-causing change in the gene KRAS, a study found.
The results of the CODEBREAK 100 phase 2 clinical trial were presented June 4, 2021, at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) annual meeting and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine. The efficacy and safety of the drug sotorasib, developed by Amgen Inc., was tested in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring a specific change, or mutation, in the DNA code for KRAS.
The KRAS mutant protein targeted in the study was p.G12C, in which a glycine building ...
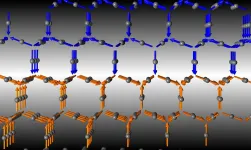
New form of silicon could enable next-gen electronic and energy devices
2021-06-04
Washington, DC--A team led by Carnegie's Thomas Shiell and Timothy Strobel developed a new method for synthesizing a novel crystalline form of silicon with a hexagonal structure that could potentially be used to create next-generation electronic and energy devices with enhanced properties that exceed those of the "normal" cubic form of silicon used today.
Their work is published in Physical Review Letters.
Silicon plays an outsized role in human life. It is the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust. When mixed with other elements, it is essential for many construction and infrastructure projects. And in pure elemental form, it ...
Social identity within the anti-vaccine movement
2021-06-04
A study of more than 1,000 demographically representative participants found that about 22 percent of Americans self-identify as anti-vaxxers, and tend to embrace the label as a form of social identity.
According to the study by researchers including Texas A&M University School of Public Health assistant professor Timothy Callaghan, 8 percent of this group "always" self-identify this way, with 14 percent "sometimes" identifying as part of the anti-vaccine movement. The results were published in the journal Politics, Groups, and Identities.
"We found these results both surprising and concerning," Callaghan said. "The fact that 22 percent of Americans at least sometimes identify as anti-vaxxers was much higher than expected and demonstrates ...
Colorectal Cancer: UVA Health Expert Helps Develop New National Screening Guidelines
2021-06-04
Most Americans should get screened for colorectal cancer beginning at age 45 instead of age 50, according to new recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, which includes UVA Health's Li Li, MD, PhD, MPH. This recommendation applies to Americans without symptoms who do not have a history of colorectal polyps or a personal or family health history of genetic disorders that increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
Colorectal cancer is the third-leading cause of cancer death in America, according to the Task Force, and an increasing number of cases are being diagnosed in younger Americans. The Task Force notes that colorectal cancer diagnoses among Americans ages 40 to 49 increased by almost 15% from 2000-02 to 2014-16. Black ...