(Press-News.org) Modelling the financial system as a network is a precondition to understanding and managing challenges of great relevance for society, including the containment of financial crises and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Financial Networks is the scientific discipline that deals with these issues. An article published in the scientific journal Nature Review Physics carries out the first comprehensive review of this exciting interdisciplinary field. By covering over 250 studies across domains, the paper is also a call for researchers in all scientific disciplines to consider the insights from the financial network models, because of their implications for citizens, public agencies and governments. Professor Guido Caldarelli from Ca' Foscari University of Venice coordinated the study, which involved Marco Bardoscia, a researcher from the Bank of England, as the first author.
"Traditional economic models describe the financial system either as a macroeconomic aggregate or, in contrast, as a collection of microeconomic actors in isolation. - Stefano Battiston, co-author and professor of Finance, at the Department of Economics of Ca' Foscari University of Venice, explains. - Both approaches are not equipped to describe those phenomena that emerge at the intermediate scale, because of interconnectedness. Financial actors are connected (directly and indirectly) via contracts, markets and institutions. These phenomena include, in particular, the propagation of risk along a chain of contracts (financial contagion), as well as the collective behaviour of investors when they stamped to get rid of assets suddenly deemed as riskier than expected (fire-sales)".
The discipline of financial networks has thus filled important scientific gaps. The importance of financial networks is widely recognised today. Many central banks use network models to carry out stress-tests. The highest financial authorities both in the US and in the EU follow macroprudential policies that recognise the key role of the interconnectedness of the financial system. Indeed, network effects played a key role in the 2007-2008 financial crisis, with an impact persisting for a decade, and they played a role also in the Covid crisis.
"There is something fascinating and special about the field of financial networks. - Guido Caldarelli, a co-author of the study and professor of Physics at the Department of Molecular Sciences and Nanosystems of Ca' Foscari, adds. - Questions that pertain to finance and economics are addressed by modelling financial actors as nodes and financial contracts as links in a network. For instance, the question of how to preserve the stability of the financial system is addressed by looking at the interplay between the network structure (i.e. the topology), the characteristics of individual nodes (the balance sheets) and the dynamic process on the nodes (the propagation of financial losses)".
This approach owes a great deal to the field of statistical physics which has been historically devoted to the challenge of explaining the emergence of macroscopic behaviour of a system from the microscopic properties of the individual entities. However, in financial networks, there are additional distinct features that raise the stakes of the challenge. The entities of the system are not particles, but agents that form expectations about the future evolution of the network and even about the policy maker's attempt to regulate the system. This leads to new scientific questions in terms of the mathematical equations that can describe such reflexivity.
"In the near future, Financial Networks will address several exciting scientific challenges - Guido Caldarelli foresees - For example, modern financial systems are composed of multiple interacting networks because of agents acting on multiple markets with different instruments. Further, modelling the financial system poses big data issues as transactions generate Terabytes of information every day. Moreover, the interaction of the financial system with the real economy is a feedback loop and still not well-understood".
One avenue of research of particular interest for Ca' Foscari's researchers is the application of financial networks in the area of sustainable finance. The European Union has set the goal to become net carbon neutral by 2050. The transition to a carbon-neutral economy will avoid the most adverse impact of global warming on current and future generations.
It will also ensure the competitiveness of the EU and of Italy. Indeed, an early transition brings opportunities. In contrast, a transition that would be first delayed and then would occur in a sudden way would bring higher risks, possibly systemic. In fact, financial institutions have large exposures to economic activities that are affected by climate policies. Therefore, financial network models are key to understanding how to facilitate the transition and mitigate climate-related financial risks.
In addition, the article demonstrates the relevance of financial networks not only for research but also for practitioners in financial authorities and in the industry. "Today, having competencies in Financial Networks gives a competitive advantage to prospective students graduating both at a Master's and PhD level. - professor Battiston adds, - Courses in this field will enrich the curricula of study not only in physics but also in economics and finance. This could apply also to future executive education programmes".
INFORMATION:
In the mid-14th century Europe was devastated by a major pandemic - the Black Death - which killed between 40 and 60 per cent of the population. Later waves of plague then continued to strike regularly over several centuries.
Plague kills so rapidly it leaves no visible traces on the skeleton, so archaeologists have previously been unable to identify individuals who died of plague unless they were buried in mass graves.
Whilst it has long been suspected that most plague victims received individual burial, this has been impossible to confirm until now. ...
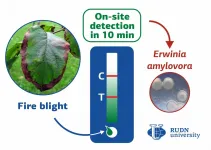
RUDN University biotechnologists have created a method for detection of bacterial infection in apple, pear, hawthorn and other plants of the Rosaceae family. The test does not require laboratory equipment, the result is ready in 10 minutes. This will allow detecting the disease quickly and prevent the spread of infection. The results are published in Physiological and Molecular Pathology of Plants.
Erwinia amylovora bacteria causes a dangerous infectious disease in plants -- a fire blight. Most plants of the Rosaceae family are vulnerable to it, for example, hawthorn, apple, pear. The bacteria causes the blossom to wither, the leaves dry up and curl, the bark develop necrotic lesions. The disease can spread through infected plants, garden tools, and with the wind, which ...
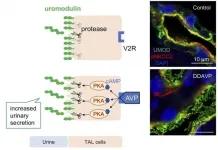
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that the secretion of uromodulin protein into urine can be induced by treatments that may protect against urinary tract infections and kidney stones, among other diseases
Tokyo, Japan - The normal function of uromodulin, a protein that is made in the kidney and secreted into the urine, remains largely unknown. However, higher levels of uromodulin in the urine are related to lower rates of urinary tract infections and kidney stones, while higher levels of this protein in kidney cells are associated with higher rates of hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Researchers from Japan have now uncovered how uromodulin secretion into the urine can be increased by the hormone vasopressin--a finding that may ...
A study performed by researchers at the Institute for Advanced Chemistry of Catalonia (IQAC-CSIC) from the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) in collaboration with Stony Brook University (USA) proposes a new strategy for the development of new drugs based on the inhibition of tyrosine kinase enzymes, molecules that activate and trigger many cellular processes. The results have been published in the Chemistry - A European Journal.
The new approach is based on the regulation of the signaling cascade of tyrosine kinases, and could lead to the development ...
Today as they did 100 years ago, doctors diagnose cancer by taking tissue samples from patients, which they usually fix in formalin for microscopic examination. In the past 20 years, genetic methods have also been established that make it possible to characterize mutations in tumors in greater detail, thus helping clinicians select the best treatment strategy.
Even tiny tissue samples can be used to detect proteins
Now, a group of researchers from the Berlin-based Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC), the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH), Charité - Universitätsmedizin ...
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina and the German Council for Sustainable Development (RNE) have published a joint position paper presenting paths to climate neutrality by 2050. In it, the Leopoldina and the RNE highlight options for action to effect the changes needed within society, at political level and in the business world, in view especially of the urgency and the historic dimensions of the transformation we face. With the paper, the Leopoldina and the RNE are consciously not seeking to engage in a race to set the most ambitious target. They are instead offering an options paper for setting the right course and covering the key implementation steps. ...
Abu Dhabi, UAE: Trans-Neptunian Objects (TNOs), small objects that orbit the sun beyond Neptune, are fossils from the early days of the solar system which can tell us a lot about its formation and evolution.
A new study led by Mohamad Ali-Dib, a research scientist at the NYU Abu Dhabi END ...
Chemical engineers at the University of Illinois Chicago and UCLA have answered longstanding questions about the underlying processes that determine the life cycle of liquid foams. The breakthrough could help improve the commercial production and application of foams in a broad range of industries.
Findings of the END ...
The glaciers of Nanga Parbat - one of the highest mountains in the world - have been shrinking slightly but continually since the 1930s. This loss in surface area is evidenced by a long-term study conducted by researchers from the South Asia Institute of Heidelberg University. The geographers combined historical photographs, surveys, and topographical maps with current data, which allowed them to show glacial changes for this massif in the north-western Himalaya as far back as the mid-1800s.
Detailed long-term glacier studies that extend the observation period ...
DALLAS, June 16, 2021 -- Findings from a small study detailing the treatment of myocarditis-like symptoms in seven people after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine in the U.S. are published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation. These cases are among those reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) documenting the development of myocarditis-like symptoms in some people who received the COVID-19 vaccine.
Myocarditis is a rare but serious condition that causes inflammation of the middle layer of the wall of the heart muscle. It can weaken the heart and affect the heart's electrical system, which keeps the heart pumping regularly. It is most often the result of an infection and/or ...