Trauma patients with COVID-19 face greater risk of complications and death
COVID-19-positive patients with traumatic injuries have six times higher risk of death and complication than patients without COVID, Penn Medicine research shows
2021-06-28
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA-- In addition to sickening and taking the lives of millions across the globe, COVID-19 complicated patient care in a range of less-direct ways, from increased incidence of END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers engineer cells to destroy malignant tumor cells but leave the rest alone
2021-06-28
HAMILTON, ON June 28, 2021 -- Researchers at McMaster University have developed a promising new cancer immunotherapy that uses cancer-killing cells genetically engineered outside the body to find and destroy malignant tumors.
The modified "natural killer" cells can differentiate between cancer cells and healthy cells that are often intermingled in and around tumors, destroying only the targeted cells.
The natural killer cells' ability to distinguish the target cells, even from healthy cells that bear similar markers, brings new promise to this branch of immunotherapy, say ...
Males help keep populations genetically healthy
2021-06-27
A few males are enough to fertilise all the females. The number of males therefore has little bearing on a population's growth. However, they are important for purging bad mutations from the population. This is shown by a new Uppsala University study providing in-depth knowledge of the possible long-term genetic consequences of sexual selection. The results are published in the scientific journal Evolution Letters.
The study supports the theory that in many animal species selection acting on males can impose the fortuitous benefit to the population of causing offspring to inherit healthy genes. Stiff competition among males results ...
Toxicity of protein involved in Alzheimer's triggered by a chemical 'switch'
2021-06-26
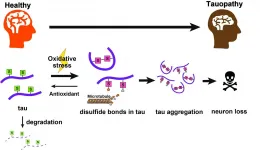
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered that a specific chemical feature of a key protein known as tau may cause it to accumulate in the brain and trigger illnesses like Alzheimer's. They found that disulfide bonds on certain amino acids act to stabilize tau and cause it to accumulate, an effect that got worse with increased oxidative stress. The identification of chemical targets triggering tau accumulation may lead to breakthrough treatments.
The tau protein is key to the healthy function of biological cells. It helps form and stabilize microtubules, the thin filaments that crisscross cell interiors to help keep them structurally rigid and provide 'highways' to shuttle molecules between organelles. However, when they ...
Edible Cholera vaccine made of powdered rice proves safe in phase 1 human trials
2021-06-26
A new vaccine to protect against deadly cholera has been made by grinding up genetically modified grains of rice. The first human trial has shown no obvious side effects and a good immune response. Researchers based at the University of Tokyo and Chiba University have published the peer-reviewed results of the Phase 1 clinical trial of the vaccine, named MucoRice-CTB, in The Lancet Microbe.
Vaccine manufacturing has made enormous strides in 2020, spurred on by COVID-19. However, the complexity of mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines has highlighted the value of inoculations that can be made, transported and stored cheaply and without refrigeration.
The MucoRice-CTB vaccine is stable at room temperature from start to finish.
"I'm very optimistic for the future of our MucoRice-CTB vaccine, ...
Elephants solve problems with personality
2021-06-26
Just as humans have their own individual personalities, new research in the Journal of Comparative Psychology shows that elephants have personalities, too. Moreover, an elephant's personality may play an important role in how well that elephant can solve novel problems.
The article was written by Lisa Barrett and Sarah Benson-Amram in the University of Wyoming's Animal Behavior and Cognition Lab, led by Benson-Amram. It may be viewed here.
The authors of the paper tested 15 Asian elephants and three African savanna elephants in three zoos across the country -- the San Diego Zoo, the Smithsonian's National Zoological Park and the Oklahoma City Zoo -- with the help of elephant caretakers.
Previous work from Barrett and Benson-Amram demonstrated ...
Differences in human, mouse brain cells have important implications for disease research
2021-06-26
FINDINGS
A UCLA-led study comparing brain cells known as astrocytes in humans and mice found that mouse astrocytes are more resilient to oxidative stress, a damaging imbalance that is a mechanism behind many neurological disorders. A lack of oxygen triggers molecular repair mechanisms in these mouse astrocytes but not in human astrocytes. In contrast, inflammation activates immune-response genes in human astrocytes but not mouse astrocytes.
BACKGROUND
Although the mouse is a ubiquitous laboratory model used in research for neurological diseases, results from studies in mice are not always applicable to humans. In fact, more than 90% of drug candidates that show preclinical promise for neurological disorders ultimately fail when tested in humans, in part ...
Hydrofracking environmental problems not that different from conventional drilling
2021-06-25
Crude oil production and natural gas withdrawals in the United States have lessened the country's dependence on foreign oil and provided financial relief to U.S. consumers, but have also raised longstanding concerns about environmental damage, such as groundwater contamination.
A researcher in Syracuse University's College of Arts and Sciences, and a team of scientists from Penn State, have developed a new machine learning technique to holistically assess water quality data in order to detect groundwater samples likely impacted by recent methane leakage during oil and gas production. Using that model, the team concluded that unconventional drilling ...
Loss of circadian regulation allows for increase in glucose production during lung cancer
2021-06-25
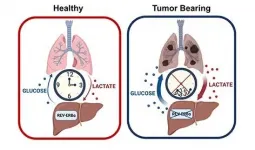
Irvine, CA - June 25, 2021 - New research from the University of California, Irvine reveals how the circadian regulation of glucose production in the liver is lost during lung cancer progression, and how the resulting increase in glucose production may fuel cancer cell growth.
The new study titled, "Glucagon regulates the stability of REV-ERBα to modulate hepatic glucose production in a model of lung cancer-associated cachexia," published today in Science Advances, illustrates how the circadian clock is regulated under conditions of stress such as during lung cancer progression and cancer-associated tissue wasting ...
Muscle's smallest building blocks disappear after stroke
2021-06-25
After suffering a stroke, patients often are unable to use the arm on their affected side. Sometimes, they end up holding it close to their body, with the elbow flexed.
In a new study, Northwestern University and Shirley Ryan AbilityLab researchers have discovered that, in an attempt to adapt to this impairment, muscles actually lose sarcomeres -- their smallest, most basic building blocks.
Stacked end to end (in series) and side to side (in parallel), sarcomeres make up the length and width of muscle fibers. By imaging biceps muscles with three noninvasive methods, the researchers found that stroke patients had fewer sarcomeres along the length ...
Mayo Clinic researchers study potential new CAR-T cell therapy for multiple myeloma
2021-06-25
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Researchers at Mayo Clinic Cancer Center are studying a potential new chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy (CAR-T cell therapy) treatment for multiple myeloma. Their findings were published on Friday, June 24, in The Lancet.
"CAR-T cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that involves harnessing the power of a person's own immune system by engineering their T cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells," says Yi Lin, M.D., a Mayo Clinic hematologist and lead author of the study.
Dr. Lin says the Food and Drug Administration approved ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Trauma patients with COVID-19 face greater risk of complications and deathCOVID-19-positive patients with traumatic injuries have six times higher risk of death and complication than patients without COVID, Penn Medicine research shows