(Press-News.org) Universal school lunch programs make students healthier, and increase their lifetime income by 3%, according to a unique study from Lund University in Sweden published in The Review of Economic Studies.
Health disparities arise early in life and play a major role in economic outcomes among adults. Yet there are few studies on the long-term effects of school-based nutrition policies aimed at counteracting them. Researchers from Lund University and Stockholm University can now show that universal school lunch programs have significant long-term benefits for students' education, general health and income.
"Today, we take school lunches for granted in Sweden. But the fact is, it was a very conscious investment when Sweden introduced free lunches in the 1940s. These cooked meals were meticulously planned in terms of nutrition. This begs the question: did it affect students' well-being in the long-term? We wanted to find out", says Petter Lundborg, professor of economics at Lund University.
Sweden, Finland and Estonia have been serving free school meals for a long time, unlike the neighboring countries Norway and Denmark, where pupils bring their own lunch. In other countries, such as the US and the UK, poorer students are offered school meals, while others pay.
In the new study, the researchers examine the Swedish school lunch program that was introduced gradually in different municipalities from the mid-1940s. The program offered nutritious school lunches to all Swedish primary school students, free of charge.. The researchers focused on the introduction of school lunches between 1959 and 1969. They discovered that the initiative had a positive impact on the height of the students, their health as young adults, the level of education they attained, and their lifetime income.
"Our study shows that universal efforts that provide children with nutritious meals can be seen as a long-term investment. In other words: ensuring that children eat well, also pays off later in life in terms of health, education and income", says Dan-Olof Rooth, professor of economics at the Institute for Social Research (SOFI) at Stockholm University.
The study shows, among other things, that both boys and girls who took part in the school meal program throughout their schooling grew taller than those who did not have access to the program. Pupils who received school meals during the entire nine years of compulsory school became almost 1 cm taller and went to university more often compared with pupils without access to the program. However, most importantly, the students had a three percent higher lifetime income.
"We also noted some interesting differences in the effects, where children from poor households benefited the most, even if children from all households benefit to a certain extent. Students from poor families had a six percent higher lifetime income, and students from other households had about a two percent higher lifetime income. The reform thus benefited all students, from both poor and rich families", says Petter Lundborg.
The results are related: the students ate nutritious food at school, they became taller and more educated, which to a large extent can explain why they had a better income through life. However, the researchers found no long-term effects on mortality, morbidity or sick leave.
The effects of school meal programs can also be caused by factors that have nothing to do with nutrition. Therefore, the researchers also collected data on school absenteeism from municipal archives in Sweden. The researchers' analysis shows that the introduction of the school lunch program did not lead to any changes in school attendance, which was high even before school meals were introduced.
"A reasonable interpretation of our results is that the students became more receptive to what they were being taught when they ate a nutritious lunch. This is in line with a previous study, which found that test results among eleven-year-olds increased during the first year after the introduction of nutritious school meals in connection with the Jamie Oliver campaign in the UK", says Dan-Olof Rooth.
Petter Lundborg and Dan-Olof Rooth - who conducted the study together with Dr. Jesper Alex-Petersen - believe that their results are relevant to many western countries today, even though the Swedish school lunch program was introduced during the 1950s and 1960s. Sweden was a rich country, where school children did not lack food, but where parents lacked knowledge about healthy eating habits. The reform made school food nutritious and the same for everyone.
"It is important for many countries even today, because school meals and their nutritional content is a recurring issue. Our results show significant long-term economic benefits of school meals. You get a lot of 'bang for your buck' - it is extremely well-invested money", concludes Petter Lundborg.
About the study:
The researchers used newly collected historical data on the gradual implementation of the program across municipalities in Sweden between the years 1959 and 1969. During this period, 265 municipalities introduced the program, with a roughly equal number of municipalities each year.
These historical data were linked to administrative records that cover the population of primary school pupils, i.e., about 1.5 million pupils born 1942-1965. Using a difference-in-differences design, they estimated the impact of the school lunch reform on a broad range of outcomes taken from income and education registers, the military enlistment register, the medical birth register, and hospitalization and mortality registers.
INFORMATION:
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this article the authors Yuhao Chen, Yue Li, Meng Du, Jinsui Yu, Fei Gao, Zhen Yuan and Zhiyi Chen from The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China, University of South China, Hunan, China and University of Macau, China discuss ultrasound neuromodulation: integrating medicine and engineering for neurological disease treatment.
Neurological diseases associated with dysfunctions of neural circuits, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), depression and epilepsy, have become increasingly prevalent. To tackle these issues, artificial stimulation or regulation ...
Niigata, Japan - Biomarkers are important determinants of appropriate and effective therapeutic approaches for various diseases including cancer. There is ample evidence pointing toward the significance of immune check point inhibitors (ICI) against cancer, and they showed promising clinical benefits to a specific group of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). Several reports demonstrated the efficacy of biomarkers such as programmed death-1 protein ligand (PD-L1), density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and tumor mutational burden (TMB), to determine the patient responsiveness for the efficient use of ICIs as therapeutics against cancer.
A high level of TMB (TMB-H), ...
Quantum technologies are based on quantum properties of light, electrons, and atoms. In recent decades, scientists have learned to master these phenomena and exploit them in applications. Thus, the construction of a quantum computer for commercial applications is also coming within reach. One of the emerging technologies that is currently being advanced very successfully is ion trap quantum computers. Here, charged particles are trapped with electromagnetic fields in a vacuum chamber and prepared in such a way that they can serve as carriers for information and be used for computing, which includes cooling them to the lowest temperatures permitted by quantum mechanics. However, the quantum mechanical ...
Various platforms which offer food home delivery services through courier services, such as riders or other types of distributors, have proliferated very quickly in recent years, especially in big cities. Due to this boom in last-mile delivery or logistics, UOC experts have studied the operation of the main food home delivery platforms, such as Just Eat, Glovo and Deliveroo, which work in the city of Barcelona, to analyse the profitability of these business models and estimate the number of orders needed to achieve this profitability.
"It's very difficult for these business models to be profitable by themselves", said Eduard J. Álvarez Palau, a researcher from the SUMA research group of the UOC's Faculty of Economics and Business, the main author of this work ...
Near-field light is invisible light at the subwavelength scale. Harnessed for a variety of practical applications, such as wireless power transfer, near-field light has an increasingly significant role in the development of miniature on-chip photonic devices. Controlling the direction of near-field light propagation has been an ongoing challenge that is of fundamental interest in photonics physics and can significantly advance a variety of applications.
So far, propagation of near-field light in a single direction is achieved by specific interactions between ...
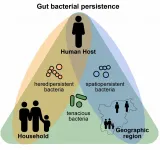
The human gut microbiome is a complex community of trillions of microbes that are constantly interacting with each other and our bodies. It supports our wellbeing, immune system and mental health - but how is it sustained?
Researchers in the UK and Germany, alongside other international collaborators, have investigated the evolution of bacteria in the human gut microbiome - asking how these microbes persist throughout their lifetimes - taking into account internal and external influencing factors.
The results of the study will help inform tailored probiotics, live bacteria found in particular foods or supplements, as well as dietary ...
The structure of a biomolecule can reveal much about its functioning and interaction with the surrounding environment. The double-helical structure of DNA and its implications for the processes of transmission of genetic information form an obvious example. In a new study by SISSA - Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati, published in Nucleic Acids Research, experimental data were combined with computer simulations of molecular dynamics to examine the conformation of an RNA fragment involved in protein synthesis and its dependence on the salts present in the solution. The research has led to a new method for high-resolution definition of the structures of biomolecules in their physiological environments. ...
BOSTON - Bronchiolitis--the most common lung infection in young children, and which is most often caused by respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV--is the leading cause of hospitalizations in U.S. infants, and about 30% of those with severe bronchiolitis later develop asthma. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has uncovered four distinct molecular subtypes of RSV bronchiolitis and has linked a certain subtype to a higher asthma risk. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
"While bronchiolitis has been considered a single ...
These are the findings of an Imperial-led study using data from thousands of children in England over a number of years, which looked at the health impact of consuming ultra-processed foods (UPFs) - food and drink heavily processed during their making, such as frozen pizzas, fizzy drinks, mass-produced packaged bread and some ready meals.
Researchers found that not only do UPFs make up a considerably high proportion of children's diets (more than 40% of intake in grams and more than 60% of calories on average), but that the higher the proportion of UPFs they consume, ...
Coronavirus disruption to weddings has highlighted the complexity and antiquity of marriage law and reinforced the need for reform, a new study shows.
During the pandemic the ease and speed with which couples were able to marry has depended on their chosen route into marriage - religious or civil - experts have found.
Rules to prevent the spread of the pandemic attempted to strike a balance between getting married as a legal event and a wedding as a social event, and this has failed to please anyone, according to the research.
As lockdown loomed, couples marrying in the Anglican church were able to apply for a common or special licence rather than waiting to ...