(Press-News.org) The newly developed method lets researchers rapidly and accurately measure stress hormones in snow leopards without the need for bulky equipment or specialised knowledge. It uses widely available equipment that can be carried into the field, allowing hormone extraction from faecal samples and analysis to be done on site.
This differs from existing approaches to hormone monitoring in wild animals, where faecal samples must be taken to laboratories for hormone extraction and analysis. These approaches are particularly limiting in remote locations, such as the Himalayas.
"Because conventional hormone monitoring methods require frozen and refrigerated chemical reagents, and laboratory equipment, it is almost impossible to use them on-site." explained Dr Kodzue Kinoshita of Kyoto University and author of the study.
The new method developed by Dr Kinoshita extracts hormones from snow leopard faeces by shaking a container with the sample mixed with ethanol by hand. A process called immunochromatography, which is used in pregnancy tests, is used to detect hormone concentrations using test strips and a smartphone application then analyses them.
The accuracy of the new method was tested on faecal samples from captive snow leopards at Kohu Yuki Zoo, Asahikawa City Asahiyama Zoo, and Nagoya Higashiyama Zoo and Botanical Gardens in Japan. Comparisons to conventional methods found that similar hormone concentrations were extracted and changes in these concentrations were also accurately detected.
Stress in animals can be associated with reduced reproductive function, so finding out what in the environment stresses animals is important for conservation.
"Simple methods like this, will allow researchers, rangers, and zookeepers, to quickly and easily assess the stress status of snow leopards." said Dr Kinoshita. "Getting this insight will be useful for the management of animal welfare and conservation planning."
Dr Kinoshita added that the new technique could also be applied to captive snow leopards and other animals. "The hormone analysed in this method is generally not species-specific, so this method can be used to assess various species, including domestic, experimental, zoo, and wild animals."
Snow leopards are listed as 'vulnerable' on the IUCN red list and are threatened by poaching, retaliatory killings for livestock attacks and climate change. It's feared these continued pressures will increase stress in snow leopards, further contributing to population declines.
Snow leopards are also notoriously difficult to study, the mountainous regions in central Asia they inhabit make finding the big cats hard and limits researchers' access to laboratories.
The novel method Dr Kinoshita developed in this study involves adding ethanol to collected snow leopard faeces and then shaking the container with two zirconia beads by hand for two minutes to extract the hormones. The extract is then dropped onto the immunochromatography test strip which turns red as a result of an antigen-antibody reaction, indicating the presence of adrenocortical stress hormones. A smartphone app is used to measure the hormone concentration from the intensity of the colour.
Although this novel method could be applied to the other species, Dr Kinoshita warns that this will need to be tested for each species to ensure the stress hormones detected in the faeces accurately reflects the stress of the animal, as these levels will vary between species.
"As a next step, I would like to apply this method to various other animals and make it more reliable." said Dr Kinoshita. "I would also like to apply it to not only to wild animals, but also to zoo animals and pets to clarify the stress of these animals and improve their living environment."
INFORMATION:
CLEVELAND, Ohio (July 7, 2021)--Estrogen has been thought to play a role in a woman's risk of developing Alzheimer disease (AD). A new study has taken a different approach to identifying risk factors for AD by examining the association between a woman's reproductive life span as an indicator of endogenous estrogen exposure and levels of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Alzheimer disease represents 60% to 70% of all dementia diagnoses, making it the most common form of dementia. Approximately ...
A new study in the Journal of the European Economic Association, published by Oxford University Press, finds that electoral districts with a larger gender pay gaps show favoritism toward male political candidates in Parliamentary elections, with fewer female candidates on the ballot.
The researchers here gathered data for seven parliamentary elections in France between 1988 and 2017. Researchers studied candidates from the Left and Right political coalitions, which account for 80% of elected members of Parliament. The researchers consulted administrative and web data on candidates and electoral outcomes, survey data on ...
Oncotarget published "Association between miRNA signatures in serum samples from epidermal growth factor inhibitor treated patients and skin toxicity" which reported that on average 70% of patients treated with EGFRIs suffer from skin toxicity.
Studies showed a correlation between overall survival and the appearance of a skin rash, which is used as a biomarker for therapy efficacy.
In this study, the authors searched for associations of miRNA expression profiles in serum, with the severity of skin rash, in order to identify tentative therapy predictive biomarkers.
In this cohort of patients treated with EGFR inhibiting monoclonal antibodies, miR-21 and miR-520e serum concentrations were negatively correlated with severity of skin rash whereas for miR-31, a positive correlation was ...
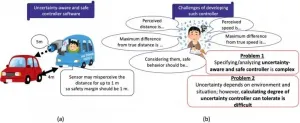
A research team consisting of Tsutomu Kobayashi, Ichiro Hasuo, Fuyuki Ishikawa, and Shinya Katsumata at the National Institute of Informatics (NII, Japan) and Rick Salay and Krzysztof Czarnecki at University of Waterloo (Canada) developed a method that automatically transforms models of controller software into models that satisfy safety requirements even when there is uncertainty in sensing the state of the environment. In addition to the transformation, the method generates formulas that represent the degree of uncertainty that the controller software can tolerate. The method can be applied to various controller systems that interact with the external environment, ...
In the line-up of wild African fruits, the marula is the best known. For thousands of years, people have depended on the trees for food, medicines, and more. It is also exported globally as the rockstar ingredient of a cream liqueur. The fruit is a success story far beyond the savannas and bushveld where the trees grow.
But there is a whole choir of other wild, indigenous fruits in Southern Africa. And some exceed daily nutritional values recommended by the WHO and others.
Research from the University of Johannesburg uncovers a variety of building blocks for protein in the fruit of 14 species. Several are analyzed for ...
Coastal communities across the world are increasingly facing up to the huge threats posed by a combination of extreme storms and predicted rises in sea levels as a result of global climate change.
However, scientists at the University of Plymouth have developed a simple algorithm-based model which accurately predicts how coastlines could be affected and - as a result - enables communities to identify the actions they might need to take in order to adapt.
The Forecasting Coastal Evolution (ForCE) model has the potential to be a game-changing advance in coastal evolution science, allowing adaptations in the shoreline to be predicted over timescales of anything from days to decades and beyond.
This broad range of timescales means that the model is capable of predicting ...
Philadelphia, July 7, 2021 - Tourette syndrome, a neurodevelopmental disorder, causes motor and phonic "tics" or uncontrollable repeated behaviors and vocalizations. People affected by Tourette syndrome can often suppress these tics for some time before the urges become overwhelming, and researchers have long wondered at the neural underpinnings of the suppression effort.
Now, in a new study using a non-invasive technique to measure brain activity called high-density electroencephalography (hdEEG), researchers at Yale School of Medicine have assessed the impact of tic suppression on functional ...
Frailty is a better predictor than factors such as age when determining how older adults fare one year after receiving critical care.
A team led by researchers from the University of Waterloo analyzed data from more than 24,000 community-dwelling older adults receiving home care in Ontario who were subsequently admitted into an intensive-care unit (ICU).
They applied three different measures for baseline frailty and found that an individual's level of frailty was linked to survival one year later. The most frail ICU survivors had only a one in five chance of living to one year after discharge.
Clinical frailty is age-related and characterized ...
The UK public is likely to take the COVID-19 pandemic less seriously once restrictions are lifted, according to new research led by Cardiff University.
Psychologists found lockdown in itself was a primary reason why so many people were willing to abide by the rules from the start - believing the threat must be severe if the government imposes such drastic measures.
The team from Cardiff and the universities of Bath and Essex examined the reasons behind headline polling support for COVID-19 measures. They carried out two UK surveys*, six months apart, during 2020. Their findings are published today in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
Lead author Dr Colin Foad said: "Surprisingly, we found that people judge the severity ...
An unknown methane-producing process is likely at work in the hidden ocean beneath the icy shell of Saturn's moon Enceladus, suggests a new study published in Nature Astronomy by scientists at the University of Arizona and Paris Sciences & Lettres University.
Giant water plumes erupting from Enceladus have long fascinated scientists and the public alike, inspiring research and speculation about the vast ocean that is believed to be sandwiched between the moon's rocky core and its icy shell. Flying through the plumes and sampling their chemical makeup, the Cassini spacecraft detected a relatively high concentration of certain molecules associated with hydrothermal vents on the bottom of Earth's oceans, specifically dihydrogen, ...