Facemasks block expired particles, despite leakage at edges
2021-06-08
(Press-News.org) A new study from the University of California, Davis and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai confirms that surgical masks effectively reduce outgoing airborne particles from talking or coughing, even after allowing for leakage around the edges of the mask. The results are published June 8 in Scientific Reports.
Wearing masks and other face coverings can reduce the flow of airborne particles that are produced during breathing, talking, coughing or sneezing, protecting others from viruses carried by those particles such as SARS-CoV2 and influenza, said Christopher Cappa, professor of civil and environmental engineering at UC Davis and corresponding author on the paper.
High-efficiency masks such as N95 respirators are designed to have a tight seal to the face, while surgical and most cloth face masks leave small gaps around the sides, which can be reduced when they are worn correctly.
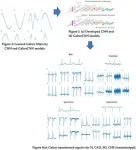
The researchers looked at particles flowing from these gaps by sitting volunteers in front of an instrument that counts airborne particles down to a size of half a micron. The 12 volunteers read aloud or coughed, with and without a surgical mask of the type widely used by the public, either with their mouth directly in front of the funnel of the particle counter, turned to the side or with their head lowered or raised to count particles passing directly through the mask or leaking around the sides.
The researchers found that wearing a mask while talking reduced particles directly through the mask by an average of 93%, from the bottom by 91%, the sides by 85% and the top by 47%, although with substantial variability between individuals. They got similar results for coughing.
Models to measure leakage
The team used simulations to model the overall reduction in particles due to wearing a mask, allowing for leakage around the edges. They calculated that the overall efficiency of masks was about 70% for talking and 90% for coughing.
"While air escape does limit the overall efficiency of surgical masks at reducing expiratory particle emissions, such masks nonetheless provide substantial reduction," Cappa said. "Our results confirm that mask wearing provides a significant reduction in the probability of disease transmission via expiratory particles, especially when both infected and susceptible individuals wear masks."
Masks also redirect the flow of air from a high-velocity plume from the talker or cougher towards anybody in front of them, Cappa said.
INFORMATION:
Additional authors on the study are: Sima Asadi, Santiago Barreda, Anthony Wexler and William Ristenpart at UC Davis and Nicole Bouvier, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. (Sima Asadi is now at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.) The work was funded by a grant from the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-08
Of all the different types of cancer known, a subtype of pancreatic cancer called pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is among the most aggressive and deadly. This disease begins in the cells that make up certain small ducts in the pancreas and progresses silently, usually causing no symptoms until advanced tumors actually obstruct these ducts or spread to other places. PDAC is not only difficult to diagnose, but also very unresponsive to available treatments. In particular, researchers have noted that PDAC cells can usually survive radiotherapy through mechanisms that remain largely unknown.
Part of the Radiation and Cancer Biology ...
2021-06-08
A new physiological measurement of heart function developed at UVA Health could improve survival for people with heart failure by identifying high-risk patients who require tailored treatments, a new study suggests.
The study is the first to show a survival benefit from wireless pressure monitoring sensors implanted in the pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary artery proportional pulse pressure, or PAPP, is a new measure of heart function, developed at UVA, that can identify patients at very high risk of hospitalization or death from systolic heart failure or pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the heart and ...
2021-06-08
Tropical cyclones (TCs) are humbling and powerful forces of nature that can have tremendous impacts on people and human populations. Meteorologists have strived to improve TC forecasting skill, hoping to save lives. In the past few decades, TC track forecasts over the western North Pacific (WNP) have progressed considerably. However, TC intensity forecasts have improved insignificantly, with only a 3-5 day lead time. Therefore, improving TC intensity forecast skill and extending lead forecast time are important and urgent issues.
To address this critical problem, a research group led by Prof. Ruifen ZHAN from the Department of Atmospheric and Ocean Sciences/Institute of Atmospheric Sciences at Fudan University, along with the Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological ...
2021-06-08
The incidence rate of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is increasing gradually and the mortality is still high. Recent advances in the genomic profile of LUAD have identified a number of driver alterations in specific genes, enabling molecular classification and targeted therapy accordingly. However, only a fraction of LUAD patients with those driver mutations could benefit from targeted therapy, and the remaining large numbers of patients were unclassified. RNA editing events are those nucleotide changes in the RNA. Currently, the role of RNA editing events ...
2021-06-08
Glass is one of the most common subjects we see every day, but the detailed structure of this non-metallic and non-liquid material has always been a major mystery in science. A research team co-led by scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has successfully discovered that the amorphous and crystalline metallic glass have the same structural building blocks. And it is the connectivity between these blocks that distinguishes the crystalline and amorphous states of the material. The findings shed light on the understanding of glass structure.
Glass is a non-crystalline amorphous solid which has widespread practical and technological use in daily life. Besides the soda-lime glass used in windows, there are many other ...
2021-06-08
Epidemiological and toxicological studies indicate that the adverse outcomes of PM2.5 exposure associated closely with the chemical composition in PM2.5. Metals in PM2.5 are highly concerned for their induced disruption of iron homeostasis in the lung and following oxidative stress, which is one of the key mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction of PM2.5 exposure. However, there is no clear evidence on whether COPD patients are more susceptible to cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction associated with exposure to metals in ambient PM2.5 than individuals without COPD. Based on a panel study, the researchers directly compared metal-associated cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction between COPD patients and healthy controls.
"We observed higher levels of heart ...
2021-06-08
Supermassive black holes (SMBH) occupy the center of galaxies, with masses ranging from one million to 10 billion solar masses. Some SMBHs are in a bright phase called active galactic nuclei (AGN).
AGNs will eventually burn out since there is a maximum mass limit for SMBHs; scientists have long since pondered when that will be.
Tohoku University's Kohei Ichikawa and his research group may have discovered an AGN towards the end of its life span by accident after catching an AGN signal from the Arp 187 galaxy.
Through observing the radio images in the galaxy using two astronomy observatories - the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Very Large Array (VLA) - ...
2021-06-08
Globally, the Earth system has thousands of terragrams (Tg) (1 Tg = 10 12 g) of mineral nanoparticles moving around the planet each year. These mineral nanoparticles are ubiquitously distributed throughout the atmosphere, oceans, waters, soils, in and/or on most living organisms, and even within proteins such as ferritin. In natural environments, mineral nanozymes can be produced by two pathways: "top down" and "bottom up" processes. Specifically, the weathering or human-promoted breakdown of bulk materials can result in nanomaterials directly (a top-down process), or nanomaterials ...
2021-06-08
A team of researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Ngee Ann Polytechnic, Singapore (NP), and the National Heart Centre Singapore (NHCS) have invented a tool that could speed up the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases.
Powered by artificial intelligence (AI), their innovation uses electrocardiograms (ECGs) to diagnose coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure to an accuracy of more than 98.5 per cent.
The joint development of the diagnostic tool is timely, as the number of deaths caused by cardiovascular disease in Singapore has increased over the past three years. According to the Singapore Heart Foundation, 29.3 per cent of all deaths in Singapore in 2019, or almost 1 out of 3 deaths in Singapore, was due to heart ...
2021-06-08
Osteoporosis is a condition that does not exhibit symptoms until there is a bone fracture, so it is said that there is a high percentage of people who remain unaware of their condition. When people are unaware their bones have weakened, the condition is left untreated, and the recent rise of the elderly population has caused an increase in bone fractures. This has a large societal impact, such as overwhelming medical costs and long-term care. Simple screenings at resident health exams are one way for an increase in osteoporosis detecting without having to go to the hospital. When suspected osteoporosis and osteopenia is properly detected and patients are encouraged to get further evaluation at the hospital, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Facemasks block expired particles, despite leakage at edges