(Press-News.org) Scientists at the University of Cambridge have identified rare genetic variants - carried by one in 3,000 people - that have a larger impact on the risk of developing type 2 diabetes than any previously identified genetic effect.
Type 2 diabetes is thought to be driven in part by inherited genetic factors, but many of these genes are yet unknown. Previous large-scale studies have depended on efficient 'array genotyping' methods to measure genetic variations across the whole genome. This approach typically does a good job at capturing the common genetic differences between people, though individually these each confer only small increases in diabetes risk.
Recent technical advances have allowed more comprehensive genetic measurement by reading the complete DNA sequences of over 20,000 genes that code for proteins in humans. Proteins are essential molecules that enable our bodies to function. In particular, this new approach has allowed for the first time a large-scale approach to study the impact of rare genetic variants on several diseases, including type 2 diabetes.
By looking at data from more than 200,000 adults in the UK Biobank study, researchers from the Medical Research Council (MRC) Epidemiology Unit at the University of Cambridge used this approach to identify genetic variants associated with the loss of the Y chromosome. This is a known biomarker of biological ageing that occurs in a small proportion of circulating white blood cells in men and indicates a weakening in the body's cellular repair systems. This biomarker has been previously linked to age-related diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cancer.
In results published today in Nature Communications, the researchers identified rare variants in the gene GIGYF1 that substantially increase susceptibility to loss of the Y chromosome, and also increase an individual's risk of developing type 2 diabetes six-fold. In contrast, common variants associated with type 2 diabetes confer much more modest increases in risk, typically much lower than two-fold.
Around 1 in 3,000 individuals carries such a GIGYF1 genetic variant. Their risk of developing type 2 diabetes is around 30%, compared to around 5% in the wider population. In addition, people who carried these variants had other signs of more widespread ageing, including weaker muscle strength and more body fat.
GIGYF1 is thought to control insulin and cell growth factor signalling. The researchers say their findings identify this as a potential target for future studies to understand the common links between metabolic and cellular ageing, and to inform future treatments.
Dr John Perry, from the MRC Epidemiology Unit and a senior author on the paper, said: "Reading an individual's DNA is a powerful way of identifying genetic variants that increase our risk of developing certain diseases. For complex diseases such as type 2 diabetes, many variants play a role, but often only increasing our risk by a tiny amount. This particular variant, while rare, has a big impact on an individual's risk."
Professor Nick Wareham, Director of the MRC Epidemiology Unit, added: "Our findings highlight the exciting scientific potential of sequencing the genomes of very large numbers of people. We are confident that this approach will bring a rich new era of informative genetic discoveries that will help us better understand common diseases such as type 2 diabetes. By doing this, we can potentially offer better ways to treat - or even to prevent - the condition."
Ongoing research will aim to understand how the loss of function variants in GIGYF1 lead to such a substantial increase in the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Their future research will also examine other links between biomarkers of biological ageing in adults and metabolic disorders.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the Medical Research Council. UK Biobank is supported Wellcome, the Medical Research Council, British Heart Foundation, Cancer Research UK, Department of Health, Northwest Regional Development Agency and the Scottish Government.
Reference
Zhao, Y. et al. GIGYF1 loss of function is associated with clonal mosaicism and adverse metabolic health. Nature Communications 2021; 07 Jul 2021; DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24504-y
DALLAS, July 7, 2021 -- Myocarditis in children is a rare yet challenging condition to treat. Diagnosis and treatment includes multiple options, and many cases of myocarditis resolve on their own, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association, "Diagnosis and Management of Myocarditis in Children," published today in Circulation, the Association's flagship journal. The scientific statement writing group reviewed the latest research to develop guidance in diagnosis and treatment for myocarditis in children.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the middle layer of the wall of the heart muscle, the myocardium, and it ...
The newly developed method lets researchers rapidly and accurately measure stress hormones in snow leopards without the need for bulky equipment or specialised knowledge. It uses widely available equipment that can be carried into the field, allowing hormone extraction from faecal samples and analysis to be done on site.
This differs from existing approaches to hormone monitoring in wild animals, where faecal samples must be taken to laboratories for hormone extraction and analysis. These approaches are particularly limiting in remote locations, such as the Himalayas.
"Because conventional hormone monitoring methods require frozen and refrigerated chemical reagents, and laboratory equipment, it is almost impossible to use them on-site." explained ...
CLEVELAND, Ohio (July 7, 2021)--Estrogen has been thought to play a role in a woman's risk of developing Alzheimer disease (AD). A new study has taken a different approach to identifying risk factors for AD by examining the association between a woman's reproductive life span as an indicator of endogenous estrogen exposure and levels of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Alzheimer disease represents 60% to 70% of all dementia diagnoses, making it the most common form of dementia. Approximately ...
A new study in the Journal of the European Economic Association, published by Oxford University Press, finds that electoral districts with a larger gender pay gaps show favoritism toward male political candidates in Parliamentary elections, with fewer female candidates on the ballot.
The researchers here gathered data for seven parliamentary elections in France between 1988 and 2017. Researchers studied candidates from the Left and Right political coalitions, which account for 80% of elected members of Parliament. The researchers consulted administrative and web data on candidates and electoral outcomes, survey data on ...
Oncotarget published "Association between miRNA signatures in serum samples from epidermal growth factor inhibitor treated patients and skin toxicity" which reported that on average 70% of patients treated with EGFRIs suffer from skin toxicity.
Studies showed a correlation between overall survival and the appearance of a skin rash, which is used as a biomarker for therapy efficacy.
In this study, the authors searched for associations of miRNA expression profiles in serum, with the severity of skin rash, in order to identify tentative therapy predictive biomarkers.
In this cohort of patients treated with EGFR inhibiting monoclonal antibodies, miR-21 and miR-520e serum concentrations were negatively correlated with severity of skin rash whereas for miR-31, a positive correlation was ...
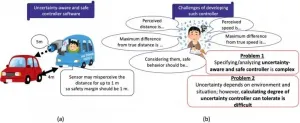
A research team consisting of Tsutomu Kobayashi, Ichiro Hasuo, Fuyuki Ishikawa, and Shinya Katsumata at the National Institute of Informatics (NII, Japan) and Rick Salay and Krzysztof Czarnecki at University of Waterloo (Canada) developed a method that automatically transforms models of controller software into models that satisfy safety requirements even when there is uncertainty in sensing the state of the environment. In addition to the transformation, the method generates formulas that represent the degree of uncertainty that the controller software can tolerate. The method can be applied to various controller systems that interact with the external environment, ...
In the line-up of wild African fruits, the marula is the best known. For thousands of years, people have depended on the trees for food, medicines, and more. It is also exported globally as the rockstar ingredient of a cream liqueur. The fruit is a success story far beyond the savannas and bushveld where the trees grow.
But there is a whole choir of other wild, indigenous fruits in Southern Africa. And some exceed daily nutritional values recommended by the WHO and others.
Research from the University of Johannesburg uncovers a variety of building blocks for protein in the fruit of 14 species. Several are analyzed for ...
Coastal communities across the world are increasingly facing up to the huge threats posed by a combination of extreme storms and predicted rises in sea levels as a result of global climate change.
However, scientists at the University of Plymouth have developed a simple algorithm-based model which accurately predicts how coastlines could be affected and - as a result - enables communities to identify the actions they might need to take in order to adapt.
The Forecasting Coastal Evolution (ForCE) model has the potential to be a game-changing advance in coastal evolution science, allowing adaptations in the shoreline to be predicted over timescales of anything from days to decades and beyond.
This broad range of timescales means that the model is capable of predicting ...
Philadelphia, July 7, 2021 - Tourette syndrome, a neurodevelopmental disorder, causes motor and phonic "tics" or uncontrollable repeated behaviors and vocalizations. People affected by Tourette syndrome can often suppress these tics for some time before the urges become overwhelming, and researchers have long wondered at the neural underpinnings of the suppression effort.
Now, in a new study using a non-invasive technique to measure brain activity called high-density electroencephalography (hdEEG), researchers at Yale School of Medicine have assessed the impact of tic suppression on functional ...
Frailty is a better predictor than factors such as age when determining how older adults fare one year after receiving critical care.
A team led by researchers from the University of Waterloo analyzed data from more than 24,000 community-dwelling older adults receiving home care in Ontario who were subsequently admitted into an intensive-care unit (ICU).
They applied three different measures for baseline frailty and found that an individual's level of frailty was linked to survival one year later. The most frail ICU survivors had only a one in five chance of living to one year after discharge.
Clinical frailty is age-related and characterized ...