INFORMATION:
Article reference: Yuhao Chen, Yue Li, Meng Du, Jinsui Yu, Fei Gao, Zhen Yuan and Zhiyi Chen, Ultrasound Neuromodulation: Integrating Medicine and Engineering for Neurological Disease Treatment. BIO Integration, 2021, https://doi.org/10.15212/bioi-2020-0026
BIO Integration is fully open access journal which will allow for the rapid dissemination of multidisciplinary views driving the progress of modern medicine.
As part of its mandate to help bring interesting work and knowledge from around the world to a wider audience, BIOI will actively support authors through open access publishing and through waiving author fees in its first years. Also, publication support for authors whose first language is not English will be offered in areas such as manuscript development, English language editing and artwork assistance.
BIOI is now open for submissions; articles can be submitted online at:
https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/bioi
Please visit http://www.bio-integration.org to learn more about the journal.
Editorial Board: https://bio-integration.org/editorial-board/
BIOI is available on the IngentaConnect platform (https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cscript/bioi) and at the BIO Integration website (http://www.bio-integration.org).
Submissions may be made using ScholarOne (https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/bioi).
There are no author submission or article processing fees.
Follow BIOI on Twitter @JournalBio; Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/BIO-Integration-Journal-108140854107716/) and LinkedIn (https://www.linkedin.com/company/bio-integration-journal/).
ISSN 2712-0074
eISSN 2712-0082
Keywords: Nanogenerator, neuromodulation, neurological disease, sonogenetics, ultrasound
Ultrasound neuromodulation: Integrating medicine and engineering for neurological disease treatment
2021-06-14
(Press-News.org) Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this article the authors Yuhao Chen, Yue Li, Meng Du, Jinsui Yu, Fei Gao, Zhen Yuan and Zhiyi Chen from The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China, University of South China, Hunan, China and University of Macau, China discuss ultrasound neuromodulation: integrating medicine and engineering for neurological disease treatment.
Neurological diseases associated with dysfunctions of neural circuits, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), depression and epilepsy, have become increasingly prevalent. To tackle these issues, artificial stimulation or regulation of specific neural circuits and nuclei are employed to alleviate or cure certain neurological diseases.
Ultrasound neuromodulation is an emerging interdisciplinary approach, which integrates medicine and engineering methodologies in the treatment. With the development of medicine and engineering, ultrasound neuromodulation has gradually been applied in the treatment of central nervous system diseases. In this review, the authors summarize the mechanism of ultrasound neuromodulation and the advances of focused ultrasound (FUS) in neuromodulation in recent years, with a special emphasis on its application in central nervous system disease treatment.
FUS shows great potential for the treatment of epilepsy, tremor, AD, depression, and brain trauma. The authors also suggest future directions of ultrasound neuromodulation in clinical settings, with a focus on fusion with genetic engineering or nanotechnology
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Histopathology-driven artificial intelligence predicts TMB-H colorectal cancer
2021-06-14
Niigata, Japan - Biomarkers are important determinants of appropriate and effective therapeutic approaches for various diseases including cancer. There is ample evidence pointing toward the significance of immune check point inhibitors (ICI) against cancer, and they showed promising clinical benefits to a specific group of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). Several reports demonstrated the efficacy of biomarkers such as programmed death-1 protein ligand (PD-L1), density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and tumor mutational burden (TMB), to determine the patient responsiveness for the efficient use of ICIs as therapeutics against cancer.
A high level of TMB (TMB-H), ...
Insulators turn up the heat on quantum bits
2021-06-14
Quantum technologies are based on quantum properties of light, electrons, and atoms. In recent decades, scientists have learned to master these phenomena and exploit them in applications. Thus, the construction of a quantum computer for commercial applications is also coming within reach. One of the emerging technologies that is currently being advanced very successfully is ion trap quantum computers. Here, charged particles are trapped with electromagnetic fields in a vacuum chamber and prepared in such a way that they can serve as carriers for information and be used for computing, which includes cooling them to the lowest temperatures permitted by quantum mechanics. However, the quantum mechanical ...
Food home delivery companies need up to 8,000 daily services to be profitable in a big city
2021-06-14
Various platforms which offer food home delivery services through courier services, such as riders or other types of distributors, have proliferated very quickly in recent years, especially in big cities. Due to this boom in last-mile delivery or logistics, UOC experts have studied the operation of the main food home delivery platforms, such as Just Eat, Glovo and Deliveroo, which work in the city of Barcelona, to analyse the profitability of these business models and estimate the number of orders needed to achieve this profitability.
"It's very difficult for these business models to be profitable by themselves", said Eduard J. Álvarez Palau, a researcher from the SUMA research group of the UOC's Faculty of Economics and Business, the main author of this work ...
Near-field routing of hyperbolic metamaterials
2021-06-14
Near-field light is invisible light at the subwavelength scale. Harnessed for a variety of practical applications, such as wireless power transfer, near-field light has an increasingly significant role in the development of miniature on-chip photonic devices. Controlling the direction of near-field light propagation has been an ongoing challenge that is of fundamental interest in photonics physics and can significantly advance a variety of applications.
So far, propagation of near-field light in a single direction is achieved by specific interactions between ...
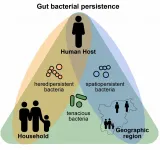
Persistence pays off in the human gut microbiome
2021-06-14
The human gut microbiome is a complex community of trillions of microbes that are constantly interacting with each other and our bodies. It supports our wellbeing, immune system and mental health - but how is it sustained?
Researchers in the UK and Germany, alongside other international collaborators, have investigated the evolution of bacteria in the human gut microbiome - asking how these microbes persist throughout their lifetimes - taking into account internal and external influencing factors.
The results of the study will help inform tailored probiotics, live bacteria found in particular foods or supplements, as well as dietary ...
RNA: A new method to discover its high-resolution structure
2021-06-14
The structure of a biomolecule can reveal much about its functioning and interaction with the surrounding environment. The double-helical structure of DNA and its implications for the processes of transmission of genetic information form an obvious example. In a new study by SISSA - Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati, published in Nucleic Acids Research, experimental data were combined with computer simulations of molecular dynamics to examine the conformation of an RNA fragment involved in protein synthesis and its dependence on the salts present in the solution. The research has led to a new method for high-resolution definition of the structures of biomolecules in their physiological environments. ...
Common lung infection in infants has different subtypes with differing asthma risks
2021-06-14
BOSTON - Bronchiolitis--the most common lung infection in young children, and which is most often caused by respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV--is the leading cause of hospitalizations in U.S. infants, and about 30% of those with severe bronchiolitis later develop asthma. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has uncovered four distinct molecular subtypes of RSV bronchiolitis and has linked a certain subtype to a higher asthma risk. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
"While bronchiolitis has been considered a single ...
Urgent action needed to reduce harms of ultra-processed foods to British children
2021-06-14
These are the findings of an Imperial-led study using data from thousands of children in England over a number of years, which looked at the health impact of consuming ultra-processed foods (UPFs) - food and drink heavily processed during their making, such as frozen pizzas, fizzy drinks, mass-produced packaged bread and some ready meals.
Researchers found that not only do UPFs make up a considerably high proportion of children's diets (more than 40% of intake in grams and more than 60% of calories on average), but that the higher the proportion of UPFs they consume, ...
Impact of COVID-19 on weddings reinforces need for marriage law reforms
2021-06-14
Coronavirus disruption to weddings has highlighted the complexity and antiquity of marriage law and reinforced the need for reform, a new study shows.
During the pandemic the ease and speed with which couples were able to marry has depended on their chosen route into marriage - religious or civil - experts have found.
Rules to prevent the spread of the pandemic attempted to strike a balance between getting married as a legal event and a wedding as a social event, and this has failed to please anyone, according to the research.
As lockdown loomed, couples marrying in the Anglican church were able to apply for a common or special licence rather than waiting to ...
Clinical trial shows cell therapy improves clinical outcomes in heart failure
2021-06-14
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - A clinical trial conducted at the University of Louisville has shown for the first time that heart failure treatments using cells derived from the patient's own bone marrow and heart resulted in improved quality of life and reduced major adverse cardiac events for patients after one year.
"This is a very important advance in the field of cell therapy and in the management of heart failure. It suggests that a treatment, given only once, can produce long-term beneficial effects on the quality of life and prognosis of these patients," said Roberto Bolli, M.D., ...