(Press-News.org) A new study disputes the prevailing hypothesis on why Mercury has a big core relative to its mantle (the layer between a planet's core and crust). For decades, scientists argued that hit-and-run collisions with other bodies during the formation of our solar system blew away much of Mercury's rocky mantle and left the big, dense, metal core inside. But new research reveals that collisions are not to blame--the sun's magnetism is.
William McDonough, a professor of geology at the University of Maryland, and Takashi Yoshizaki from Tohoku University developed a model showing that the density, mass and iron content of a rocky planet's core are influenced by its distance from the sun's magnetic field. The paper describing the model was published on July 2, 2021, in the journal Progress in Earth and Planetary Science.
"The four inner planets of our solar system--Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars--are made up of different proportions of metal and rock," McDonough said. "There is a gradient in which the metal content in the core drops off as the planets get farther from the sun. Our paper explains how this happened by showing that the distribution of raw materials in the early forming solar system was controlled by the sun's magnetic field."
McDonough previously developed a model for Earth's composition that is commonly used by planetary scientists to determine the composition of exoplanets. (His seminal paper on this work has been cited more than 8,000 times.)
McDonough's new model shows that during the early formation of our solar system, when the young sun was surrounded by a swirling cloud of dust and gas, grains of iron were drawn toward the center by the sun's magnetic field. When the planets began to form from clumps of that dust and gas, planets closer to the sun incorporated more iron into their cores than those farther away.
The researchers found that the density and proportion of iron in a rocky planet's core correlates with the strength of the magnetic field around the sun during planetary formation. Their new study suggests that magnetism should be factored into future attempts to describe the composition of rocky planets, including those outside our solar system.
The composition of a planet's core is important for its potential to support life. On Earth, for instance, a molten iron core creates a magnetosphere that protects the planet from cancer-causing cosmic rays. The core also contains the majority of the planet's phosphorus, which is an important nutrient for sustaining carbon-based life.
Using existing models of planetary formation, McDonough determined the speed at which gas and dust was pulled into the center of our solar system during its formation. He factored in the magnetic field that would have been generated by the sun as it burst into being and calculated how that magnetic field would draw iron through the dust and gas cloud.
As the early solar system began to cool, dust and gas that were not drawn into the sun began to clump together. The clumps closer to the sun would have been exposed to a stronger magnetic field and thus would contain more iron than those farther away from the sun. As the clumps coalesced and cooled into spinning planets, gravitational forces drew the iron into their core.
When McDonough incorporated this model into calculations of planetary formation, it revealed a gradient in metal content and density that corresponds perfectly with what scientists know about the planets in our solar system. Mercury has a metallic core that makes up about three-quarters of its mass. The cores of Earth and Venus are only about one-third of their mass, and Mars, the outermost of the rocky planets, has a small core that is only about one-quarter of its mass.
This new understanding of the role magnetism plays in planetary formation creates a kink in the study of exoplanets, because there is currently no method to determine the magnetic properties of a star from Earth-based observations. Scientists infer the composition of an exoplanet based on the spectrum of light radiated from its sun. Different elements in a star emit radiation in different wavelengths, so measuring those wavelengths reveals what the star, and presumably the planets around it, are made of.
"You can no longer just say, 'Oh, the composition of a star looks like this, so the planets around it must look like this,'" McDonough said. "Now you have to say, 'Each planet could have more or less iron based on the magnetic properties of the star in the early growth of the solar system.'"
The next steps in this work will be for scientists to find another planetary system like ours--one with rocky planets spread over wide distances from their central sun. If the density of the planets drops as they radiate out from the sun the way it does in our solar system, researchers could confirm this new theory and infer that a magnetic field influenced planetary formation.
INFORMATION:
The research paper, "Terrestrial planet compositions controlled by accretion disk magnetic field," McDonough, W. F. and Yoshizaki, T., was published on July 2, 2021, in the journal Progress in Earth and Planetary Science.
Media Relations Contact: Kimbra Cutlip, 301-405-9463, kcutlip@umd.edu
University of Maryland College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences
2300 Symons Hall
College Park, Md. 20742
http://www.cmns.umd.edu
@UMDscience
About the College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences
The College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences at the University of Maryland educates more than 9,000 future scientific leaders in its undergraduate and graduate programs each year. The college's 10 departments and more than a dozen interdisciplinary research centers foster scientific discovery with annual sponsored research funding exceeding $200 million.
Ibaraki, Japan - The flavor of a tomato is an interaction between its taste and aroma. Now, researchers from Japan and the United States have revealed that the pigments that determine the colors of tomatoes also affect their flavor.
In a study published this month, researchers from University of Tsukuba developed a new method to rapidly measure the pigment profiles of tomatoes and used the technique to explore how pigments affect the taste and aroma of different tomato varieties.
The color of tomatoes is produced by combinations of different types of pigments, including carotenoids and chlorophylls. These pigments can also affect the accumulation of flavor-related compounds such as sugars, which affect the taste of tomatoes, and volatile ...
A surprising study by UNSW on the behaviour of unrelated lizards in very different parts of the world has demonstrated how evolution can lead to different species learning the same skills.
The study in Ecology Letters documents how the Anolis lizard species in the Caribbean, and the Draco lizard species in Southeast Asia, have solved the challenge of communicating with one another to defend territories and attract mates.
It found males from both species perform elaborate head bob and push up displays, and rapidly extend and retract their often large and conspicuously coloured dewlap, or ...
The muskrat, a stocky brown rodent the size of a Chihuahua - with a tail like a mouse, teeth like a beaver and an exceptional ability to bounce back from rapid die-offs - has lived for thousands of years in one of Earth's largest freshwater deltas, in northeastern Alberta, Canada.
Today, this delta lies within one of the largest swaths of protected land in North America: a national park five times the size of Yellowstone that's home to the planet's biggest herd of free-roaming bison and the last natural nesting ground for the endangered whooping crane. It's also central to the culture ...
Guadalupe fur seals (Arctocephalus townsendi) have established a large resting colony in the Gulf of California--bringing the total number of sites where this endangered species now occurs to just four. This new haul-out was discovered on El Farallón de San Ignacio Island, along the mainland coast of Mexico, according to researchers from Mexico and the University of British Columbia.
Guadalupe fur seals were hunted for their furs and declared extinct in the late 1800's. However, 14 individuals were discovered on Guadalupe Island in 1950--and the population has grown since then. While still designated as vulnerable to extinction, according to IUCN, the population is believed to total 41,000 individuals and is growing ...
In an Australian world-first, researchers have successfully repurposed two existing medications to reduce the severity of sleep apnoea in people by at least 30 per cent.
Affecting millions around the world, sleep apnoea is a condition where the upper airway from the back of the nose to the throat closes repetitively during sleep, restricting oxygen intake and causing people to wake as often as 100 times or more per hour.
Those with untreated sleep apnoea are more likely to develop cardiovascular disease, dementia and depression, and are two to four times more likely to crash a car than the general population.
Despite almost thirty years of research, there are no approved drug therapies to treat the condition.
Professor Danny Eckert, Principal ...
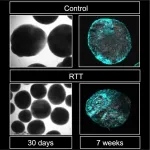
Fukuoka, Japan--Medical researchers led by Kyushu University have revealed a possible underlying genetic pathway behind the neurological dysfunction of Rett syndrome. The team found that deficiencies in key genes involved in the pathology triggers neural stem cells to generate less neurons by producing more astrocytes--the brain's maintenance cells.
The researchers hope that the molecular pathology they identified, as reported in the journal Cell Reports, can lead to potential therapeutic targets for Rett syndrome in the future.
Rett syndrome is a progressive neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impairments in cognition and coordination--with varying severity--and occurs in roughly one in every 10,000 to 15,000 female births. However, it ...
Japanese astronomers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) technique to remove noise in astronomical data due to random variations in galaxy shapes. After extensive training and testing on large mock data created by supercomputer simulations, they then applied this new tool to actual data from Japan's Subaru Telescope and found that the mass distribution derived from using this method is consistent with the currently accepted models of the Universe. This is a powerful new tool for analyzing big data from current and planned astronomy surveys.
Wide area survey data can be used to study the large-scale structure of the Universe through measurements of gravitational lensing patterns. In gravitational lensing, the ...
Microorganisms produce natural products, for example, as disease-causing virulence factors or as defense substances against predators and competitors. A team led by Dr. Robin Teufel and first author Ying Duan from the Institute of Biology II at the Faculty of Biology of the University of Freiburg, together with researchers from the University of Bonn, have now discovered a novel enzyme that is crucial for the production of so-called bacterial tropone natural products. The researchers presented their results in the current issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Previously unknown enzyme type
Bacteria found in terrestrial and marine environments produce tropone natural products, among other things, when they interact symbiotically with plants, algae or lower animals, for ...
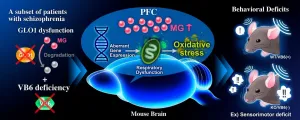
Methylglyoxal (MG) is a highly reactive α-ketoaldehyde formed endogenously as a byproduct of the glycolytic pathway. MG accumulates under conditions of hyperglycemia, impaired glucose metabolism, or oxidative stress. An excess of MG formation causes mitochondrial impairment and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production that further increases oxidative stress. It also leads to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) due to MG reacting with proteins, DNA, and other biomolecules, which can induce aberrant inflammation via binding to receptors for AGEs (RAGE). To remove the toxic MG, ...
This insight is the result of the close collaboration of several research groups at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology. A team around Cedric Hahn and Gunter Wegener recently discovered ethane-degrading microbes at hydrothermal vents of the Guaymas Basin at a water depth of 2,000 meters in the Gulf of California. They named it Ethanoperedens thermophilum, which means "heat-loving ethane-eater". Cedric Hahn a PhD student from the research group Molecular Ecology cultured the ethane-degrading microbes in the laboratory. Hahn, Wegener and colleagues of the research group Microbial Metabolism, Tristan Wagner and Olivier Lemaire took a closer look at these microorganisms. This collaborative work unraveled the secrets behind ...