(Press-News.org) Significantly higher rates of child intensive care admissions for unintentional cannabis poisonings have been seen following legalization of the drug in Canada.
Researchers from The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids), based in Toronto, found a four-fold increase in unintentional poisonings in children under the age of 12 and a three-fold increase in intensive care admissions for severe cannabis poisoning in the first two years following cannabis legalization.
However, the overall number of visits per month for cannabis intoxications to the SickKids Emergency Department (ED) remained consistent when comparing the pre- and post-legalization periods. The findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal END
Severe cannabis intoxication and rates of ingestion in children rise after legalization
2021-06-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIST laser 'comb' systems now measure all primary greenhouse gases in the air
2021-06-30
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have upgraded their laser frequency-comb instrument to simultaneously measure three airborne greenhouse gases -- nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide and water vapor -- plus the major air pollutants ozone and carbon monoxide.
Combined with an earlier version of the system that measures methane, NIST's dual comb technology can now sense all four primary greenhouse gases, which could help in understanding and monitoring emissions of these heat-trapping gases implicated in climate change. The newest comb system can also help assess urban air quality.
These NIST instruments identify gas signatures by precisely measuring the amounts of light ...
Fecal records show Maya population affected by climate change
2021-06-30
A McGill-led study has shown that the size of the Maya population in the lowland city of Itzan (in present-day Guatemala) varied over time in response to climate change. The findings, published recently in Quaternary Science Reviews, show that both droughts and very wet periods led to important population declines.
These results are based on using a relatively new technique involving looking at stanols (organic molecules found in human and animal faecal matter) taken from the bottom of a nearby lake. Measurements of stanols were used to estimate changes in population size and to examine how they align with information about climate variability and changes in vegetation drawn from other biological and archaeological sources.
By using the technique, the researchers were able ...
Buttoned up biomolecules
2021-06-30
Increasing our understanding of cellular processes requires information about the types of biomolecules involved, their locations, and their interactions. This requires the molecules to be labeled without affecting physiological processes (bioorthogonality). This works when the markers are very quickly and selectively coupled using small molecules and "click chemistry". In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team of researchers has now introduced a novel type of click reaction that is also suitable for living cells and organisms.
As an example, labeling biomolecules allows for the localization and characterization of tumors ...
COVID-19-mRNA vaccine induces good immune response against coronavirus variants
2021-06-30
A new Finnish study shows that 180 health care workers who had received two doses of the Pfizer and Biontech vaccine have very good antibody responses against the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The immune response was as strong against the alpha variant (formerly the UK variant) but was somewhat decreased against the beta variant (formerly the South Africa variant).
Finnish researchers from the University of Turku and University of Helsinki together with Turku University Hospital, Helsinki University Hospital, and the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare studied the immune response induced by the coronavirus vaccinations, which started in Finland in December. The researchers analysed vaccine responses ...
Eel products in the EU and the UK need better regulation
2021-06-30
Growing in popularity, unagi kabayaki - grilled freshwater eel in soy sauce - can be found on the menu of many Japanese restaurants, and is stocked by Asian shops and in specialist supermarkets. But new research tracing the DNA of eel fillets used for this dish has found that fraudulent food labelling is rife, with a third of the products violating EU regulations on the provision of food information. With certain species of eels now endangered, the researchers say that accurate labelling on these products is vital if the global eel trade is to be sustainable.
The European eel is a critically ...
Floods may be nearly as important as droughts for future carbon accounting
2021-06-30
Plants play an essential role in curbing climate change, absorbing about one-third of the carbon dioxide emitted from human activities and storing it in soil so it doesn't become a heat-trapping gas. Extreme weather affects this ecosystem service, but when it comes to understanding carbon uptake, floods are studied far less than droughts - and they may be just as important, according to new research.
In a global analysis of vegetation over more than three decades, Stanford University researchers found that photosynthesis - the process by which plants take up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere - was primarily influenced by floods and heavy rainfall nearly as often as droughts in many locations. The paper, published in Environmental Research Letters on June ...
Mixing it up: A low-cost way to make efficient, stable perovskite solar cells
2021-06-30
A key component of next-generation solar panels can be created without expensive, high-temperature fabrication methods, demonstrating a pathway to large scale, low-cost manufacturing for commercial applications.
Nickel oxide (NiO) is used as an inexpensive hole-transport layer in perovskite solar cells because of its favourable optical properties and long-term stability.
Making high-quality NiO films for solar cells usually requires an energy intensive and high-temperature treatment process called thermal annealing, which is not only costly, but also incompatible with plastic substrates, until now precluding the use of ...
Thinking in 3D improves mathematical skills
2021-06-30
Spatial reasoning ability in small children reflects how well they will perform in mathematics later. Researchers from the University of Basel recently came to this conclusion, making the case for better cultivation of spatial reasoning.
Good math skills open career doors in the natural sciences as well as technical and engineering fields. However, a nationwide study on basic skills conducted in Switzerland in 2019 found that schoolchildren achieved only modest results in mathematics. But it seems possible to begin promoting math skills from a young ...
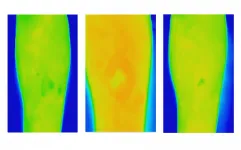
Thermal imaging offers early alert for chronic wound care
2021-06-30
New research shows thermal imaging techniques can predict whether a wound needs extra management, offering an early alert system to improve chronic wound care.
It is estimated that 1-2% of the population will experience a chronic wound during their lifetime in developed countries - in the US, chronic wounds affect about 6.5 million patients with more than US$25 billion each year spent by the healthcare system on treating related complications.*
The Australian study shows textural analysis of thermal images of venous leg ulcers (VLUs) can detect whether a wound needs extra management as early as week two for clients receiving treatment at home.
The clinical study by RMIT University and Bolton Clarke, published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports, is the first to investigate ...
Extreme events: Ecosystems offer cost effective protection
2021-06-30
Decision-makers around the world are increasingly interested in using ecosystem solutions such as mangroves, coral reefs, sand dunes and forests on steep slopes to help buffer the impacts from hazard events and protect populations. But what evidence exists to show the efficacy of nature-based solutions over man-made protective measures to reduce the impacts of the increasing numbers of hazard events humanity faces due to climate change?
An international, multi-disciplinary team of 28 researchers has examined nearly 20 years' worth of peer-reviewed studies on the impacts of ecosystem-based disaster ...