(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, June 9, 2021 -- The World Health Organization and the Centers for Disease Control recommend keeping a certain distance between people to prevent the spread of COVID-19. These social distancing recommendations are estimated from a variety of studies, but further research about the precise mechanism of virus transport from one person to another is still needed.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Stony Brook University, Harvard, ETH Zurich, and Hanyang University demonstrate normal breathing indoors without a mask can transport saliva droplets capable of carrying virus particles to a distance of 2.2 meters, or 7.2 feet, in a matter of 90 seconds.
The use of a face mask significantly reduces the distance these droplets travel. After almost two minutes, the saliva droplets restricted by a mask had traveled only 0.72 meters, under 2.4 feet and well below the distance of 1.8 meters, or 6 feet, suggested by the CDC.
The study used computer simulations with a more realistic model for the situation of interest than those used in previous studies. Previous work considered aerosol transport after coughing or sneezing, while this study specifically looked at normal human breathing. A normal breath produces periodic jet flows that contain saliva droplets, but the velocity at which the jet travels is less than a tenth that of a cough or sneeze.
The investigators found even normal breathing produces a complex field of vortices that can move saliva droplets away from the person's mouth. The role of these vortices has not previously been understood.
"Our results show that normal breathing without a facial mask generates periodic trailing jets and leading circular vortex rings that propagate forward and interact with the vortical flow structures produced in prior breathing cycles," said author Ali Khosronejad.
This complex vorticity field can transport aerosol droplets over long distances. A face mask dissipates the kinetic energy of the jet produced by an exhaled breath, disrupting the vortices and limiting the movement of virus-laden droplets.
The investigators considered the effect of evaporation of the saliva droplets. In the case of no mask, they found the saliva droplets near the front of the plume of exhaled breath had partially evaporated, reaching a size of only one-tenth of a micron. In stagnant indoor air, droplets this size would not settle to the ground for days.
The use of a mask partially redirects the exhaled breath downward and significantly restricts forward movement of the plume, so the risk of suspended droplets remaining in the air is substantially reduced.
"To simplify the breathing process, we did not consider the flow of air-saliva mixture through the nose and solely accounted for the flow through the mouth," Khosronejad said. "In future studies, we will explore the effect of normal breathing via both the nose and mouth."
INFORMATION:
The article "A computational study of expiratory particle transport and vortex dynamics during breathing with and without face masks" is authored by Ali Khosronejad, Seokkoo Kang, Fabian Wermelinger, Petros Koumoutsakos and Fotis Sotiropoulos. The article appears in Physics of Fluids (DOI: 10.1063/5.0054204) and can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0054204.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
Summer rainfall on the Tibetan Plateau is highly predictable on multiyear timescales in large ensemble predictions, according to a research team led by ZHOU Tianjun from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The study, published in Science Advances on June 9, shows evidence that the predictable signal of summer rainfall across the hinterland of the Tibetan Plateau is substantially underestimated in state-of-the-art decadal prediction models.
The predictable signal is so weak that it can be concealed by unpredictable noise. "The too weak predictable signal arises from the low signal-to-noise ratios in models in comparison with the real world," ...
A new study at the University of Chicago Medicine and Washington University found that a single inhalation session with 25% nitrous oxide gas was nearly as effective as 50% nitrous oxide at rapidly relieving symptoms of treatment-resistant depression, with fewer adverse side effects. The study, published June 9 in Science Translational Medicine, also found that the effects lasted much longer than previously suspected, with some participants experiencing improvements for upwards of two weeks.
These results bolster the evidence that non-traditional treatments may be a viable option for patients whose depression is not responsive to typical antidepressant medications. It may also provide a rapidly effective treatment option for patients in crisis.
Often called "laughing gas," nitrous ...
A single, one-hour treatment that involves breathing in a mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide -- otherwise known as laughing gas -- significantly improved symptoms in people with treatment-resistant depression, according to new data from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the University of Chicago.
In a phase 2 clinical trial, the researchers demonstrated that symptoms of depression improve rapidly following treatment with inhaled nitrous oxide. Further, they reported the benefits can last for several weeks.
The findings are published June 9 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
"A large percentage of patients don't respond to standard antidepressant therapies -- the ...
A new study unexpectedly identified tiny deposits of elemental copper and iron within the brains of two deceased people with Alzheimer's disease. The findings could help scientists better understand how these elemental metals, which were uncovered in the cores of amyloid plaques, contribute to neurodegenerative diseases and could point to a target for alternative Alzheimer's therapies. While enzymes and proteins containing positively charged copper and iron ions have been known to control key processes in the human brain, little has been known about how the organ mineralizes iron and copper, including the formation of elemental metallic nanoparticles, which ...
(Boston)--Should treatment of alcoholics be different based on gender? Yes, according to a new study that shows that alcoholic men and women respond differently to their disease resulting in different levels of brain activity and brain abnormalities. Research indicates that they distinguish facial expressions differently and that this is an important clue as to how treatment strategies might be tailored.
Chronic long-term Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) or "alcoholism," is a harmful condition that has been associated with deficits in emotion and memory, including memory for the emotional expressions of faces. In addition to its effects on memory for facial emotions, AUD also has been associated with impairments ...
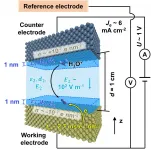
PSI researchers have developed a new tomography method with which they can measure chemical properties inside catalyst materials in 3-D extremely precisely and faster than before. The application is equally important for science and industry. The researchers published their results today in the journal Science Advances.
The material group of vanadium phosphorus oxides (VPOs) is widely used as a catalyst in the chemical industry. VPOs have been used in the production of maleic anhydride since the 1970s. Maleic anhydride in turn is the starting material for the ...
Widespread adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles over traditional electric vehicles requires fuel cells that can convert hydrogen and oxygen safely into water - a serious implementation problem.
Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder are addressing one aspect of that roadblock by developing new computational tools and models needed to better understand and manage the conversion process. Hendrik Heinz, an associate professor in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, is leading the effort in partnership with the University of California Los Angeles. His team recently published new findings on the subject in Science Advances.
Fuel cell electric vehicles combine ...
A single one-hour treatment with nitrous oxide - also known as laughing gas - can relieve symptoms of treatment-resistant depression for several weeks, according to a phase 2 clinical trial involving 28 participants. By showing that a 25% concentration of the gas still has therapeutic effects, the results suggest that lower concentrations of nitrous oxide could be useful against depression in the clinic while bringing a lower risk of side effects. Inhaled nitrous oxide is commonly used as a sedative agent in dental and medical offices, but the gas has also attracted attention as a possible treatment for depression. A previous study showed that nitrous oxide had marked ...
New Curtin research has shown how a readily available, cheap and safe-to-use product found in the medicine cabinet of most homes could be the key to better ecological restoration practices with major benefits for the environment and agriculture.
The study revealed that aspirin, which naturally occurs in the bark of the willow tree and other plants, can improve the survival of grass species important for ecological restoration and sustainable pasture when applied in a seed coating.
Lead researcher Dr Simone Pedrini from the ARC Centre for Mine Site Restoration in Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences, said salicylic acid has been used for its medicinal properties for more than 4000 years and its modern synthetic version, acetylsalicylic acid, or aspirin, is one ...
Our genetic material is stored in our cells in a specific way to make the meter-long DNA molecule fit into the tiny cell nucleus of each body cell. An international team of researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing, the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Ageing research at the University of Cologne, the University College London and the University of Michigan have now been able to show that rapamycin, a well-known anti-ageing candidate, targets gut cells specifically to alter the way of DNA storage inside these cells, and thereby promotes gut health and longevity. This effect has been observed in flies and mice. The researchers believe this finding will open up new possibilities for targeted therapeutic interventions ...