New research reveals remarkable resilience of sea life in the aftermath of mass extinctions
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) Pioneering research has shown marine ecosystems can start working again, providing important functions for humans, after being wiped out much sooner than their return to peak biodiversity.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and published today in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, paves the way for greater understanding of the impact of climate change on all life forms.
The international research team found plankton were able to recover and resume their core function of regulating carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere more than twice as fast as they regained full levels of biodiversity.
Senior author Daniela Schmidt, Professor of Palaeobiology at the University of Bristol, said: "These findings are hugely significant, given growing concern around the extinctions of species in response to dramatic environmental shifts. Our study indicates marine systems can accommodate some losses in terms of biodiversity without losing full functionality, which provides hope. However, we still don't know the precise tipping point so the focus should very much remain on preserving this fragile relationship and protecting biodiversity."
While previous research has shown that functionality resumes quicker than biodiversity in algae, this is the first study to corroborate the discovery further up the food chain in zooplankton, which are vital for sea life as part of the food web supporting fish.
The scientists analysed tiny organisms called foraminifer, the size of grains of sand, from the mass extinction, known as the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg), which took place around 66 million years ago and eradicated three-quarters of the Earth's plant and animal species. This is the most catastrophic event in the evolutionary history of modern plankton, as it resulted in the collapse of one of the ocean's primary functions, the 'biological pump' which sucks vast amounts of carbon dioxide out of atmosphere into the ocean where it stays buried in sediments for thousands of years. The cycle not only influences nutrient availability for marine life, but also carbon dioxide levels outside the sea and therefore the climate at large.
Lead author Dr Heather Birch, a former researcher at the university's School of Earth Sciences and Cabot Institute for the Environment, said: "Our research shows how long - approximately 4 million years - it can take for an ecosystem to fully recover after an extinction event. Given human impact on current ecosystems, this should make us mindful. However, importantly the relationship between marine organisms and the marine carbon pump, which affects atmosphere CO2, appears not to be closely related."
Professor Schmidt added: "The results highlight the importance of linking climate projections with ecosystems models of coastal and open ocean environments to improve our ability to understand and forecast the impact of climate-induced extinctions on marine life and their services to people, such as fishing. Further research is needed to look at what happens and whether the same patterns are evident higher up the food web, for instance with fish."
INFORMATION:
Paper
'Ecosystem Function after the K/Pg Extinction: Decoupling of Marine Carbon Pump and Diversity' in Proceedings of the Royal Society B by Heather Birch, Daniela Schmidt, Helen Coxall, Dick Croon, and Andrew Ridgewell
Notes to editors
Professor Daniela Schmidt is available for interview.
To arrange this, please email d.schmidt@bristol.ac.uk and Victoria Tagg, Media & PR Manager (Research) at the University of Bristol: victoria.tagg@bristol.ac.uk
Photos
https://fluff.bris.ac.uk/fluff/u2/oc20541/bZfApSp3FrzHFwVf49ZJlQ1RO/
At the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary, not only dinosaurs went extinct. The loss of species in the upper part of the ocean had profound impacts on its diversity and function. Image shows small deprived Cretaceous fauna after the extinction.
Photo credit: Brian Huber
https://fluff.bris.ac.uk/fluff/u3/oc20541/egqwab_XB6T_xqaPbtioSg1Ru/
Image shows large diverse Cretaceous fauna before the extinction.
Photo credit: Brian Huber
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
An accurate, non-invasive, and low-cost method of testing for COVID-19 using samples taken from the screens of mobile phones has been developed by a team led by UCL researchers at Diagnosis Biotech.
The study, published in eLife and led by Dr Rodrigo Young (UCL Institute of Ophthalmology), analysed swabs from smartphone screens rather than directly from people, and found that people who tested positive by the regular nasal swabbing PCRs were also positive when samples were taken from phone screens.
The new method - known as Phone Screen Testing (PoST) - detected the COVID-19 virus on the phones of 81 to 100% of contagious people with a high viral load, suggesting it is as accurate as antigen lateral flow tests.
Globally active screening for COVID-19 is still a priority ...
2021-06-23
Modern weather forecasts rely heavily on data retrieved from numerical weather prediction models. These models continue to improve and have advanced considerably throughout more than half a century. However, forecast reliability depends on the quality and accuracy of initialization data, or a sample of the current global atmosphere when the model run is started. This process of bringing surface observations, radiosonde data, and satellite imagery together to create a picture of the initial atmospheric state is called data assimilation. Satellite upgrades have significantly improved this process, providing more data than ever before. Several recent studies show ...
2021-06-23
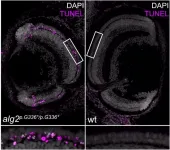
A rare genetic defect that affects the so-called ALG2 gene can cause serious metabolic diseases in humans. It does so through the defective formation of proteins and sugar molecules. Until now, its rareness and complexity made it difficult to study this congenital glycosylation disorder. A research team led by Prof. Dr Joachim Wittbrodt and Dr Thomas Thumberger from the Centre for Organismal Studies (COS) of Heidelberg University has finally succeeded in introducing the underlying mutation in the ALG2 gene in a fish model, thus allowing the causes of these complex diseases to be studied at the molecular level.
Human cells are kept alive by the activity of millions of proteins. As they mature, these proteins ...
2021-06-23
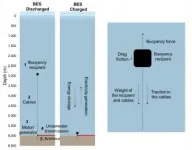
What do pipes and anchors have to do with storing energy? More than you might think! A new IIASA-led study explored the potential of a lesser known, but promising sustainable energy storage system called Buoyancy Energy Storage.
There is general consensus that renewable energy sources will play an important role in ensuring a healthier and more sustainable future for the planet and its people, and many countries are indeed already seeing such technologies displacing "dirty" fossil fuels in the power sector in an effort to lower emissions. The biggest problem with renewable energy sources, however, is that power supply is intermittent, meaning that the energy output at any given time does not necessarily meet the demand at that time. ...
2021-06-23
Our homes and offices are only as solid as the ground beneath them. When that solid ground turns to liquid -- as sometimes happens during earthquakes -- it can topple buildings and bridges. This phenomenon is known as liquefaction, and it was a major feature of the 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand, a magnitude 6.3 quake that killed 185 people and destroyed thousands of homes.
An upside of the Christchurch quake was that it was one of the most well-documented in history. Because New Zealand is seismically active, the city was instrumented ...
2021-06-23
Several eye clinics around Sweden are seeing a rise in eye damage related to the racket sport padel. In an article in the Journal of the Swedish Medical Association (Läkartidningen), eye researchers affiliated with the University of Gothenburg state that padel is a potential high-risk sport for eye injuries, and that wearing protective goggles is a good idea.
Ball sports are often associated with an increased risk of eye injuries, and the risk seems to be even greater with padel, a sport that is now highly popular in Sweden (and should not be confused with the North American "paddle tennis").
"The ...
2021-06-23
ITHACA, N.Y. - Coming soon to a lab tabletop near you: a method of magneto-thermal imaging that offers nanoscale and picosecond resolution previously available only in synchrotron facilities.
This innovation in spatial and temporal resolution will give researchers extraordinary views into the magnetic properties of a range of materials, from metals to insulators, all from the comfort of their labs, potentially boosting the development of magnetic storage devices.
"Magnetic X-ray microscopy is a relatively rare bird," said Greg Fuchs, associate professor of applied and engineering physics, who led the project. "The magnetic ...
2021-06-23
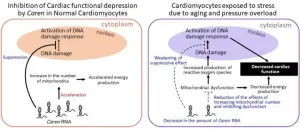
A research collaboration based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has identified a novel lncRNA, Caren, that is abundantly expressed in cardiomyocytes. They showed that it enhances energy production by increasing the number of mitochondria in cardiomyocytes, and inhibits activation of the ATM protein, a key player in the DNA damage response pathway that accelerates heart failure severity. Caren RNA in cardiomyocytes is reduced by aging and high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to heart failure, and markedly reduced in the hearts of heart failure patients. The researchers believe that ...
2021-06-23
Eating 2.5 grams of pure natural cocoa powder serves to improve visual acuity in healthy young adults and in daylight conditions, according to research by the Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) and the ICTAN (Institute of Food and Nutrition Science and Technology) of the CSIC.
The study, published in the Journal of Functional Foods, analyse the effects of two dietary polyphenols: cocoa flavanols and red berry anthocyanins.
"Although this was the baseline hypothesis, we did not see any effect either on adaptation to darkness or on visual acuity measured in low light conditions (mesopic vision), either with cocoa or with berries," indicates María Cinta Puell Marín, researcher at the Optometry and Vision ...
2021-06-23
Children who were exposed to higher levels of trace minerals manganese and selenium during their mothers' pregnancy had a lower risk of high blood pressure in childhood, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers analyzed the levels of toxic metals and trace minerals in blood samples drawn from nearly 1,200 women in the Boston area who gave birth between 2002 and 2013. They found that higher levels of selenium or manganese in the mothers' blood were associated with lower blood pressure readings in their children ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New research reveals remarkable resilience of sea life in the aftermath of mass extinctions