(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) demonstrate that innovative projects spearheaded by United Nations (UN) country offices are remodeling the institution and expanding its role. Digital initiatives, particularly those scaled through headquarters, were shown to have the strongest impact, changing ways of working, embedding new skills, and restructuring teams across the UN. These findings, published in the Journal of Management Studies, highlight that fostering even single innovative projects could lead to fundamental transformations in the UN.
How do International Organizations build innovation capabilities through intrapreneurship and entrepreneurial behavior? To answer this question, researchers Tina Ambos and Katherine Tatarinov of the Geneva School of Economics and Management (GSEM) at the UNIGE looked at how innovative projects, particularly those born in country offices, are changing the institutional system in a sustainable way.
The role of digital technology
In one of the case studies conducted for this research, a refugee cash transfer initiative using blockchain widened the responsible UN body's role from 'ending poverty and hunger' to that more closely resembling a fintech company or development bank. By providing a platform for aid delivery, the organization is now helping its partners bypass unstable third-parties and save on transaction costs. "Such new activities often stretch the original mission of the organization", explains Tina Ambos, professor of international management at GSEM and director of the i2i Hub for Innovation and Cross-Sector Partnerships. "The use of blockchain could spread across the entire UN system, changing the ways of working and increasing transparency."
Sensitive data on vulnerable groups held by the UN often means that digital innovation cannot be outsourced. This results in the organization upgrading its institutional knowledge and creating new teams to manage digital projects, which were found to have the biggest impact on how the UN operates overall. "Other skills have also been internalized, such as technical skills and human-centered design approaches", says co-author and PhD student Katherine Tatarinov. "After learning in one context, the UN was able to test different technologies in its sites of operation according to local needs without depending on external experts."
Innovation units were found to be key in helping the UN scale initiatives by driving forward dynamic solutions. Such units nurture initiatives through boot camps, cross-sectoral connections, helping teams overcome internal barriers, and broadcasting new learnings to the entire organization. The UN also involves local people to ensure sustainability and maximize social impact. End-users, such as refugees, are often active members of development teams, helping ensure that projects 'do no harm.'
The power of bottom-up innovation
Innovations often start life in UN country offices, where staff need to respond quickly to unfolding crises. To circumvent slow central procedures, in-country innovators may decide not to involve the headquarters. Good ideas then spread from country to country, such as an anonymous SMS polling tool designed to gauge opinions on taboo topics in remote communities. "The idea grew organically, as other country offices could see the value of access to data on taboo topics", says Tina Ambos. Such country-level innovations can achieve scale and have been shown to change the organization's culture when digital technology is involved.
Innovation champions at the country level are willing to employ workarounds to avoid head office bureaucracy, because they are motivated to solve an urgent problem - rather than by internal rewards or recognition. They are therefore able to access funds and forge partnerships which may have been disregarded by the large, centralized machinery of the UN, but which nevertheless align with broader organizational values.
"Strict hierarchies, risk-averse donors, and lengthy sign-off processes can stifle ideas, yet international organizations need to innovate to stay relevant", says co-author Katherine Tatarinov. "Greater public scrutiny, funding challenges, and the push towards digital means that bodies like the UN need to reinvent themselves - their culture, identity, and management styles. By becoming more responsive and fostering innovative ideas, they can better achieve their missions and our shared global goals." The study findings show that the seed from one good idea can grow throughout a complex organization like the UN, changing it from the inside, and creating new space for enterprising ideas to flourish.
INFORMATION:
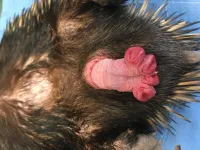
Scientists from the University of Melbourne and University of Queensland have revealed the mystery behind the unique reproductive parts of the much-loved echidna.
In the paper, "The Unique Penile Morphology of the Short-Beaked Echidna, Tachyglossus aculeatus", the team detail how the male monotreme's testes never descend, have no scrotum, and when not in use, their penis is stored internally.
They also detail how the echidna penis has four heads, which are actually rosette-like glans at the end. Just two of the four glans ever become functional during erection ...
Led by Professor Andreas Hartmann, from the University of Freiburg (Germany), the researchers analyzed the presence of several pollutants in water from many karst aquifers of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East, relating fast infiltration processes to an increased concentration of these substances. The findings of this research are published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
This way, they warn that during rainfall events -when aquifers recharge, especially during autumn rainfall- the concentration of pollutants and pathogenic microorganisms can significantly exceed the safe levels, causing serious consequences for human consumption.
"About one quarter of the ...
Obesity is generally linked to poor eating habits and the availability of tasty, high-calorie foods. However, a new study led by researchers from the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Research Unit in the Department of Radiology at Hospital del Mar and the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has found that more elements are involved. Thanks to images obtained by functional magnetic resonance imaging, the researchers found that certain parts of the brains of obese children show alterations with respect to normal-weight or overweight children of the same age. ...
At the heart of almost every sufficiently massive galaxy there is a black hole whose gravitational field, although very intense, affects only a small region around the centre of the galaxy. Even though these objects are thousands of millions of times smaller than their host galaxies our current view is that the Universe can be understood only if the evolution of galaxies is regulated by the activity of these black holes, because without them the observed properties of the galaxies cannot be explained.
Theoretical predictions suggest that as these black holes grow they generate sufficient energy to heat ...
New research has revealed that people with the ability to visualise vividly have a stronger connection between their visual network and the regions of the brain linked to decision-making. The study also sheds light on memory and personality differences between those with strong visual imagery and those who cannot hold a picture in their mind's eye.
The research, from the University of Exeter, published in Cerebral Cortex Communications, casts new light on why an estimated one-three per cent of the population lack the ability to visualise. This phenomenon was named "aphantasia" by the University of Exeter's Professor Adam Zeman in 2015 Professor Zeman called those with highly ...
Homocysteine (HCY) is a sulfur-containing aminoacid, which attract more and more attention as the increase of homocysteine level associates with a number of pathological conditions. Hyperhomocysteinemia (hHCY) is an elevation of HCY level in plasma and develops due to genetic mutations of enzymes involved in regulation of HCY metabolism, nutritional deficiencies of vitamins B12, B6 and folate; chronic renal failure; alcoholism, smoking, excess coffee consumption, hypothyroidism; taking a number of medications like antiepileptic drugs and LDOPA; and aging. hHcy is a well-known ...
The movement of electrons can have a significantly greater influence on spintronic effects than previously assumed. This discovery was made by an international team of researchers led by physicists from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). Until now, a calculation of these effects took, above all, the spin of electrons into consideration. The study was published in the journal "Physical Review Research" and offers a new approach in developing spintronic components.
Many technical devices are based on conventional semiconductor electronics. Charge currents are used to store and process information in these components. However, this electric current generates heat and energy is lost. To get around this problem, ...
BOSTON - In the three months since Johnson & Johnson's COVID-19 vaccine received emergency use authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, more than 10 million Americans have received the vaccine, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The single-shot viral vector vaccine -- developed in collaboration with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) immunologist Dan Barouch, MD, PhD -- was authorized for use based on clinical trial data showing strong clinical efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19 in the United States, Latin ...
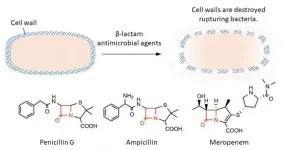
A joint research project based in Kumamoto University, Japan has developed a new, highly sensitive analytical method that can detect degraded β-lactam antibacterial agents used in the treatment of bacterial infections. With this method, researchers found that reactive sulfur species produced by bacteria degrade and inactivate β-lactam antibiotics.
Bacteria are different from animal cells in that their outer layer is covered with a rigid structure called a cell wall. β-lactam antimicrobial agents interfere with the processes that form the cell wall. This results in bacteria no longer being able to withstand their own internal pressure so they rupture and die. β-lactam antimicrobial agents are very potent ...
For nearly half a century, astrophysicists and organic chemists have been on the hunt for the origins of C6H6, the benzene ring - an elegant, hexagonal molecule comprised of 6 carbon and 6 hydrogen atoms.
Astrophysicists say that the benzene ring could be the fundamental building block of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons or PAHs, the most basic materials formed from the explosion of dying, carbon-rich stars. That swirling mass of matter would eventually give shape to the earliest forms of carbon - precursors to molecules some scientists say are connected to ...