(Press-News.org) When Erin Hecht was earning her Ph.D. in neuroscience more than a decade ago, she watched a nature special on the Russian farm-fox experiment, one of the best-known studies on animal domestication.
The study, running since 1958, tries to replicate the natural domestication of wolves to dogs by selectively breeding two strains of silver foxes so they exhibit certain behaviors. Scientists breed one to be tame and display dog-like behaviors with people, such as licking and tail wagging. The other is bred to react with defensive aggression when faced with human contact, while a third strain acts as the control and isn't bred for any specific behaviors.
Hecht, who's now an assistant professor in the Harvard Department of Human Evolutionary Biology, was fascinated by the experiment, which has helped scientists closely analyze the effects of domestication on genetics and behavior. But, she also thought something was missing.
"In that TV show, there was nothing about the brain," Hecht said. "I thought it was kind of crazy that there's this perfect opportunity to be studying how changes in brain anatomy are related to changes in the genome and changes in behavior, but nobody was really doing it yet."
Hecht acted fast and sent an email to Lyudmila N. Trut, the scientist running the Siberian institute where the Russian foxes were being studied. Fast forward to today and that email was foundational for a new study reporting on the surprising brain changes that occur in the Russian fox-farm experiment. Published Monday in the journal JNeurosci, the paper raises questions about some of the leading theories on domesticated animals' brains.
By analyzing MRI scans of the foxes, Hecht and her colleagues showed that both the foxes bred to be tame and those bred for aggression have larger brains and more grey matter than the brain of the control group (the foxes not bred for any particular behavior). These findings run in contrast to studies on chickens, sheep, cats, dogs, horses, and other animals that have shown domesticated species have smaller brains with less grey matter, than their wild forebears.
The team of researchers from Harvard, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Emory University, Cornell University, and the Russian Institute of Cytology and Genetics, explain the increase in size and grey matter, but can't yet be sure why this happens without further study. Their leading hypothesis centers on how the tame and aggressive strain have both been bred for specific behaviors at an accelerated time frame than many other domesticated animals. Dogs, for example, have been domesticated for at least 15,000 years.
"Both the tame and aggressive strains have been subject to intense, sustained selection on behavior, while the conventional strain undergoes no such intentional selection," they wrote. "Thus, it is possible that fast evolution of behavior, at least initially, may generally proceed via increases in grey matter."
As they analyzed the MRI scans, the research team noticed another surprise: similarities in the ways that the brains of the aggressive and tame foxes were changing. Both, for instance, showed enlargement in many of the same grey matter regions, including the prefrontal cortex, the amygdala, the hippocampus, and the cerebellum. This was despite the foxes being bred for opposite behaviors.
Results suggest that selection for opposite behavioral responses, in this case tame-versus-aggressive behavior, can produce similar changes in brain anatomy. The findings also suggest that significant changes to the structure and organization of the nervous system can evolve very quickly. In fact, it can happen within the span of less than a hundred generations.
Taken together, the researchers say the study's findings suggest existing ideas of brain changes in domestication may need revising, and that the brains of other animals, including humans, may have gone through similarly abrupt morphological shifts during times a sudden selection on behavior (rapid changes in environment or climate) occurred.
Next steps in the research include observing the foxes' brains scans at a cellular level.
The researchers believe there's a lot left to be learned from the Russian farm foxes and domesticated species, in general. That's because when a species splits from its wild counterpart, its brain, body, and behavior undergo rapid changes. Studying the foxes and other domesticated animals provides a window into these complex evolutionary processes.
"It's a more simple and straightforward way to see how evolution changes brains than we can achieve with just studying naturally occurring evolved brain changes," Hecht said.
INFORMATION:
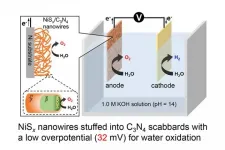
Niigata, Japan - In the recent past, there has been a paradigm shift towards renewable sources of energy in order to address the concerns pertaining to environmental degradation and dwindling fossil fuels. A variety of alternative green energy sources such as solar, wind, hydrothermal, tidal etc., have been gaining attention to reduce the global carbon footprints. One of the key challenges with these energy generation technologies is that they are intermittent and are not continuously available.
"We cannot use solar energy at night and wind energy when the wind is not blowing. But we can store the generated electricity in some other forms and utilize it whenever required. That is how water splitting bridges the gap and has emerged as a very promising energy storage ...
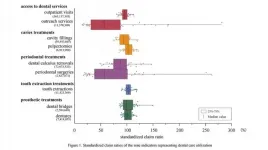
Tsukuba, Japan - Inequitable access to health care is a pressing global health concern, and care of our teeth is no exception. In fact, the World Health Organization established the Global Goals for Oral Health 2020 in its efforts to help counter socioeconomic-related imbalances. Economically advanced Japan has plentiful dentists, as well as a universal health insurance system, yet it also has oral care-related inequities, according to a new study.
A team of researchers centered at University of Tsukuba in Japan examined a huge set of claims and checkup data in search of regional and socioeconomic trends. Their findings included the key observation that regional lower ...
The potential of a class of materials called perovskites to enable solar cells to better absorb sunlight for energy production is widely known. However, this potential has yet to be fully realised, particularly under real-world operating conditions.
New research published today in the prestigious journal Nature Energy, has revealed defects in a popular perovskite light absorber that impede solar cell performance. The researchers found a change in the nature and density of these 'intragrain planar defects' correlated with a change in solar cell performance.
The discovery by an international team of researchers, led by Monash ...
Cities and nations around the globe are shooting for carbon neutrality, with some experts already talking about the need to ultimately reach carbon negativity. Carbon footprint declarations are used in construction to ease product selection for low carbon building, but these standards don't yet exist for green elements like soil, bushes and plants. A new study led by Aalto University is the first to map out how green infrastructure can be a resource for cities on the path to carbon neutrality.
The study, done in collaboration with the Natural Resources Institute Finland (Luke) and the University of Helsinki, charted out the lifecycle phases of plants, soils and mulches to determine the basic considerations needed to create standards for products commonly used in green ...
The National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA) of Malaysia has granted a conditional registration for a safe, effective hepatitis C treatment developed by a public-private partnership bringing together the Malaysian Ministry of Health, not-for-profit research and development organization Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi), Egyptian pharmaceutical company Pharco, Malaysian pharmaceutical company Pharmaniaga Berhad, and non-governmental-organization Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF).
This is the very first drug for hepatitis C virus (HCV) to be developed through South-South collaboration and with funding and clinical support from non-profit organizations.
This partnership ...
A current challenge for sustainable aquaculture is how to increase the quantities of farmed fish while also reducing waste products that can lead to the accumulation of harmful fish sludge. New research aims to understand how this fish waste can be treated for use in aquaponics systems, by removing excessive carbon, yet preserving the mineral nutrients required by plants to grow.
In this study in Frontiers in Plant Science, researchers from the Department of Marine Sciences at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, demonstrate a novel and effective way to convert this fish sludge into plant fertilizer and therefore improving the nutrients available for plants in hydroponic ...
DNA is an abundant and nutritious food source for microbes
The diet of microbes is vast: They are able to use different molecules as nutrients, including biomolecules such as proteins and lipids of dead and decaying organisms. This includes so called extracellular DNA molecules which are not or no longer present in intact cells. "From the bacteria's perspective DNA is particularly nutritious," says Kenneth Wasmund, a microbiologist at the Centre for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science (CMESS) at the University of Vienna and lead author of the study. "It's essentially a fertilizer. After all, it is a chain of millions of pieces of sugar and phosphorus- and nitrogen-containing bases." Extracellular ...
Universal school lunch programs make students healthier, and increase their lifetime income by 3%, according to a unique study from Lund University in Sweden published in The Review of Economic Studies.
Health disparities arise early in life and play a major role in economic outcomes among adults. Yet there are few studies on the long-term effects of school-based nutrition policies aimed at counteracting them. Researchers from Lund University and Stockholm University can now show that universal school lunch programs have significant long-term benefits for students' education, general health and income.
"Today, we take school lunches for granted in Sweden. But the fact is, it was a very conscious ...
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this article the authors Yuhao Chen, Yue Li, Meng Du, Jinsui Yu, Fei Gao, Zhen Yuan and Zhiyi Chen from The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China, University of South China, Hunan, China and University of Macau, China discuss ultrasound neuromodulation: integrating medicine and engineering for neurological disease treatment.
Neurological diseases associated with dysfunctions of neural circuits, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), depression and epilepsy, have become increasingly prevalent. To tackle these issues, artificial stimulation or regulation ...
Niigata, Japan - Biomarkers are important determinants of appropriate and effective therapeutic approaches for various diseases including cancer. There is ample evidence pointing toward the significance of immune check point inhibitors (ICI) against cancer, and they showed promising clinical benefits to a specific group of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). Several reports demonstrated the efficacy of biomarkers such as programmed death-1 protein ligand (PD-L1), density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and tumor mutational burden (TMB), to determine the patient responsiveness for the efficient use of ICIs as therapeutics against cancer.
A high level of TMB (TMB-H), ...