Persistent insomnia symptoms since childhood associated with mood, anxiety disorders
Study emphasizes importance of early interventions to address insomnia symptoms in children
2021-06-09
(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL - A 15-year longitudinal study shows that childhood insomnia symptoms that persist into adulthood are strong determinants of mood and anxiety disorders in young adults.
Results show that insomnia symptoms persisting from childhood through adolescence and into adulthood were associated with a 2.8-fold increased risk of internalizing disorders. Insomnia symptoms that newly developed over the course of the study were associated with a 1.9-fold increased risk of internalizing disorders. No increased risk of internalizing disorders was found for those children in whom insomnia symptoms remitted during the study period.
"We found that about 40% of children do not outgrow their insomnia symptoms in the transition to adolescence and are at risk of developing mental health disorders later on during early adulthood," said lead author Julio Fernandez-Mendoza, who has a doctorate in psychobiology and is an associate professor at Penn State College of Medicine. He is a psychologist board certified in behavioral sleep medicine at Penn State Health Sleep Research and Treatment Center in Hershey, Pennsylvania.
Data were analyzed from the Penn State Child Cohort, a population-based sample of 700 children with a median age of 9 years. The researchers had followed up 8 years later with 421 participants when they were adolescents (median age of 16 years) and now 15 years later with 492 of them when they were young adults (median age of 24 years). Insomnia symptoms were defined as moderate-to-severe difficulties initiating or maintaining sleep.
The symptoms were parent-reported in childhood and self-reported in adolescence and young adulthood. The presence of internalizing disorders was defined as a self-report of a diagnosis or treatment for mood and/or anxiety disorders. Results were adjusted for sex, race/ethnicity, age, and any prior history of internalizing disorders or use of medications for mental health problems.
According to the authors, childhood insomnia symptoms have been shown to be associated with internalizing disorders, which include depressive disorders and anxiety disorders. "These new findings further indicate that early sleep interventions are warranted to prevent future mental health problems, as children whose insomnia symptoms improved over time were not at increased risk of having a mood or anxiety disorder as young adults," said Fernandez-Mendoza.
INFORMATION:
The research abstract was published recently in an online supplement of the journal Sleep and will be presented as an oral presentation on Sunday, June 13, during Virtual SLEEP 2021. SLEEP is the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
This study was supported by funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health. For a copy of the abstract, "Developmental Trajectories of Insomnia and Risk of Internalizing Disorders in Young Adulthood," or to arrange an interview with the study author or an AASM spokesperson, please contact AASM Communications Coordinator Corinne Lederhouse at 630-737-9700, ext. 9366, or clederhouse@aasm.org.
About the American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Established in 1975, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is advancing sleep care and enhancing sleep health to improve lives. The AASM has a combined membership of 11,000 accredited member sleep centers and individual members, including physicians, scientists and other health care professionals (aasm.org).
About the Sleep Research Society
The Sleep Research Society (SRS) is a professional membership society that advances sleep and circadian science. The SRS provides forums for the exchange of information, establishes and maintains standards of reporting and classifies data in the field of sleep research, and collaborates with other organizations to foster scientific investigation on sleep and its disorders. The SRS also publishes the peer-reviewed, scientific journals Sleep and Sleep Advances (sleepresearchsociety.org).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-09
MELVILLE, N.Y., June 9, 2021 -- The world is filled with myriad sounds that can overwhelm a person with relentless acoustics. Noise is so prevalent in everyday life that the concept and achievement of comfortable quiet is hard to define.
During the 180th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, which will be held virtually June 8-10, Aggelos Tsaligopoulos, from the University of the Aegean, will describe how quiet could be measured in the hopes of better understanding its impact on people. The session, "Towards a new understanding of the concept of quietness," will take place Wednesday, ...
2021-06-09
In a major scientific leap, University of Queensland researchers have created a quantum microscope that can reveal biological structures that would otherwise be impossible to see.
This paves the way for applications in biotechnology, and could extend far beyond this into areas ranging from navigation to medical imaging.
The microscope is powered by the science of quantum entanglement, an effect Einstein described as "spooky interactions at a distance".
Professor Warwick Bowen, from UQ's Quantum Optics Lab and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Engineered Quantum Systems (EQUS), said it was the first entanglement-based sensor with performance beyond the best possible existing technology.
"This breakthrough will spark all sorts of new technologies - from better navigation ...
2021-06-09
While the IPCC is in the midst of the drafting cycle of the Sixth Assessment Report, whose publication will start in the second half of 2021 - one of the most relevant events for the global climate change community, there is an ongoing debate on how to assess the feasibility of ambitious climate mitigation scenarios developed through integrated assessment models and to what extent they are actually achievable in the real world. In their new study published in Environmental Research Letters, researchers from the RFF-CMCC European Institute on Economics and the Environment (EIEE) and IIASA developed a systematic ...
2021-06-09
What The Study Did: An observational study of more than 27,000 veterans who received a positive test result for COVID-19 reports that risk factors such as housing problems, financial hardship, alcohol use, tobacco use and substance use weren't associated with higher mortality.
Authors: J. Daniel Kelly, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.13031)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please ...
2021-06-09
What The Study Did: This study looked at whether there was an association between rideshare use, motor vehicle crash traumas and impaired driving convictions in Houston, Texas, by comparing traumas and convictions before and after the introduction of Uber.
Authors: Christopher R. Conner, M.D., Ph.D., of the McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.2227)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
2021-06-09
A condition that affects the blood, known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), may be associated the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine in rare cases, research suggests.
The very small increased risk of the condition - which is characterised by low platelet counts - is estimated to be 11 per million doses, similar to figures seen in vaccines for flu and MMR.
A low number of platelets - blood cells that help prevent blood loss when vessels are damaged - can result in no symptoms or can lead to an increased risk of bleeding or, in some cases, clotting.
Researchers say that the increased chance of developing ITP after receiving the vaccine remains smaller than the risk of developing it because of Covid-19 and should ...
2021-06-09
Batteries have come a long way since Volta first stacked copper and zinc discs together 200 years ago. While the technology has continued to evolve from lead-acid to lithium-ion, many challenges still exist--like achieving higher density and suppressing dendrite growth. Experts are racing to address the growing, global need for energy-efficient and safe batteries.
The electrification of heavy-duty vehicles and aircraft requires batteries with more energy density. A team of researchers believes a paradigm shift is necessary to make a significant impact in battery technology for these industries. ...
2021-06-09
Scientists from the lab of Franz Klein from the Department of Chromosome Biology at the Max Perutz Labs, a joint venture of the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna, have now discovered that cells sometimes liberate DNA fragments at sites of paired, or double, DSBs. Whilst this presents an obvious risk of germline mutations as a consequence of erroneous repair or of integration of fragments from elsewhere at break sites, it may also be a source of evolutionary diversity. The study is published as a research article in Nature.
Genetic information in humans is encoded in 23 chromosome pairs, where one pair consists of two slightly different copies or homologs. One is inherited from the father and one from the mother. Human gametes, however, are haploid - they start ...
2021-06-09
Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) demonstrate that innovative projects spearheaded by United Nations (UN) country offices are remodeling the institution and expanding its role. Digital initiatives, particularly those scaled through headquarters, were shown to have the strongest impact, changing ways of working, embedding new skills, and restructuring teams across the UN. These findings, published in the Journal of Management Studies, highlight that fostering even single innovative projects could lead to fundamental transformations in the UN.
How do International Organizations build innovation capabilities ...
2021-06-09
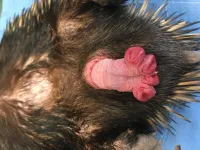
Scientists from the University of Melbourne and University of Queensland have revealed the mystery behind the unique reproductive parts of the much-loved echidna.
In the paper, "The Unique Penile Morphology of the Short-Beaked Echidna, Tachyglossus aculeatus", the team detail how the male monotreme's testes never descend, have no scrotum, and when not in use, their penis is stored internally.
They also detail how the echidna penis has four heads, which are actually rosette-like glans at the end. Just two of the four glans ever become functional during erection ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Persistent insomnia symptoms since childhood associated with mood, anxiety disorders
Study emphasizes importance of early interventions to address insomnia symptoms in children