Patients with acute myocarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: This study describes four patients who presented with acute myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination.
Authors: Raymond J. Kim, M.D., of the Duke Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Center in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2828)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and editorials are linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2828?guestAccessKey=2451cf5d-3edf-44e1-9813-d7703fe94760&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=062921
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
What The Study Did: Researchers describe myocarditis presenting after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in 23 patients within the Military Health System.
Authors: Jay Montgomery, M.D., of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, and Margaret Ryan, M.D., M.P.H., of the Naval Medical Center San Diego, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
2021-06-29
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Ruth Howie presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2021: Cancer treatments can cause premature ovarian failure (POI) including in girls who want to become mothers eventually. Ovarian tissue cryopreservation (OTC) provides a future fertility option but is invasive, has risks and evidence indicates that most girls don't develop POI. So, doctors face the dilemma of how to offer OTC appropriately.
Now, an assessment tool has been found to help predict correctly which female cancer patients aged under 18 years will develop POI and should therefore be offered OTC. Results from a long-term follow-up study of 423 girls and young women show nearly a quarter (24%; n = 9) of the 37 assessed as high ...
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 - For more than 60 years, algae have been studied as a potential feedstock for biofuel production, but the cellulose in their cell wall makes it hard to access the critical molecules inside and convert them to biogas.
In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, an international research team reports their success in using urea and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, commonly known as lye or caustic soda) as a pretreatment of algae, which breaks down cellulose and more than doubles biogas production under their initial experimental conditions.
"We were ...
2021-06-29
With advances in medical science driving progress against childhood brain tumors, today three out of four young patients survive at least five years beyond diagnosis. However, the outcomes look grim when malignant cells spread, or metastasize.
Such is the case with medulloblastoma, a type of brain cancer that arises in the cerebellum, at the back of the head. Although rare in absolute terms -- about 350 cases emerge each year, 60 percent of them in children -- medulloblastoma is the most common and deadliest form of pediatric brain cancer. Metastasis ...
2021-06-29
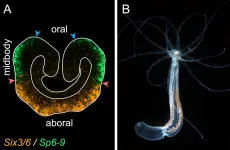
In a new article in Nature Communications, a research group led by Grigory Genikhovich at the University of Vienna has found that the way the main body axis of sea anemones is patterned by different intensities of β-catenin signaling is similar to that of sea urchins and vertebrates. This suggests that this axial patterning mechanism already existed about 650 million years ago.
The positioning of all anatomical structures in an embryo is determined by systems of molecular coordinates, which are called body axes. Different regulatory genes are activated at specific locations along the body axes to drive the development of all body parts in correct places.
This process is very ...
2021-06-29
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich researchers have shown how RNA-binding proteins modulate synaptic responses that mediate the transmission of nerve cell impulses.
Cells in the central nervous system possess a high degree of flexibility, which enables them to adapt to fluctuating demands and respond to changing patterns of neuronal activity. This is achieved by modulating the connections between nerve cells, which are mediated by structures called synapses that determine how neighboring neurons respond to stimulation. These adjustments in turn require the intracellular transport of mRNAs. Consequently, the required proteins ...
2021-06-29
Earthworms experience constant chemical interactions with bacteria, fungi, plants and small invertebrates across soil ecosystems. Even within their tissues, earthworms harbor symbiotic microbes and small animal parasites that trigger internal metabolic responses such as innate immunity. To reveal the fundamental processes that enable animal-microbe symbioses to form and persist, we have to study their metabolic interactions in situ. By combining novel imaging techniques, a team of researchers around Benedikt Geier from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology ...
2021-06-29
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and the UK investigated the safety and efficacy of new chemistry in antisense oligonucleotides used to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a debilitating genetic disease. Their results may lead to the development of drugs with less toxicity and fewer injections needed thanks to prolonged action. The paper was published in the journal Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.
Antisense oligonucleotides are single stranded chemically modified fragments of DNA that target pre-messenger RNA, short bits of genetic information a ribosome reads to make a protein. Depending on how a particular antisense oligonucleotide works, the target mRNA can either be destroyed or undergo subtle changes in how it's spliced, i.e. how exons, the ...
2021-06-29
Russian scientists have experimentally proved the existence of a new type of quasiparticle - previously unknown excitations of coupled pairs of photons in qubit chains. This discovery could be a step towards disorder-robust quantum metamaterials. The study was published in Physical Review B.
Superconducting qubits are a leading qubit modality today that is currently being pursued by industry and academia for quantum computing applications. However, the performance of quantum computers is largely affected by decoherence that contributes to a qubits extremely short lifespan and causes computational errors. Another ...
2021-06-29
Pioneering research has revealed the erosion of ancient sediments found deep beneath Antarctic ice could be a vital and previously unknown source of nutrients and energy for abundant microbial life.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and published today in Nature's Communications Earth & Environment journal, sheds new light on the many compounds supporting various microbes which form part of a huge subglacial ecosystem.
Lead author Dr Beatriz Gill Olivas, a Post-Doctoral Research Associate at the University of Bristol, said: "Although the study focused on samples obtained from a single ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Patients with acute myocarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination