Butterfly effect can double travel of virus-laden droplets
Small pockets of virus-laden air can detach from an exhaled breath, traveling in a ballistic manner and reaching large distances from a COVID-infected individual
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Computer simulations have been used with great success in recent months to visualize the spread of the COVID-19 virus in a variety of situations. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers explain how turbulence in the air can create surprising and counterintuitive behavior of exhaled droplets, potentially laden with virus.
Investigators from the University of Florida and Lebanese American University carried out detailed computer simulations to test a mathematical theory they developed previously. They found nearly identical exhalations could spread in different directions when miniscule initial variations are substantially amplified by turbulence. This is the so-called butterfly effect.
The investigators call the volume of exhaled air in one cough or sneeze a puff. They found most liquid droplets that could potentially contain virus remain within the puff as it spreads. However, a small number of droplets are ejected from the puff at near-ballistic speeds, vastly overshooting the major portion of the exhaled air.
The droplets shooting out of the puff like bullets are larger than the norm, while those that remain within the puff are smaller. Additionally, the authors found the portion of the puff advancing at a higher speed would drag a few droplets with it. This turbulence-induced mechanism provides an explanation for why ejected droplets sometimes go so far from the source.
"One of our interesting findings was that a small portion of the puff of air could detach," author Nadim Zgheib said. "The detached portion resembles a vortex ring-like structure and advances at relatively quickly along a direction that deviates slightly from the flow direction."
The peeled-off portions are ring shaped, allowing the separated pockets of air to advance at higher speed, potentially spreading dangerous virus-laden droplets over a large area.
"We noticed that the center of the separated puff is practically void of any droplets," said author Jorge Salinas.
The direction this detached portion travels cannot be predicted. Multiple runs revealed detached pockets of virus-laden air could travel in many directions, reaching large distances from the potentially infected person.
While droplets are dragged along by the peeled-off pocket of air, others remain stranded within the main body of the puff. The density of these droplets is considerably higher than the surrounding air, so they tend to settle out under gravity and eventually land on the ground or surfaces below.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Investigation of theoretical scaling laws using large eddy simulations for airborne spreading of viral contagion from sneezing and coughing," is authored by Kai Liu, Majid Allahyari, Jorge S. Salinas, Nadim Zgheib, and S. Balachandar. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on June 29, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0054651). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0054651.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- As pervasive as they are in everyday uses, like encryption and security, randomly generated digital numbers are seldom truly random.
So far, only bulky, relatively slow quantum random number generators (QRNGs) can achieve levels of randomness on par with the basic laws of quantum physics, but researchers are looking to make these devices faster and more portable.
In Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, scientists from China present the fastest real-time QRNG to date to make the devices quicker and more portable. The ...
2021-06-29
What The Study Did: This study describes four patients who presented with acute myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination.
Authors: Raymond J. Kim, M.D., of the Duke Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Center in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2828)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
2021-06-29
What The Study Did: Researchers describe myocarditis presenting after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in 23 patients within the Military Health System.
Authors: Jay Montgomery, M.D., of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, and Margaret Ryan, M.D., M.P.H., of the Naval Medical Center San Diego, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
2021-06-29
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Ruth Howie presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2021: Cancer treatments can cause premature ovarian failure (POI) including in girls who want to become mothers eventually. Ovarian tissue cryopreservation (OTC) provides a future fertility option but is invasive, has risks and evidence indicates that most girls don't develop POI. So, doctors face the dilemma of how to offer OTC appropriately.
Now, an assessment tool has been found to help predict correctly which female cancer patients aged under 18 years will develop POI and should therefore be offered OTC. Results from a long-term follow-up study of 423 girls and young women show nearly a quarter (24%; n = 9) of the 37 assessed as high ...
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 - For more than 60 years, algae have been studied as a potential feedstock for biofuel production, but the cellulose in their cell wall makes it hard to access the critical molecules inside and convert them to biogas.
In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, an international research team reports their success in using urea and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, commonly known as lye or caustic soda) as a pretreatment of algae, which breaks down cellulose and more than doubles biogas production under their initial experimental conditions.
"We were ...
2021-06-29
With advances in medical science driving progress against childhood brain tumors, today three out of four young patients survive at least five years beyond diagnosis. However, the outcomes look grim when malignant cells spread, or metastasize.
Such is the case with medulloblastoma, a type of brain cancer that arises in the cerebellum, at the back of the head. Although rare in absolute terms -- about 350 cases emerge each year, 60 percent of them in children -- medulloblastoma is the most common and deadliest form of pediatric brain cancer. Metastasis ...
2021-06-29
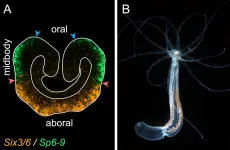
In a new article in Nature Communications, a research group led by Grigory Genikhovich at the University of Vienna has found that the way the main body axis of sea anemones is patterned by different intensities of β-catenin signaling is similar to that of sea urchins and vertebrates. This suggests that this axial patterning mechanism already existed about 650 million years ago.
The positioning of all anatomical structures in an embryo is determined by systems of molecular coordinates, which are called body axes. Different regulatory genes are activated at specific locations along the body axes to drive the development of all body parts in correct places.
This process is very ...
2021-06-29
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich researchers have shown how RNA-binding proteins modulate synaptic responses that mediate the transmission of nerve cell impulses.
Cells in the central nervous system possess a high degree of flexibility, which enables them to adapt to fluctuating demands and respond to changing patterns of neuronal activity. This is achieved by modulating the connections between nerve cells, which are mediated by structures called synapses that determine how neighboring neurons respond to stimulation. These adjustments in turn require the intracellular transport of mRNAs. Consequently, the required proteins ...
2021-06-29
Earthworms experience constant chemical interactions with bacteria, fungi, plants and small invertebrates across soil ecosystems. Even within their tissues, earthworms harbor symbiotic microbes and small animal parasites that trigger internal metabolic responses such as innate immunity. To reveal the fundamental processes that enable animal-microbe symbioses to form and persist, we have to study their metabolic interactions in situ. By combining novel imaging techniques, a team of researchers around Benedikt Geier from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology ...
2021-06-29
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and the UK investigated the safety and efficacy of new chemistry in antisense oligonucleotides used to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a debilitating genetic disease. Their results may lead to the development of drugs with less toxicity and fewer injections needed thanks to prolonged action. The paper was published in the journal Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.
Antisense oligonucleotides are single stranded chemically modified fragments of DNA that target pre-messenger RNA, short bits of genetic information a ribosome reads to make a protein. Depending on how a particular antisense oligonucleotide works, the target mRNA can either be destroyed or undergo subtle changes in how it's spliced, i.e. how exons, the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Butterfly effect can double travel of virus-laden droplets
Small pockets of virus-laden air can detach from an exhaled breath, traveling in a ballistic manner and reaching large distances from a COVID-infected individual