Belowground microbial solutions to aboveground plant problems
2021-07-05
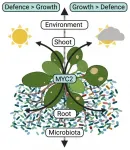
(Press-News.org) Land plants - plants that live primarily in terrestrial habitats and form vegetation on earth - are anchored to the ground through their roots, and their performance depends on both the belowground soil conditions and the aboveground climate. Plants utilize sunlight to grow through the process of photosynthesis where light energy is converted to chemical energy in chloroplasts, the powerhouses of plant cells. Therefore, the amount and quality of light perceived by chloroplasts through light absorbing pigments, such as chlorophyll, is a defining factor in plant growth and health. A substantial amount of the chemical compounds produced during the conversion of light energy to chemical energy, termed photoassimilates (mainly sugars), is translocated to the plant root compartment and invested in the surrounding soil to sustain microbial growth. Consequently, roots harbour complex microbial communities of bacteria and filamentous eukaryotes (i.e., fungi and oomycetes), and the composition of these communities profoundly influences plant performance. However, the extent to which plants can take advantage of belowground microbes to orchestrate aboveground stress responses remains largely unexplored. Now, in a new study published in Nature Plants, Stéphane Hacquard and his colleagues from the Department of Plant-Microbe Interactions at the MPIPZ in Cologne, Germany, shed light on these aboveground-belowground connections.
To tackle this question, the first author of the study Shiji Hou performed experiments where the aboveground light conditions and the belowground microbial conditions could be controlled. By comparing the growth of Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale Cress) grown in the absence of root microbes (i.e., germ-free) to those colonized by a complex community of 183 bacteria, 24 fungi and 7 oomycetes, the researchers observed that the presence of microbes rescued the plant growth-deficiency observed under low light conditions. Inoculation experiments with leaf pathogens further indicated that plants colonized by microbes were also more resistant to aboveground leaf pathogens than germ-free control plants, indicating that the presence of root microbes can promote both plant growth and defense under low light.
By comparing growth and defense responses of colonized plants between the two light conditions, the scientists observed that investment in growth under low light conditions came at the cost of defense, since microbiota-induced defense responses were reduced and plants were more susceptible to leaf pathogens under low light. Based on this observation, the authors of the study then hypothesized that when light conditions are suboptimal, plants favor microbe-induced growth over microbe-induced defense responses. To test this hypothesis, the researchers screened different A. thaliana mutants to identify those that failed to invest in growth under low light. Consistent with their hypothesis, the identified mutants were better at resisting leaf pathogens instead. Furthermore, the scientists found that the presence of the host transcription factor MYC2 was crucial to tip the balance in favor of microbiota-induced growth instead of microbiota-induced defense under low light conditions.
The researchers then went on to investigate whether the make-up of the microbial community belowground could explain aboveground investment in growth at the expense of defense under low light. To do this, they analyzed the composition of the root microbiota across the different A. thaliana mutants and observed that the bacterial community composition was markedly different depending on whether the different plants invested in growth under low light. This experiment led to the identification of 67 bacterial strains that were predicted to be associated with plant growth rescue under low light. To test a potential causal link, the researchers prepared three different bacterial communities composed of either: 1) all 183 strains, 2) the 183 strains lacking the 67 strains predicted to be important for growth rescue or 3) the 67 strains alone. Remarkably, A. thaliana wild-type plants colonized with the 67-member community invested in growth under low light, whereas those colonized by the community lacking these bacterial strains did not, instead favoring better resistance to leaf infection by pathogens.
In the words of study lead Stéphane Hacquard: "Our results suggest that plant growth and defense responses are engaged in different feedback loops with the root microbiota depending on aboveground light conditions. It is likely that light-induced change in root exudation profiles is an important mechanism that stimulates the growth of particular beneficial bacterial root commensals that boost plant growth, in the expense of defense responses under low light". The observation that microbiota-root-shoot-circuits exist in plants is reminiscent of recent results obtained in the context of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in animals, where a direct link between gut commensals and brain functions was uncovered. The results suggest that bacterial root and gut commensals have important functions in modulating stress responses not only locally, but also in distant host organs.
These findings have important applications for utilizing belowground microbes to promote aboveground stress responses in plants. By applying the knowledge gained in this study it would now be conceivable to design synthetic microbial communities with modular functions that could be used to promote plant resistance to particular biotic or abiotic stresses, and ultimately promote plant health in nature.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-05
MADISON, Wis. -- About 100 additional wolves died over the winter in Wisconsin as a result of the delisting of grey wolves under the Endangered Species Act, alongside the 218 wolves killed by licensed hunters during Wisconsin's first public wolf hunt, according to new research.
The combined loss of 313 to 323 wolves represents a decline in the state's wolf population of between 27% and 33% between April 2020 and April 2021. Researchers estimate that a majority of these additional, uncounted deaths are due to something called cryptic poaching, where poachers hide evidence of illegal killings.
The findings are the first estimate of Wisconsin's wolf population since the public hunt in February, which ended early after hunters ...
2021-07-05
The theory that modern society is too clean, leading to defective immune systems in children, should be swept under the carpet, according to a new study by researchers at UCL and the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
In medicine, the 'hygiene hypothesis' states that early childhood exposure to particular microorganisms protects against allergic diseases by contributing to the development of the immune system.
However, there is a pervading view (public narrative) that Western 21st century society is too hygienic, which means toddlers and children are likely to be less exposed to germs in early life and so become less resistant to allergies.
In this paper, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, researchers point to four significant reasons which, ...
2021-07-05
Research published today has demonstrated the viability of 3D-printed tissue scaffolds that harmlessly degrade while promoting tissue regeneration following implantation.
The scaffolds showed highly promising tissue-healing performance, including the ability to support cell migration, the 'ingrowth' of tissues, and revascularisation (blood vessel growth).
Professor Andrew Dove, from the University of Birmingham's School of Chemistry, led the research group and is the lead author on the paper published in Nature Communications, which characterises the physical properties of the scaffolds, and explains how their 'shape memory' is key to promoting tissue regeneration. ...
2021-07-05
Flies have discriminating taste. Like a gourmet perusing a menu, they spend much of their time seeking sweet nutritious calories and avoiding bitter, potentially toxic food. But what happens in their brains when they make these food choices?
Yale researchers discovered an interesting way to find out. They tricked them.
In a study that could also help illuminate how people make food choices, the researchers gave hungry fruit flies the choice between sweet, nutritious food laced with bitter quinine and a less sweet, but not bitter, food containing fewer calories. Then, using neuroimaging, they tracked neural activity in their brains as they made these tough choices.
So which won? Calories or better taste?
"It depends on how hungry they are," said Michael Nitabach, professor of ...
2021-07-05
Researchers at Uppsala University have discovered lymph node-like structures close to the tumour in brain cancer patients, where immune cells can be activated to attack the tumour. They also found that immunotherapy enhanced the formation of these structures in a mouse model. This discovery suggests new opportunities to regulate the anti-tumour response of the immune system.
Glioma is a deadly brain tumour with a dismal prognosis. One reason why brain tumours are very hard to treat is that our immune system, which is designed to detect and destroy foreign ...
2021-07-05
Although most Canadians die from predictable causes and have health needs that can be met at home, only 20% of people receive a physician home visit in their last year of life.
To help understand the changing care needs of older adults as they age and when they might be nearing the end of their lives, a team of researchers developed the Risk Evaluation for Support: Predictions for Elder-Life in the Community Tool (RESPECT).
The calculator, which predicts death within 6 months, is based on data from more than 491 000 community-dwelling older adults who used home care in the 6-year period between 2007 and 2013.
"The RESPECT calculator allows families and their loved ...
2021-07-05
Oncotarget published "Carcinoma cells that have undergone an epithelial-mesenchymal transition differentiate into endothelial cells and contribute to tumor growth" which reported that the authors investigated whether EMT can confer endothelial attributes upon carcinoma cells, augmenting tumor growth and vascularization.
Hypoxic regions, demarcated by HIF-1α staining, exhibited focal areas of E-cadherin loss and elevated levels of vimentin and the EMT-mediator FOXC2. Implantation of MCF-7 cells, co-mixed with human mammary epithelial cells overexpressing the EMT-inducer Snail, markedly ...
2021-07-05
Oncotarget published "Perioperative changes in the plasma metabolome of patients receiving general anesthesia for pancreatic cancer surgery" which reported that little is known about the impact of anesthesia on the plasma metabolome, although many metabolites have been shown to modulate the function of various immune cells, making it particularly interesting in the context of oncological surgery.
In this study longitudinal dynamics in the plasma metabolome during general anesthesia in patients undergoing pancreatic surgery were analyzed.
Prospective, observational study with 10 patients diagnosed with pancreatic malignancy and subjected to elective resection surgery under general anesthesia.
Plasma metabolites were quantified at ...
2021-07-05
Oncotarget published "Genome wide DNA methylation landscape reveals glioblastoma's influence on epigenetic changes in tumor infiltrating CD4+ T cells" which reported that whole-genome bisulfite sequencing of tumor infiltrating and blood CD4 T-cell from GBM patients showed 13571 differentially methylated regions and a distinct methylation pattern of methylation of tumor infiltrating CD4 T-cells with significant inter-patient variability.
The methylation changes also resulted in transcriptomic changes with 341 differentially expressed genes in CD4 tumor infiltrating T-cells compared to blood.
Analysis of specific genes involved in CD4 differentiation and function revealed differential methylation status of TBX21, GATA3, RORC, FOXP3, IL10 and ...
2021-07-05
Inadequate exposure to UVB light from the sun may be associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer, particularly in older age groups, according to a study using data on 186 countries, published in the open access journal BMC Public Health.
Researchers at the University of California San Diego, USA investigated possible associations between global levels of UVB light in 2017 and rates of colorectal cancer for different countries and age groups in 2018.
The authors found that lower UVB exposure was significantly correlated with higher rates of colorectal cancer across all ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Belowground microbial solutions to aboveground plant problems