(Press-News.org) HOUSTON - (June 11, 2021) - Scientific studies describing the most basic processes often have the greatest impact in the long run. A new work by Rice University engineers could be one such, and it's a gas, gas, gas for nanomaterials.
Rice materials theorist Boris Yakobson, graduate student Jincheng Lei and alumnus Yu Xie of Rice's Brown School of Engineering have unveiled how a popular 2D material, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), flashes into existence during chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Knowing how the process works will give scientists and engineers a way to optimize the bulk manufacture of MoS2 and other valuable materials classed as transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), semiconducting crystals that are good bets to find a home in next-generation electronics.
Their study in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano focuses on MoS2's "pre-history," specifically what happens in a CVD furnace once all the solid ingredients are in place. CVD, often associated with graphene and carbon nanotubes, has been exploited to make a variety of 2D materials by providing solid precursors and catalysts that sublimate into gas and react. The chemistry dictates which molecules fall out of the gas and settle on a substrate, like copper or silicone, and assemble into a 2D crystal.
The problem has been that once the furnace cranks up, it's impossible to see or measure the complicated chain of reactions in the chemical stew in real time.
"Hundreds of labs are cooking these TMDs, quite oblivious to the intricate transformations occurring in the dark oven," said Yakobson, the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Materials Science and NanoEngineering and a professor of chemistry.
"Here, we're using quantum-chemical simulations and analysis to reveal what's there, in the dark, that leads to synthesis."
Yakobson's theories often lead experimentalists to make his predictions come true. (For example, boron buckyballs.) This time, the Rice lab determined the path molybdenum oxide (MoO3) and sulfur powder take to deposit an atomically thin lattice onto a surface.
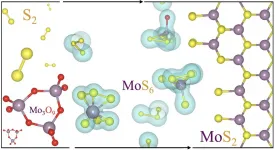
The short answer is that it takes three steps. First, the solids are sublimated through heating to change them from solid to gas, including what Yakobson called a "beautiful" ring-molecule, trimolybdenum nonaoxide (Mo3O9). Second, the molybdenum-containing gases react with sulfur atoms under high heat, up to 4,040 degrees Fahrenheit. Third, molybdenum and sulfur molecules fall to the surface, where they crystallize into the jacks-like lattice that is characteristic of TMDs.
What happens in the middle step was of the most interest to the researchers. The lab's simulations showed a trio of main gas phase reactants are the prime suspects in making MoS2: sulfur, the ring-like Mo3O9 molecules that form in sulfur's presence and the subsequent hybrid of MoS6 that forms the crystal, releasing excess sulfur atoms in the process.
Lei said the molecular dynamics simulations showed the activation barriers that must be overcome to move the process along, usually in picoseconds.
"In our molecular dynamics simulation, we find that this ring is opened by its interaction with sulfur, which attacks oxygen connected to the molybdenum atoms," he said. "The ring becomes a chain, and further interactions with the sulfur molecules separate this chain into molybdenum sulfide monomers. The most important part is the chain breaking, which overcomes the highest energy barrier."
That realization could help labs streamline the process, Lei said. "If we can find precursor molecules with only one molybdenum atom, we would not need to overcome the high barrier of breaking the chain," he said.
Yakobson said the study could apply to other TMDs.
"The findings raise oftentimes empirical nanoengineering to become a basic science-guided endeavor, where processes can be predicted and optimized," he said, noting that while the chemistry has been generally known since the discovery of TMD fullerenes in the early '90s, understanding the specifics will further the development of 2D synthesis.
"Only now can we 'sequence' the step-by-step chemistry involved," Yakobson said. "That will allow us to improve the quality of 2D material, and also see which gas side-products might be useful and captured on the way, opening opportunities for chemical engineering."
The Department of Energy Basic Energy Sciences program supported the research, and computations were performed at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center.
INFORMATION:
Read the abstract at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.1c03103.
This news release can be found online at https://news.rice.edu/2021/06/11/rice-lab-peers-inside-2d-crystal-synthesis/
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Related materials:
Yakobson Research Group: https://biygroup.blogs.rice.edu
Department of Materials Sciences and NanoEngineering: https://msne.rice.edu/
George R. Brown School of Engineering: https://engineering.rice.edu/
Video:
https://youtu.be/3Us5-NLarxE
An animation by Rice University engineers shows the incorporation of MoS6 into a crystal lattice of molybdenum disulfide. (Credit: Yakobson Research Group/Rice University)
Image for download:
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/06/0614_MOS2-1-WEB.jpg
Three gas-phase molecules react at high temperatures during chemical vapor deposition to form molybdenum disulfide, a two-dimensional semiconductor that could find use in next-generation electronics. In this illustration, molybdenum atoms are purple, oxygen is red and sulfur is yellow. (Credit: Illustration by Jincheng Lei/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,978 undergraduates and 3,192 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
jfalk@rice.edu
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
mikewilliams@rice.edu
RUDN University scientists together with colleagues from Switzerland proved in a clinical trial the effectiveness of a new dosage form -- amorphous solid dispersion. This is the first such study in humans to show the mechanism of action of this form of drug release. In the future, it will help to increase the effectiveness of drugs and use new active substances for treatment. The results of the study are published in Pharmaceuticals.
One of the main reasons for the dropout of new oral drugs at the preclinical and clinical stages of development is low bioavailability. The drug itself can be effective, but it is poorly absorbed in the body because of its low solubility. Amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) is a new ...
The 17-year cicadas emerging dramatically by the billions in 15 U.S. states from Georgia to New York and west to Illinois are making quite a racket--a uniquely North American phenomenon--but thousands of other cicada species on the planet also spend most of their lives underground, many of them emerging below the radar of human perception. Because most cicada species don't emerge simultaneously like species in the genus Magicicada--the periodical cicadas--little is known about their natural history. Driven by unusual attention to detail and curiosity, Annette Aiello, staff entomologist at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama, joined a very select group of ...
Environmental bacteria and fungi that end up in the belly of honeybees may be essential to their survival in a changing world as bee populations dwindle due to pesticides, poor nutrition, habitat destruction and declining genetic diversity.
Like many animals, bees have an internal armory. Their guts are home to a multitude of microbes that perform vital functions, from aiding digestion to breaking down toxins and fending off parasites. "A healthy gut microbiota makes bees more resilient to threats such as pathogens and climate change," says KAUST research scientist Ramona Marasco, "highlighting the need to understand how different microbes help their host."
Extensive research into the microbiome ...
Some 42% of patients attending a dedicated diabetes clinic have signs of established chronic kidney disease, the first detailed research of its kind in Ireland has revealed.
The study was carried out by academics at NUI Galway and clinicians at University Hospital Galway Diabetes Centre and involved more than 4,500 patients in the west of Ireland.
The findings suggest that, despite careful medical management, a relatively high proportion of people with diabetes in Ireland are developing chronic kidney disease over time and are at risk of kidney failure and other complications of poor kidney function.
Diabetes ...
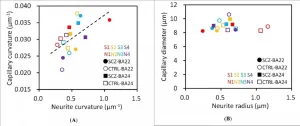
Drs. Itokawa, Mizutani and colleagues performed microtomography experiments the BL20XU beamline of the SPring-8 synchrotron radiation facility and found that brain capillary structures show a correlation with their neuron structures.
Brain blood vessels constitute a micrometer-scale vascular network responsible for supply of oxygen and nutrition. In this study, we analyzed cerebral tissues of the anterior cingulate cortex and superior temporal gyrus of schizophrenia cases and age/gender-matched controls by using synchrotron radiation microtomography or micro-CT in order to examine the three-dimensional structure of cerebral vessels.
All post-mortem human cerebral tissues were collected ...
A new species of large prehistoric croc that roamed south-east Queensland's waterways millions of years ago has been documented by University of Queensland researchers.
PhD candidate Jorgo Ristevski, from UQ's School of Biological Sciences, led the team that named the species Gunggamarandu maunala after analysing a partial skull unearthed in the Darling Downs in the nineteenth century.
"This is one of the largest crocs to have ever inhabited Australia," Mr Ristevski said.
"At the moment it's difficult to estimate the exact overall size of Gunggamarandu since all we have is the back of the skull - but it was big.
"We estimate the skull would have been at least 80 centimetres long, and based on comparisons with living crocs, this indicates a total ...
Summer picnics and barbecues are only a few weeks away! As excited as you are to indulge this summer, Escherichia coli bacteria are eager to feast on the all-you-can-eat buffet they are about to experience in your gut.
However, something unexpected will occur as E. coli cells end their journey through your digestive tract. Without warning, they will find themselves swimming in your toilet bowl, clinging to the last bits of nutrients attached to their bodies. How do these tiny organisms adapt to survive sudden starvation? Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis wondered.
Close examination of nutrient-deprived E. coli ...
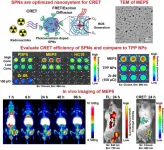
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 12:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021) - Researchers have successfully developed a novel cancer treatment approach that utilizes Cerenkov radiation energy to target and destroy cancer cells more effectively. The approach uses light from decaying radiopharmaceuticals, known as Cerenkov luminescence, as an energy source to activate semiconducting polymer nanoparticles that kill cancer cells. This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging's 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Over the past several decades, many studies have been conducted on photodynamic therapy, ...
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and is characterized by neurodegeneration in regions of the brain involved in memory and learning. Amyloid beta and tau are two toxic proteins that build up in disease and cause eventual neuronal death, but little is known about how other cells in the brain react during disease progression.
A new study from the ASU-Banner Neurodegenerative Research Center (NDRC) and MIT/Koch Institute sheds new light on how disease processes manifest in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Diego Mastroeni of the NDRC teamed up Forest White and Douglas Lauffenburger, colleagues in MIT's Department of Biological Engineering, to explore how protein ...
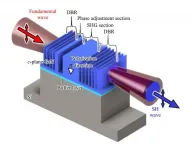
Osaka, Japan - Researchers from the Graduate School of Engineering and the Center for Quantum Information and Quantum Biology at Osaka University unveiled a new solid state second-harmonic generation (SHG) device that converts infrared radiation into blue light. This work may lead to a practical daily-use deep ultraviolet light source for sterilization and disinfection.
Recently, deep ultraviolet (DUV) light sources have been attracting much attention in sterilization and disinfection. In order to realize a bactericidal effect while ensuring user safety, a wavelength range of 220-230 nm is desirable. ...