(Press-News.org) Understanding cellular metabolism - how a cell uses energy- could be key to treating a wide array of diseases, including vascular diseases and cancer.
While many techniques can measure these processes among tens of thousands of cells, researchers have been unable to measure them at the single-cell level.
Researchers at the University of Chicago's Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering and Biological Sciences Division have developed a combined imaging and machine learning technique that can, for the first time, measure a metabolic process at both the cellular and sub-cellular levels.
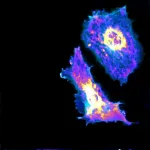
Using a genetically encoded biosensor paired with artificial intelligence, the researchers were able to measure glycolysis, the process of turning glucose into energy, of single endothelial cells, the cells that line blood vessels.
They found that when these cells move and contract, they use more glucose, and they also found that cells uptake glucose through a previously unknown receptor. Understanding this process could lead to better treatments for cancer and vascular diseases, including COVID-19.
The research, published in Nature Metabolism, was led by Assoc. Prof. Yun Fang and co-led by Asst. Prof. Jun Huang, with former postdoctoral fellow and now Asst. Prof David Wu and biophysical sciences graduate student Devin Harrison.
"Understanding cellular metabolism is universally important," Huang said. "By measuring single-cell metabolism, we potentially have a new way of treating a wide range of diseases."
"This is the first time that we can visualize cellular metabolism at different temporal and spatial scales, even at the subcellular level, which could fundamentally change the language and approach for researchers to study cellular metabolism," Fang said.
Measuring glycolysis
Endothelial cells normally provide a tight layer inside blood vessels, but they can contract, leaving gaps within this layer, when they need help from the immune system. Abnormal contraction can cause leaky blood vessels, leading to heart attack or stroke. Such contraction in blood vessels around the lungs can also cause fluid to leak in, which happens in the case of acute respiratory distress syndrome. (This often occurs in patients with severe cases of COVID-19.)
To better understand how cells metabolize energy to fuel this contraction, the researchers turned to Förster resonance energy transfer sensors--genetically encoded biosensors that can measure the amount of lactate inside cells. Lactate is the byproduct of glycolysis.
Though the researchers did not create the sensors, by pairing the sensors with machine learning algorithms, they created an even more powerful technique that allowed them to image cells, analyze the data, and parse out glycolysis reactions at the cellular and subcellular levels.
"Now we can look at and understand details within the cells, like certain areas of cells where there is an increase of glycolysis," Fang said. "This is a key technological innovation."
They were able to measure just how much glucose cells used when they contracted and moved, and they also found a new mechanism of glucose transport mediated by the cell's cytoskeleton - a receptor called GLUT3 - that these cells use to uptake glucose.
Creating new treatments
Understanding how glycolysis works at the cellular level could ultimately lead to treatments that inhibit this process when beneficial - in the case of leaky blood vessels in patients with atherosclerosis, for example. It could also help patients whose immune systems are overreacting to COVID-19, for example, and need help closing the gaps within their endothelial cells around their lungs.
"If we can find a way to inhibit contraction, we could lessen the acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19 patients," Fang said.
It also has important implications in treating cancer. Endothelial migration and proliferation, driven by glycolysis, are major cellular processes involved in vascular growth, which is necessary for tumor survival and growth. Understanding just how this works could help researchers both destroy tumors and inhibit tumor growth.
It could also be useful in CAR T-cell therapy, which recruits the body's own immune system to fight tumors. While the therapy has been lifesaving for some, many patients don't respond to it. Since endothelial cells are important for allowing T-cells to infiltrate tumors and cellular metabolism is instrumental to T-cell functions, researchers believe that modulating cellular metabolism could help create a better immunotherapy system.
The researchers are currently testing such inhibitors to treat COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome at Argonne National Laboratory.
"Can we ultimately reprogram cells through metabolism?" Huang said. "It's an important question, and we need to understand just how metabolism works. There is huge potential here, and this is just the starting point."
INFORMATION:
Other authors on the paper include Teodora Szasz, Chih-Fan Yeh, Tzu-Pin Shentu, Angelo Meliton, Ru-Ting Huang, Zhenjie Zhou, and Gökhan Mutlu.
Citation: "Single-cell metabolic imaging reveals a SLC2A3-dependent glycolytic burst in motile endothelial cells," Wu, D., Harrison, D.L., Szasz, T. et al. Nature Metabolism, May 24, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-021-00390-y
PHILADELPHIA - Sour taste does not have the nearly universal appeal that sweet taste does. Slightly sour foods or drinks such as yogurt and lemon juice are yummy to many, but such highly sour foods as spoiled milk are yucky, even dangerous. Like humans, many other animals, including insects, prefer slightly acidic over very acidic foods.
Evolutionary biologists surmise that the need for sour detection to be finely tuned is a two-sided coin: slightly acidic foods can enhance digestion and stimulate saliva production; relative sour-to-sweet taste can signal optimal ripeness of fruit; and extremely sour food, as with bitter taste, is a warning to what not to ingest. However, despite this usefulness, how do animals discern different concentrations ...
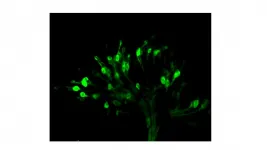
The brain presents different states depending on the communication between billions of neurons, and this network is the basis of all our perceptions, memories, and behaviours. It is often considered a "black box", with difficult access for clinicians and researchers, as few limited tools are available to perform accurate and spaciotemporal studies on brain neuronal behaviour. Now, researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in collaboration with August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS) and have added some light to the subject: they succeeded for the first time in controlling neuronal activity in the brain using a molecule responsive to light.
The study included participants ...
MADISON - In early January 2021, travelers returning to Tokyo, Japan, from Amazonas, Brazil, were screened for COVID-19 at the airport. A few days later, the National Institute of Infectious Disease of Japan announced that the travelers had returned with a new variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
That variant, known as gamma, or P.1, led to a deadly surge in COVID-19 cases in Brazil this spring, and has now spread across the world. More than 200 cases have been detected in Wisconsin. Whether current vaccines are as effective against the gamma variant remains unknown.
In a new study using variant virus recovered from one of the original travelers, ...
University of Delaware disaster researcher A.R. Siders said it's time to put all the options on the table when it comes to discussing climate change adaptation.
Managed retreat -- the purposeful movement of people, buildings and other assets from areas vulnerable to hazards -- has often been considered a last resort. But Siders said it can be a powerful tool for expanding the range of possible solutions to cope with rising sea levels, flooding and other climate change effects when used proactively or in combination with other measures.
Siders, a core faculty member in UD's Disaster Research Center, and Katharine J. Mach, associate professor at the University ...
KIYATEC, Inc. announced today the publication of new peer-reviewed data that establishes clinically meaningful prediction of patient-specific responses to standard of care therapy, prior to treatment, in newly diagnosed glioblastoma (GBM) and other high-grade glioma (HGG) patients. The results, the interim data analysis of the company's 3D-PREDICT clinical study, were published June 16, 2021 in Neuro-Oncology Advances, an open access clinical journal.
A goal of the study, which continues to enroll, was for the test's prospective, patient-specific response prediction to achieve statistical significance for ...
Researchers from Bentley University, in partnership with Waltham Council on Aging in Massachusetts, and as part of a study funded by the National Science Foundation, have been exploring how the elderly use smart speakers at home. Waltham, a satellite city about eight miles west of Cambridge has a population of about 60,000, with about one in six being an elderly citizen. The purpose of the study was to understand how the elderly use the smart speaker technology at home. A smart speaker is a hardware device that is always-on. When a wake-word triggers the software contained in the device, the smart speaker listens to the command to provide a response or carry out the command (accessing resources ...
When Ana K. Spalding, a Research Associate at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) and Assistant Professor of Marine and Coastal Policy at Oregon State University (OSU) talks about mentorship in academia, she describes it as meaningful relationship. It goes beyond conversations about research and publications, and into shared experiences. This is just one approach--proposed by Spalding and 23 other women scientists from around the world, in a new article published in PLOS Biology--that calls for a shift in the value system of science to emphasize a more equal, diverse and inclusive academic culture.
The authors came together after reading a ...
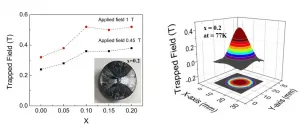
Superconductors are something like a miracle in the modern world. Their unique property of zero resistance can revolutionize power transmission and transport (e.g., Maglev train). However, most of the conventional superconductors require cooling down to extremely low temperatures that can only be achieved with liquid helium, a rather expensive coolant. Material scientists are now investigating "high-temperature superconductors" (HTSs) that can be cooled to a superconducting state by using the significantly cheaper liquid nitrogen (which has a remarkably higher temperature than liquid helium). ...
TROY, N.Y. -- Optoelectronic materials that are capable of converting the energy of light into electricity, and electricity into light, have promising applications as light-emitting, energy-harvesting, and sensing technologies. However, devices made of these materials are often plagued by inefficiency, losing significant useful energy as heat. To break the current limits of efficiency, new principles of light-electricity conversion are needed.
For instance, many materials that exhibit efficient optoelectronic properties are constrained by inversion symmetry, a physical property that limits engineers' control of electrons in the material and their options for designing novel or efficient devices. In research published today in Nature ...
With sorghum poised to become an important crop grown by Pennsylvania farmers, Penn State researchers, in a new study, tested more than 150 germplasm lines of the plant for resistance to a fungus likely to hamper its production.
Sorghum, a close relative to corn, is valuable for yielding human food, animal feed and biofuels. Perhaps its most notable attribute is that the grain it produces is gluten free. Drought resistant and needing a smaller amount of nutrients than corn to thrive, sorghum seems to be a crop that would do well in the Keystone State's ...