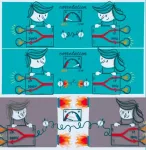
(Press-News.org) Stuttgart/Boulder - It is not the first time that spiders have served as biological models in the research field of soft robotics. The hydraulic actuation mechanisms they apply to move their limbs when weaving their web or hunting for prey give them powers many roboticists and engineers have drawn inspiration from.
A team of researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Germany and at the University of Boulder in Colorado in the US has now found a new way to exploit the principles of spiders' joints to drive articulated robots without any bulky components and connectors, which weigh down the robot and reduce portability and speed. Their slender and lightweight simple structures impress by enabling a robot to jump 10 times its height. At the end of May, the team's work titled "Spider-inspired electrohydraulic actuators for fast, soft-actuated joints" was published in END
Electrohydraulic arachno-bot a fascinating lightweight
Fast and efficient nature-inspired joints power robotic systems
2021-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Inducing and tuning spin interactions in layered material
2021-06-16
Magnetic-spin interactions that allow spin-manipulation by electrical control allow potential applications in energy-efficient spintronic devices.
An antisymmetric exchange known as Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) is vital to form various chiral spin textures, such as skyrmions, and permits their potential application in energy-efficient spintronic devices.
Published this week, a Chinese-Australia collaboration has for the first time illustrated that DMI can be induced in a layered material tantalum-sulfide (TaS2) by intercalating iron atoms, and can further be tuned by gate-induced proton intercalation.
REALIZING AND TUNING DMI IN VAN-DER-WAALS MATERIAL TaS2
Searching ...
Small numbers of cells in a tumor could be key enablers of cancer metastasis
2021-06-16
WASHINGTON --Just a small number of cells found in tumors can enable and recruit other types of cells nearby, allowing the cancer to spread to other parts of the body, report END ...
Natural killers: Using the body's cells to target breast cancer
2021-06-16
It sounds like a plot from a Quentin Tarantino movie -- something sets off natural killers and sends them on a killing spree.
But instead of characters in a movie, these natural killers are part of the human immune system and their targets are breast cancer tumor cells. The triggers are fusion proteins developed by Clemson University researchers that link the two together.
"The idea is to use this bifunctional protein to bridge the natural killer cells and breast cancer tumor cells," said Yanzhang (Charlie) Wei, a professor in the College of Science's Department of Biological Sciences. "If the two cells are brought close enough together through this receptor ligand connection, the natural killer cells can release what I call killing machinery to have the tumor cells killed."
It's ...
Poison frog tadpoles can survive (almost) anywhere
2021-06-16
A group of researchers from the University of Jyvaskyla and Stanford University were part of an expedition to French Guiana to study tropical frogs in the Amazon. Various amphibian species of this region use ephemeral pools of water as their nurseries, and display unique preferences for specific physical and chemical characteristics. Despite species-specific preferences, researchers were surprised to find tadpoles of the dyeing poison frog surviving in an incredible range of both chemical (pH 3-8) and vertical (0-20 m in height) deposition sites. This research was published in the journal Ecology and Evolution in June 2021.
Neotropical frogs are special because, unlike species in temperate regions, many tropical frogs ...
Measuring the elimination of plastic particles from the body in mice
2021-06-16
Postdoctoral Researcher Outi Keinänen from the University of Helsinki developed a method to radiolabel plastic particles in order to observe their biodistribution on the basis of radioactivity with the help of positron emission tomography (PET). As a radiochemist, Keinänen has in her previous radiopharmaceutical studies utilised PET imaging combined with computed tomography (CT), which produces a very accurate image of the anatomical location of the radioactivity signal.
In the recently completed study, radiolabelled plastic particles were fed to mice, and their elimination from the body was followed with PET-CT scans. This was the first time that ...
'Overly stringent' criteria early in the pandemic led to missed diagnoses of COVID-19
2021-06-16
Research published today in the Journal of General Virology has identified missed cases of SARS-CoV-2 by retrospective testing of throat swabs.
Researchers at the University of Nottingham screened 1,660 routine diagnostic specimens which had been collected at a Nottingham hospital between 2 January and 11 March 2020 and tested for SARS-CoV-2 by PCR. At this stage of the pandemic, there was very little COVID-19 testing available in hospitals, and to qualify patients had to meet a strict criterion, including recent travel to certain countries in Asia or contact with a known positive case.
Three previously unidentified cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection were identified by the retrospective screening, including one from a 75-year-old ...
Quantum-nonlocality at all speeds
2021-06-16
The phenomenon of quantum nonlocality defies our everyday intuition. It shows the strong correlations between several quantum particles some of which change their state instantaneously when the others are measured, regardless of the distance between them. While this phenomenon has been confirmed for slow moving particles, it has been debated whether nonlocality is preserved when particles move very fast at velocities close to the speed of light, and even more so when those velocities are quantum mechanically indefinite. Now, researchers from the University of Vienna, the Austrian Academy of Sciences and the Perimeter Institute report in the latest issue of Physical Review Letters that ...
Particles with 'eyes' allow a closer look at rotational dynamics
2021-06-16
Tokyo, Japan - Colloids--mixtures of particles made from one substance, dispersed in another substance--crop up in numerous areas of everyday life, including cosmetics, food and dyes, and form important systems within our bodies. Understanding the behavior of colloids therefore has wide-ranging implications, yet investigating the rotation of spherical particles has been challenging. Now, an international team including researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science has created particles with an off-center core or "eye" that can be tracked ...
CNIO researchers find molecular switch that allows organisms to adapt to fasting conditions
2021-06-16
Getting energy and nutrients from the environment - that is, eating - is such an important function that it has been regulated through sophisticated mechanisms over hundreds of millions of years. Some of these mechanisms are only now beginning to be unravelled. A group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) has found one of their key components - a switch that controls the ability of organisms to adapt to low cellular nutrient levels.
The protein involved is RagA, which is part of the mTOR molecular pathway, whose importance in metabolic activity regulation has been known for decades now. CNIO researchers have found that if RagA is continuously activated, cells do not know that there are no sufficient nutrients and so ...
A backdoor in mobile phone encryption from the 90s still exists
2021-06-16
The encryption algorithm GEA-1 was implemented in mobile phones in the 1990s to encrypt data connections. Since then, it has been kept secret. Now, a research team from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB), together with colleagues from France and Norway, has analysed the algorithm and has come to the following conclusion: GEA-1 is so easy to break that it must be a deliberately weak encryption that was built in as a backdoor. Although the vulnerability is still present in many modern mobile phones, it no longer poses any significant threat to users, according to the researchers.
Backdoors not useful according to researchers
"Even though intelligence services and ministers of the interior understandably want such backdoors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Electrohydraulic arachno-bot a fascinating lightweightFast and efficient nature-inspired joints power robotic systems