Exploring an epidemic's meaning from the perspective of nursing
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA (June 7, 2021) - An article written almost 30 years ago helps frame social constructs around the COVID-19 pandemic. By reviewing the essay, an historian of nursing at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing) extends that construct to include nurses and patients, delivering a local and personal meaning to the epidemic experience.
In an essay in the Bulletin of the History of Medicine, Julie A. Fairman, PhD, RN, FAAN, Endowed Chair, the Nightingale Professor in Honor of Nursing Veterans, and Professor of Nursing at Penn Nursing, reviews Charles Rosenberg's 1992 article about the AIDS epidemic. Using Rosenberg's theme, she further develops the meaning of an epidemic from the nursing perspective.
"Even as we have experienced different kinds of infectious epidemics over the last century (Ebola, AIDS), Rosenberg's three interrelated stages still help us understand, from a sociological perspective, how society constructs the meaning of epidemics and manages policies, structures, and post-epidemic explanations," says Fairman. "Asking the question 'What is an epidemic?' from the perspective of nurses illustrates how a different cast of expert actors generate meanings that can then be part of a broader understanding of epidemics in general."
Fairman argues that the meaning of epidemics from the perspective of nurses, their patients, and their history injects a more layered approach to the question. Where Rosenberg wrote from the perspective of the history of medicine with the intent to understand the relationship between social structure, meaning and ideology, Fairman writes from the perspective of nurses and patients.
"A nursing perspective illustrates the construction of the meaning of an epidemic from the experiences of the patient and professional nurse, from the ground up rather than from the top down," writes Fairman. "It offers different questions exploring the experiences of patients, families, and practitioners, as well as their hopes, expectations, fears, and needs."
"Epidemics from the Perspective of Professional Nursing: Beyond Germs, Public Health, and Pot Banging" is available online.
INFORMATION:
About the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
The University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing is one of the world's leading schools of nursing. For the sixth year in a row, it is ranked the #1 nursing school in the world by QS University and is consistently ranked highly in the U.S. News & World Report annual list of best graduate schools. Penn Nursing is ranked as one of the top schools of nursing in funding from the National Institutes of Health. Penn Nursing prepares nurse scientists and nurse leaders to meet the health needs of a global society through innovation in research, education, and practice. Follow Penn Nursing on: Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, & Instagram.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-07
Metal halide perovskites have been under intense investigation over the last decade due to the remarkable rise in their performance in optoelectronic devices such as solar cells or light-emitting diodes. Despite tremendous progress in this field, many fundamental aspects of the photophysics of perovskite materials remain unknown, such as a detailed understanding of their defect physics and charge recombination mechanisms. These are typically studied by measuring the photoluminescence - i.e. the emission of light upon photoexcitation - of the material in both the steady-state and transient regimes. ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Md. (June 7, 2021) - Healthy habits are particularly important during pregnancy. Four new studies being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE look at how supplements, eating habits and physical activity can affect various aspects of health during pregnancy.
Prenatal supplements might influence bacterial composition of breast milk
Breast milk contains a unique mix of bacteria - known as its microbiota - that plays an important role in child health. In a new study, researchers from Purdue University examined whether diet or supplements taken prenatally affected the microbiota of breast milk in 771 mothers participating in the CHILD Cohort Study. The analysis revealed that supplements, but not dietary patterns, were linked with changes in human milk microbiota ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Only 5% of men and 9% of women are getting the recommended daily amount of dietary fiber, according to a study being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE. Insufficient fiber intake is associated with a higher risk of heart disease and diabetes, two of the most common diseases in the U.S.
"These findings should remind people to choose fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits and vegetables to reduce their risk for heart disease," said Derek Miketinas, PhD, RD, an assistant professor at Texas Woman's University, the study's ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Reducing food waste is crucial to our ability to feed the growing human population but will not fully solve the problem alone, according to a new study based on a computational model.
Researchers calculate that the world already produces enough protein and energy to feed 9.7 billion people--the projected population as of 2050--if food waste were cut in half. However, projections indicate global food production will still fall short in terms of micronutrients that our bodies need to stay healthy, including calcium, iron, vitamin E and others.
"Reducing food waste would give us enough protein and food energy to feed the 2050 population today--but not enough of the essential ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- According to a new study, people who eat faster or take larger bites are more likely to eat more at a meal. The research, which is being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE, provides new insight into the factors that might contribute to overeating.
The study also adds more evidence that people eat more when given larger portions. The researchers found that study participants ate, on average, 43% more when the portion size of a meal was increased by 75%.
"Although studies have consistently found that people eat more when they are served larger portions, less is known about why this happens or why some people ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Md. (June 7, 2021) - Superfoods like turmeric and honey have long been recognized for their ability to promote health and wellness. New studies being presented at END ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- What we eat during childhood can affect the health of individuals--and populations--for years to come. As rates of childhood obesity continue to rise, five studies being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE bring new insights into the diets of children and teens around the world.
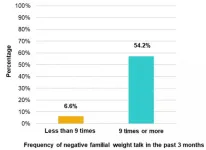
Families report substantial child weight gain during COVID-19
Researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University surveyed over 400 parents about their children's weight and eating habits before the COVID-19 pandemic and at two points during ...
2021-06-07
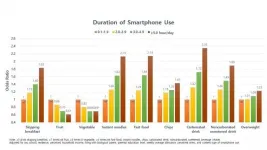
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Even moderate smartphone use may influence teens' diet and weight, according to a new study of more than 53,000 Korean adolescents. Teens who used a smartphone for more than 2 hours per day were significantly more likely to eat more junk food and fewer fruits and vegetables than those spending less time on their phone. Teens spending more than 3 hours per day on a smartphone were significantly more likely to be overweight or obese.
"While earlier studies have shown that TV watching is an important factor that increases the risk of obesity in children and adolescents, little is known about the effects of modern screen time such as smartphone use on diet and obesity," said Hannah Oh, ScD, assistant professor at ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Studies being presented at END ...
2021-06-07
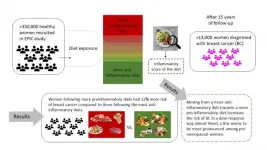
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- A new study of more than 350,000 women found that women with diets incorporating more foods that increase inflammation in the body had a 12% increase in their risk of breast cancer compared to women who consume more anti-inflammatory diets. The new findings are being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE.
The study authors found that moving from a more anti-inflammatory diet toward one that increases inflammation upped breast cancer risk in an almost linear manner. Foods that increase inflammation include red and processed meat; high-fat foods such as butter, margarines and frying fats; and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Exploring an epidemic's meaning from the perspective of nursing