Autopsy Study of Patients With/Without COVID-19
JAMA Neurology
2021-06-11
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: This autopsy study examines differences in skeletal muscle and myocardial inflammation in patients who died with COVID-19 versus other diseases.
Authors: Tom Aschman, M.D., and Werner Stenzel, M.D., of the Charite-Universitatsmedizin Berlin, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.2004)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.2004?guestAccessKey=40d23043-3b0c-4611-8c85-d11526b0b96f&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=061121
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-11
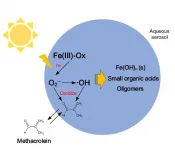
The Fenton reaction is a chemical transition involving hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and the ferrous (iron) ion, which acts as a catalyst. This process is used to destroy hazardous contaminants in wastewater through oxidation. In the atmosphere, a similar reaction, or "Fenton-like" reaction, occurs continuously with ferric oxalate([Fe(III)(C2O4)3]3-) and aerosols suspended in the air. This is the most frequent chemical reaction that occurs in the atmosphere. A particle's ability to oxidize is directly related to its phase, either gaseous or aqueous, which has an important impact on secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation. Therefore, research is necessary not only to evaluate the contribution of this ...
2021-06-11
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine used an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to sift through terabytes of gene expression data -- which genes are "on" or "off" during infection -- to look for shared patterns in patients with past pandemic viral infections, including SARS, MERS and swine flu.
Two telltale signatures emerged from the study, published June 11, 2021 in eBiomedicine. One, a set of 166 genes, reveals how the human immune system responds to viral infections. A second set of 20 signature genes predicts the severity of a patient's disease. For example, the need to hospitalize or use ...
2021-06-11
Astronomers from University of Warwick and University of Exeter modelling the future of unusual planetary system found a solar system of planets that will 'pinball' off one another
Today, the system consists of four massive planets locked in a perfect rhythm
Study shows that this perfect rhythm is likely to hold for 3 billion years - but the death of its sun will cause a chain reaction and set the interplanetary pinball game in motion
Four planets locked in a perfect rhythm around a nearby star are destined to be pinballed around their solar system when their sun eventually dies, according to a study led by the University of Warwick that peers into its future.
Astronomers have modelled how the change in gravitational forces in the system as a result ...
2021-06-11
When is a weed not a weed?
Can native plants be weeds?
Sweet pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum) was once a well-behaved tree growing in gullies from Gippsland in Victoria up to Brisbane in Queensland.
But it is now a major problem, leading to an almost complete suppression of native vegetation where it has invaded. Programs to clear it have successfully allowed indigenous plants to return, and within 15 years, with moderate follow up, treated sites are well on the way to successful restoration.
However, there has been some debate on whether this is good or bad for birds such as the threatened Powerful Owl.
New research by Monash University scientists from the School of Biological Sciences published today in Ecological Solutions and ...
2021-06-11
Astronomers have spotted a giant 'blinking' star towards the centre of the Milky Way, more than 25,000 light years away.
An international team of astronomers observed the star, VVV-WIT-08, decreasing in brightness by a factor of 30, so that it nearly disappeared from the sky. While many stars change in brightness because they pulsate or are eclipsed by another star in a binary system, it's exceptionally rare for a star to become fainter over a period of several months and then brighten again.
The researchers believe that VVV-WIT-08 may belong to a new class of 'blinking giant' binary star system, where a giant star ? 100 times larger ...
2021-06-11
Oncotarget published "The presence of polymorphisms in genes controlling neurotransmitter metabolism and disease prognosis in patients with prostate cancer: a possible link with schizophrenia" reported that polymorphisms of neurotransmitter metabolism genes were studied in patients with prostate cancer (PC) characterized by either reduced or extended serum prostate-specific antigen doubling time corresponding to unfavorable and favorable disease prognosis respectively.
The following gene polymorphisms known to be associated with neuropsychiatric disorders were investigated:
A. The STin2 VNTR in the serotonin transporter SLC6A4 gene;
B. The 30-bp VNTR in the monoamine oxidase A MAOA gene;
C. The Val158Met polymorphism in the catechol-ortho-methyltransferase ...
2021-06-11
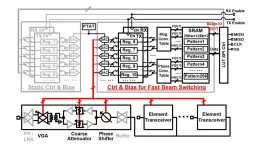
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) and NEC Corporation jointly develop a 28-GHz phased-array transceiver that supports efficient and reliable 5G communications. The proposed transceiver outperforms previous designs in various regards by adapting fast beam switching and leakage cancellation mechanism.
With the recent emergence of innovative technologies, such as the Internet of Things, smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and smart mobility, our world is on the brink of a new age. This stimulates the use of millimeter-wave bands, which have far more signal bandwidth, to accommodate these new ideas. 5G can offer data ...
2021-06-10
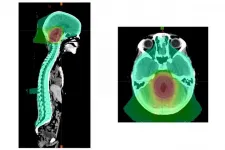
Medulloblastoma is a rare but devastating childhood brain cancer. This cancer can spread through the spinal fluid and be deposited elsewhere in the brain or spine. Radiation therapy to the whole brain and spine followed by an extra radiation dose to the back of the brain prevents this spread and has been the standard of care. However, the radiation used to treat such tumors takes a toll on the brain, damaging cognitive function, especially in younger patients whose brains are just beginning to develop.
A national study led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and St. Jude Children's Research Hospital suggests that children with what is called "average risk medulloblastoma" can receive a radiation "boost" to a smaller ...
2021-06-10
Metformin is a widely prescribed blood sugar-lowering drug. It is often used as an early therapy (in combination with diet and lifestyle changes) for type 2 diabetes, which afflicts more than 34 million Americans.
Metformin works by lowering glucose production in the liver, reducing blood sugar levels that, in turn, improve the body's response to insulin. But scientists have also noted that metformin possesses anti-inflammatory properties, though the basis for this activity was not known.
In a study published online June 8, 2021 in the journal END ...
2021-06-10
Married men who don't help out around the house tend to bring home bigger paychecks than husbands who play a bigger role on the domestic chores front.
New research from the University of Notre Dame shows that "disagreeable" men in opposite-sex marriages are less helpful with domestic work, allowing them to devote greater resources to their jobs, which results in higher pay.
In contemporary psychology, "agreeableness" is one of the "Big Five" dimensions used to describe human personality. It generally refers to someone who is warm, sympathetic, kind and cooperative. Disagreeable people do not tend to exhibit these characteristics, and they tend to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Autopsy Study of Patients With/Without COVID-19
JAMA Neurology