(Press-News.org) Near-field light is invisible light at the subwavelength scale. Harnessed for a variety of practical applications, such as wireless power transfer, near-field light has an increasingly significant role in the development of miniature on-chip photonic devices. Controlling the direction of near-field light propagation has been an ongoing challenge that is of fundamental interest in photonics physics and can significantly advance a variety of applications.
So far, propagation of near-field light in a single direction is achieved by specific interactions between the electric dipole and the magnetic dipole in a system, which has led to inevitable complexities in device design. Hyperbolic metamaterials (HMMs), an important class of artificial anisotropic material with hyperbolic isofrequency contours, have attracted attention due to their unique ability to control near-field light by enabling subwavelength confinement of electromagnetic waves. Large wave-vector modes in HMMs are of particular interest because those modes are easier to integrate and have a smaller loss of energy at transfer.
Near-field routing of hyperbolic metamaterials
Flexible control of the propagating direction of near-field light can be realized with hyperbolic metamaterials, using an all-electric metasource
2021-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
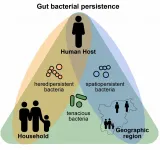
Persistence pays off in the human gut microbiome
2021-06-14
The human gut microbiome is a complex community of trillions of microbes that are constantly interacting with each other and our bodies. It supports our wellbeing, immune system and mental health - but how is it sustained?
Researchers in the UK and Germany, alongside other international collaborators, have investigated the evolution of bacteria in the human gut microbiome - asking how these microbes persist throughout their lifetimes - taking into account internal and external influencing factors.
The results of the study will help inform tailored probiotics, live bacteria found in particular foods or supplements, as well as dietary ...
RNA: A new method to discover its high-resolution structure
2021-06-14
The structure of a biomolecule can reveal much about its functioning and interaction with the surrounding environment. The double-helical structure of DNA and its implications for the processes of transmission of genetic information form an obvious example. In a new study by SISSA - Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati, published in Nucleic Acids Research, experimental data were combined with computer simulations of molecular dynamics to examine the conformation of an RNA fragment involved in protein synthesis and its dependence on the salts present in the solution. The research has led to a new method for high-resolution definition of the structures of biomolecules in their physiological environments. ...
Common lung infection in infants has different subtypes with differing asthma risks
2021-06-14
BOSTON - Bronchiolitis--the most common lung infection in young children, and which is most often caused by respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV--is the leading cause of hospitalizations in U.S. infants, and about 30% of those with severe bronchiolitis later develop asthma. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has uncovered four distinct molecular subtypes of RSV bronchiolitis and has linked a certain subtype to a higher asthma risk. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
"While bronchiolitis has been considered a single ...
Urgent action needed to reduce harms of ultra-processed foods to British children
2021-06-14
These are the findings of an Imperial-led study using data from thousands of children in England over a number of years, which looked at the health impact of consuming ultra-processed foods (UPFs) - food and drink heavily processed during their making, such as frozen pizzas, fizzy drinks, mass-produced packaged bread and some ready meals.
Researchers found that not only do UPFs make up a considerably high proportion of children's diets (more than 40% of intake in grams and more than 60% of calories on average), but that the higher the proportion of UPFs they consume, ...
Impact of COVID-19 on weddings reinforces need for marriage law reforms
2021-06-14
Coronavirus disruption to weddings has highlighted the complexity and antiquity of marriage law and reinforced the need for reform, a new study shows.
During the pandemic the ease and speed with which couples were able to marry has depended on their chosen route into marriage - religious or civil - experts have found.
Rules to prevent the spread of the pandemic attempted to strike a balance between getting married as a legal event and a wedding as a social event, and this has failed to please anyone, according to the research.
As lockdown loomed, couples marrying in the Anglican church were able to apply for a common or special licence rather than waiting to ...
Clinical trial shows cell therapy improves clinical outcomes in heart failure
2021-06-14
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - A clinical trial conducted at the University of Louisville has shown for the first time that heart failure treatments using cells derived from the patient's own bone marrow and heart resulted in improved quality of life and reduced major adverse cardiac events for patients after one year.
"This is a very important advance in the field of cell therapy and in the management of heart failure. It suggests that a treatment, given only once, can produce long-term beneficial effects on the quality of life and prognosis of these patients," said Roberto Bolli, M.D., ...
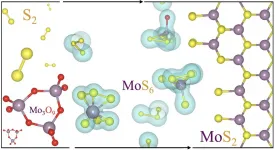
Rice lab peers inside 2D crystal synthesis
2021-06-14
HOUSTON - (June 11, 2021) - Scientific studies describing the most basic processes often have the greatest impact in the long run. A new work by Rice University engineers could be one such, and it's a gas, gas, gas for nanomaterials.
Rice materials theorist Boris Yakobson, graduate student Jincheng Lei and alumnus Yu Xie of Rice's Brown School of Engineering have unveiled how a popular 2D material, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), flashes into existence during chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Knowing how the process works will give scientists and engineers a way to optimize the bulk manufacture ...
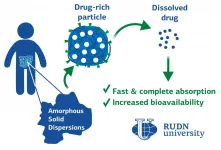
RUDN University scientists in pharmaceutical technology proved effectiveness of new dosage form
2021-06-14
RUDN University scientists together with colleagues from Switzerland proved in a clinical trial the effectiveness of a new dosage form -- amorphous solid dispersion. This is the first such study in humans to show the mechanism of action of this form of drug release. In the future, it will help to increase the effectiveness of drugs and use new active substances for treatment. The results of the study are published in Pharmaceuticals.
One of the main reasons for the dropout of new oral drugs at the preclinical and clinical stages of development is low bioavailability. The drug itself can be effective, but it is poorly absorbed in the body because of its low solubility. Amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) is a new ...
Rearing cicadas
2021-06-14
The 17-year cicadas emerging dramatically by the billions in 15 U.S. states from Georgia to New York and west to Illinois are making quite a racket--a uniquely North American phenomenon--but thousands of other cicada species on the planet also spend most of their lives underground, many of them emerging below the radar of human perception. Because most cicada species don't emerge simultaneously like species in the genus Magicicada--the periodical cicadas--little is known about their natural history. Driven by unusual attention to detail and curiosity, Annette Aiello, staff entomologist at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama, joined a very select group of ...
Into the belly of the bee
2021-06-14
Environmental bacteria and fungi that end up in the belly of honeybees may be essential to their survival in a changing world as bee populations dwindle due to pesticides, poor nutrition, habitat destruction and declining genetic diversity.
Like many animals, bees have an internal armory. Their guts are home to a multitude of microbes that perform vital functions, from aiding digestion to breaking down toxins and fending off parasites. "A healthy gut microbiota makes bees more resilient to threats such as pathogens and climate change," says KAUST research scientist Ramona Marasco, "highlighting the need to understand how different microbes help their host."
Extensive research into the microbiome ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] Near-field routing of hyperbolic metamaterialsFlexible control of the propagating direction of near-field light can be realized with hyperbolic metamaterials, using an all-electric metasource