Steering wind turbines creates greater energy potential
Incorporating networked wind farms, time-dependent wind estimation models into a multiobjective solution for improving power extraction
2021-06-29
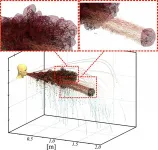
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- As wind passes through a turbine, it creates a wake that decreases the downstream average wind velocity. The faster the spin of the turbine blades relative to the wind speed, the greater the impact on the downstream wake profile.
For wind farms, it is important to control upstream turbines in an efficient manner so downstream turbines are not adversely affected by upstream wake effects. In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign show by designing controllers based on viewing the wind farm system as a coupled network, it is possible to extract power more efficiently.
"If you think of a wind farm as a group of turbines each vying for the incoming wind, if every turbine is greedy and tries to maximize its own power, the system as a whole is suboptimal," said author Lucas Buccafusca. "Our work seeks to design controls for turbines to work collectively, thereby improving performance."
The researchers apply a model predictive control (MPC) framework for varying wind velocities and incorporate wake steering techniques to demonstrate there can be a potential benefit to incorporating these methods into future wind turbine control algorithms. The researchers aim to mitigate the effects of turbulence and power spikes caused by wind passing through upstream turbines.
"When observing the power extractions, it is surprising just how much the gains can be for even small wind turbine arrays simply by implementing wake steering techniques," said Buccafusca.
The researchers found having control algorithms that consider downstream effects results in a noticeable increase in performance. The method for assigning turbine controls used axial induction factors and yaw misalignment controls that were shown via wake steering simulations to validate the results.
The researchers plan to explore applying similar methods to a distributed wind turbine energy problem, where each turbine has a local battery based on excess energy provided. The battery can return that energy when supply is low, such as when the wind velocity is too low to meet the grid operator's demand.
While the researchers focused primarily on the wind turbine power tracing problem, the same multiobjective MPC framework can be used in a variety of distributed optimization or consensus problems.
INFORMATION:
The article "Multiobjective model predictive control design for wind turbines and farms" is authored by Lucas Buccafusca and Carolyn Beck. The article will appear in Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy on June 29, 2021 (DOI: 10 1063/5.0039707). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0039707.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Many meteorites, which are small pieces from asteroids, do not experience high temperatures at any point in their existence. Because of this, these meteorites provide a good record of complex chemistry present when or before our solar system was formed 4.57 billion years ago.
For this reason, researchers have examined individual amino acids in meteorites, which come in a rich variety and many of which are not in present-day organisms.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Harvard University show the existence of a systematic group of amino acid polymers across several members ...
2021-06-29
The oldest strain of Yersinia pestis--the bacteria behind the plague that caused the Black Death, which may have killed as much as half of Europe's population in the 1300s--has been found in the remains of a 5,000-year-old hunter-gatherer. A genetic analysis publishing June 29 in the journal Cell Reports reveals that this ancient strain was likely less contagious and not as deadly as its medieval version.
"What's most astonishing is that we can push back the appearance of Y. pestis 2,000 years farther than previously published studies suggested," says senior author Ben Krause-Kyora, head of the aDNA Laboratory at the University of Kiel in Germany. ...
2021-06-29
Ten million years before the well-known asteroid impact that marked the end of the Mesozoic Era, dinosaurs were already in decline. That is the conclusion of the Franco-Anglo-Canadian team led by CNRS researcher Fabien Condamine from the Institute of Evolutionary Science of Montpellier (CNRS / IRD / University of Montpellier), which studied evolutionary trends during the Cretaceous for six major families of dinosaurs, including those of the tyrannosaurs, triceratops, and hadrosaurs. Using a novel statistical modelling method that limited bias associated with gaps in the fossil record, they demonstrated that, for dinosaurs 76 million years ...
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Computer simulations have been used with great success in recent months to visualize the spread of the COVID-19 virus in a variety of situations. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers explain how turbulence in the air can create surprising and counterintuitive behavior of exhaled droplets, potentially laden with virus.
Investigators from the University of Florida and Lebanese American University carried out detailed computer simulations to test a mathematical theory they developed previously. They found nearly identical exhalations could spread in different ...
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- As pervasive as they are in everyday uses, like encryption and security, randomly generated digital numbers are seldom truly random.
So far, only bulky, relatively slow quantum random number generators (QRNGs) can achieve levels of randomness on par with the basic laws of quantum physics, but researchers are looking to make these devices faster and more portable.
In Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, scientists from China present the fastest real-time QRNG to date to make the devices quicker and more portable. The ...
2021-06-29
What The Study Did: This study describes four patients who presented with acute myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination.
Authors: Raymond J. Kim, M.D., of the Duke Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Center in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2828)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
2021-06-29
What The Study Did: Researchers describe myocarditis presenting after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in 23 patients within the Military Health System.
Authors: Jay Montgomery, M.D., of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, and Margaret Ryan, M.D., M.P.H., of the Naval Medical Center San Diego, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
2021-06-29
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Ruth Howie presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2021: Cancer treatments can cause premature ovarian failure (POI) including in girls who want to become mothers eventually. Ovarian tissue cryopreservation (OTC) provides a future fertility option but is invasive, has risks and evidence indicates that most girls don't develop POI. So, doctors face the dilemma of how to offer OTC appropriately.
Now, an assessment tool has been found to help predict correctly which female cancer patients aged under 18 years will develop POI and should therefore be offered OTC. Results from a long-term follow-up study of 423 girls and young women show nearly a quarter (24%; n = 9) of the 37 assessed as high ...
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 - For more than 60 years, algae have been studied as a potential feedstock for biofuel production, but the cellulose in their cell wall makes it hard to access the critical molecules inside and convert them to biogas.
In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, an international research team reports their success in using urea and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, commonly known as lye or caustic soda) as a pretreatment of algae, which breaks down cellulose and more than doubles biogas production under their initial experimental conditions.
"We were ...
2021-06-29
With advances in medical science driving progress against childhood brain tumors, today three out of four young patients survive at least five years beyond diagnosis. However, the outcomes look grim when malignant cells spread, or metastasize.
Such is the case with medulloblastoma, a type of brain cancer that arises in the cerebellum, at the back of the head. Although rare in absolute terms -- about 350 cases emerge each year, 60 percent of them in children -- medulloblastoma is the most common and deadliest form of pediatric brain cancer. Metastasis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Steering wind turbines creates greater energy potential
Incorporating networked wind farms, time-dependent wind estimation models into a multiobjective solution for improving power extraction