(Press-News.org) Most fish rely on water to feed, using suction to capture their prey. A new study, however, shows that snowflake morays can grab and swallow prey on land without water thanks to an extra set of jaws in their throats.
After a moray eel captures prey with its first set of jaws, a second set of "pharyngeal jaws" then reaches out to grasp the struggling prey and pull it down into the moray's throat. Rita Mehta, an associate professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz, first described this astonishing feeding mechanism in a 2007 Nature paper.
The new study, published June 7 in the Journal of Experimental Biology, shows that these pharyngeal jaws enable at least one species of moray to feed on land.
"Most fishes really need water to feed," Mehta said. "This is the first example of a fish that can feed on land without relying on water."
Reports of snowflake morays coming out of the water to grab crabs on the shore prompted her to take a closer look, she said. "These particular moray eels tend to eat hard-shelled prey like crabs, and I would see reports in the literature of them moving out of the water and lunging for crabs, but it was unclear what happened next."
Even fish well adapted to an amphibious lifestyle, such as mudskippers, need water to swallow their food. "Mudskippers come up onto mudflats and grab prey like small crabs and insects. They get around the challenge of swallowing on land by sucking up water and then using the water they have reserved in their mouth to swallow," Mehta said.
Snowflake morays can do it without water because of their unusual feeding mechanics.
"They have highly moveable pharyngeal jaws in their throat," she said. "Once the moray captures prey in its oral jaws, the pharyngeal jaws grab onto the prey again and move it further back into the esophagus. This mechanical movement does not rely on water."
Demonstrating that snowflake morays can eat on land, however, was no easy task. It took Mehta and a team of undergraduates over five years to train seven snowflake morays to slither up a ramp onto a platform, grab a piece of fish, and swallow it before returning to the water.
"They feel safer in the water, so at first they would just grab the fish and go straight back into the water with it," she said. "I relied on a team of dedicated and enthusiastic undergraduate researchers to work on training them."
Coauthor Kyle Donohoe was especially helpful, she said, because of his animal training experience from working with marine mammals as a research assistant at the Pinniped Cognition and Sensory Systems Laboratory next to Mehta's lab at UCSC's Long Marine Laboratory.
Once the eels were trained to feed on the platform, Mehta documented this unusual feeding behavior on video. She said the feeding performance of young snowflake morays is as good on land as it is in water.
"As a result, these particular morays can utilize very different environments for food resources," she said.
INFORMATION:
Forty years ago, the first cases of HIV/AIDS in the U.S began to raise public awareness- but new research highlights the struggle people living with the disease still face against stigma, discrimination and negative labelling in their own families, communities and even amongst healthcare professionals.
A new study by Flinders University researchers interviewed 20 HIV healthcare providers including doctors, nurses, and counsellors in Yogyakarta and Belu districts, Indonesia to examine their experiences when treating patients with HIV. Their responses indicated admission of ...
A trial using mice has shown that a diet high in sugar from childhood could lead to significant weight gain, persistent hyperactivity and learning impairments
Many people on 'western' diets consume four times more the sugar recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO)
Reducing sucrose intake in mice by four-fold prevented sugar-induced increase in weight gain, supporting the WHO's recommendations of 25g per person a day.
Children who consume too much sugar could be at greater risk of becoming obese, hyperactive, and cognitively impaired, as adults, according to the results of a new study of mice led by ...
Propylene oxide (PO) is one of the important propylene derivatives with high reactivity, which is used extensively as raw material for the manufacture of numerous commercial chemicals. The titanosilicate-catalyzed hydrogen peroxide propylene oxide process (HPPO) is considered to be most advantageous because it is highly economical and ecofriendly, giving only H2O as the theoretical byproduct and achieving high PO selectivity under mild reaction conditions. The industrial HPPO process is generally carried out in a fixed-bed reactor using the shaped titanosilicate catalysts. Unfortunately, the inert and non-porous binders in shaping ...
The geometric isolation of metal species in single-atom catalysis (SACs) not only maximizes the atomic utilization efficiency, but also endows SACs with unique selectivity in various transformations.
The coordination environment of isolated metal atoms in SACs determines the catalytic performance. However, it remains challenging to modulate the coordinative structure while still maintain the single-atom dispersion.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. ZHANG Tao and Prof. WANG Aiqin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences fabricated Ru1/NC ...
CHICAGO --- Having trouble falling or staying asleep may leave you feeling tired and frustrated. It also could subtract years from your life expectancy, according to a new study from Northwestern Medicine and the University of Surrey in the United Kingdom (UK).
The effect was even greater for people with diabetes who experienced sleep disturbances, the study found. Study participants with diabetes who experienced frequent sleep disturbances were 87% more likely to die of any cause (car accident, heart attack, etc.) during the 8.9-year study follow-up period compared to people without diabetes or sleep disturbances. They were 12% more likely to die over this period than those who had diabetes but not frequent sleep disturbances.
"If you don't have diabetes, your sleep ...
In a paper published by the Journal of Sleep Research, researchers reveal how they examined data* from half a million middle-aged UK participants asked if they had trouble falling asleep at night or woke up in the middle of the night.
The report found that people with frequent sleep problems are at a higher risk of dying than those without sleep problems. This grave outcome was more pronounced for people with Type-2 diabetes: during the nine years of the research, the study found that they were 87 per cent more likely to die of any cause than people without diabetes ...
Durham, NC - Critically ill COVID-19 patients treated with non-altered stem cells from umbilical cord connective tissue were more than twice as likely to survive as those who did not have the treatment, according to a study published today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine.
The clinical trial, carried out at four hospitals in Jakarta, Indonesia, also showed that administering the treatment to COVID-19 patients with an added chronic health condition such as diabetes, hypertension or kidney disease increased their survival more than fourfold.
All 40 patients who took part in the double-blind, controlled, ...
A new study from the University of California, Davis and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai confirms that surgical masks effectively reduce outgoing airborne particles from talking or coughing, even after allowing for leakage around the edges of the mask. The results are published June 8 in Scientific Reports.
Wearing masks and other face coverings can reduce the flow of airborne particles that are produced during breathing, talking, coughing or sneezing, protecting others from viruses carried by those particles such as SARS-CoV2 and influenza, said Christopher Cappa, professor ...
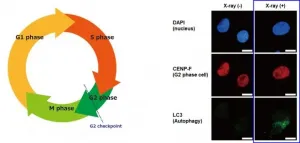
Of all the different types of cancer known, a subtype of pancreatic cancer called pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is among the most aggressive and deadly. This disease begins in the cells that make up certain small ducts in the pancreas and progresses silently, usually causing no symptoms until advanced tumors actually obstruct these ducts or spread to other places. PDAC is not only difficult to diagnose, but also very unresponsive to available treatments. In particular, researchers have noted that PDAC cells can usually survive radiotherapy through mechanisms that remain largely unknown.
Part of the Radiation and Cancer Biology ...
A new physiological measurement of heart function developed at UVA Health could improve survival for people with heart failure by identifying high-risk patients who require tailored treatments, a new study suggests.
The study is the first to show a survival benefit from wireless pressure monitoring sensors implanted in the pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary artery proportional pulse pressure, or PAPP, is a new measure of heart function, developed at UVA, that can identify patients at very high risk of hospitalization or death from systolic heart failure or pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the heart and ...