(Press-News.org) Beetles are creatures with built-in body armor. They are tiny tanks covered with hard shells, also known as exoskeletons, protecting their soft, skeleton-less bodies inside. In addition to providing armored protection, the beetle's exoskeleton offers functions like sensory feedback and hydration control. Notably, the exoskeletons of many beetles are also brilliantly colored and patterned, which enhances visual communication with other beetles and organisms.
Ling Li, lead investigator and assistant professor in mechanical engineering, has joined colleagues from six other universities to investigate the interplay between mechanical and optical performance in beetle exoskeletons. They discovered that the structures providing mechanical support are also key players in optical framework. Their findings were published in the END
Microstructure found in beetle's exoskeleton contributes to color and damage resistance
2021-06-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify muscle proteins whose quantity is reduced in type 2 diabetes
2021-06-29
Globally, more than 400 million people have diabetes, most of them suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Before the onset of actual type 2 diabetes, people are often diagnosed with abnormalities in glucose metabolism that are milder than those associated with diabetes. The term used to indicate such cases is prediabetes. Roughly 5-10% of people with prediabetes develop type 2 diabetes within a year-long follow-up.
Insulin resistance in muscle tissue is one of the earliest metabolic abnormalities detected in individuals who are developing type 2 diabetes, and the phenomenon is already seen in prediabetes.
In a collaborative study, researchers from the University of Helsinki, the ...
Researchers pinpoint unique growing challenges for soybeans in Africa
2021-06-29
URBANA, Ill. - Despite soybean's high protein and oil content and its potential to boost food security on the continent, Africa produces less than 1% of the world's soybean crop. Production lags, in part, because most soybean cultivars are bred for North and South American conditions that don't match African environments.
Researchers from the Soybean Innovation Lab (SIL), a U.S. Agency for International Development-funded project led by the University of Illinois, are working to change that. In a new study, published in Agronomy, they have developed methods to help breeders improve soybean cultivars specifically for African environments, with the intention of creating fast-maturing ...
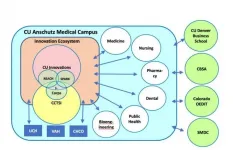
CU Anschutz called a 'case study' for commercializing medical breakthroughs
2021-06-29
A new study highlights the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus as an example of how an academic medical center can turn groundbreaking research into commercial products that improve patient care and public health.
The paper, published recently in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, focuses on the unique ecosystem at CU Anschutz responsible for these innovations. And it specifically details the campus's collaborative culture and how biomedical research is commercialized.
The campus has successfully turned academic research into a variety of products. CU Anschutz, for example, developed two vaccines for shingles, Zostavax and Shingrix, and ...
Turning plastic into foam to combat pollution
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Biodegradable plastics are supposed to be good for the environment. But because they are specifically made to degrade quickly, they cannot be recycled.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Canterbury in New Zealand have developed a method to turn biodegradable plastic knives, spoons, and forks into a foam that can be used as insulation in walls or in flotation devices.
The investigators placed the cutlery, which was previously thought to be "nonfoamable" plastic, into a chamber filled with carbon dioxide. ...
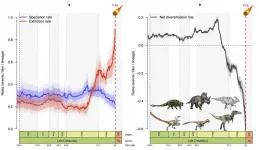
Dinosaurs were in decline before the end, according to new study
2021-06-29
The death of the dinosaurs 66 million years ago was caused by the impact of a huge asteroid on the Earth. However, palaeontologists have continued to debate whether they were already in decline or not before the impact.
In a new study, published today in the journal Nature Communications, an international team of scientists, which includes the University of Bristol, show that they were already in decline for as much as ten million years before the final death blow.
Lead author, Fabien Condamine, a CNRS researcher from the Institut des Sciences de l'Evolution de Montpellier (France), said: "We looked at the six most abundant dinosaur families through the whole of the Cretaceous, spanning from 150 to 66 million ...
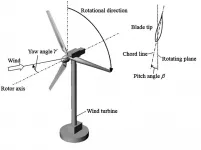
Steering wind turbines creates greater energy potential
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- As wind passes through a turbine, it creates a wake that decreases the downstream average wind velocity. The faster the spin of the turbine blades relative to the wind speed, the greater the impact on the downstream wake profile.
For wind farms, it is important to control upstream turbines in an efficient manner so downstream turbines are not adversely affected by upstream wake effects. In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign show by designing controllers based on viewing ...
Polymers in meteorites provide clues to early solar system
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Many meteorites, which are small pieces from asteroids, do not experience high temperatures at any point in their existence. Because of this, these meteorites provide a good record of complex chemistry present when or before our solar system was formed 4.57 billion years ago.
For this reason, researchers have examined individual amino acids in meteorites, which come in a rich variety and many of which are not in present-day organisms.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Harvard University show the existence of a systematic group of amino acid polymers across several members ...
This 5,000-year-old man had the earliest known strain of plague
2021-06-29
The oldest strain of Yersinia pestis--the bacteria behind the plague that caused the Black Death, which may have killed as much as half of Europe's population in the 1300s--has been found in the remains of a 5,000-year-old hunter-gatherer. A genetic analysis publishing June 29 in the journal Cell Reports reveals that this ancient strain was likely less contagious and not as deadly as its medieval version.
"What's most astonishing is that we can push back the appearance of Y. pestis 2,000 years farther than previously published studies suggested," says senior author Ben Krause-Kyora, head of the aDNA Laboratory at the University of Kiel in Germany. ...
Decline of dinosaurs underway long before asteroid fell
2021-06-29
Ten million years before the well-known asteroid impact that marked the end of the Mesozoic Era, dinosaurs were already in decline. That is the conclusion of the Franco-Anglo-Canadian team led by CNRS researcher Fabien Condamine from the Institute of Evolutionary Science of Montpellier (CNRS / IRD / University of Montpellier), which studied evolutionary trends during the Cretaceous for six major families of dinosaurs, including those of the tyrannosaurs, triceratops, and hadrosaurs. Using a novel statistical modelling method that limited bias associated with gaps in the fossil record, they demonstrated that, for dinosaurs 76 million years ...
Butterfly effect can double travel of virus-laden droplets
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Computer simulations have been used with great success in recent months to visualize the spread of the COVID-19 virus in a variety of situations. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers explain how turbulence in the air can create surprising and counterintuitive behavior of exhaled droplets, potentially laden with virus.
Investigators from the University of Florida and Lebanese American University carried out detailed computer simulations to test a mathematical theory they developed previously. They found nearly identical exhalations could spread in different ...