Aging-related conditions increase treatment burden in older cancer patients
Research finds multiple chronic conditions, rural residence main contributors to increased healthcare visits
2021-07-07
(Press-News.org) DANVILLE, Pa. - Having multiple chronic health conditions and living in a rural area were the top two factors affecting increased healthcare system contact among older patients with bladder cancer, a research team has found.
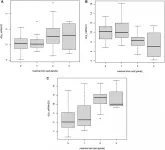
The Geisinger-led team evaluated 73,395 Medicare beneficiaries age 66 and older who had been diagnosed with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer to assess their treatment burden, defined as the number of days the patients had contact with a health system in the year following diagnosis.
Nearly two-thirds of the patients had multiple co-existing chronic conditions at the time of bladder cancer diagnosis, as well as other aging-related conditions, including a history of falls, cognitive impairment, depression, weight loss or urinary incontinence. The mean treatment burden for the group was 8.9 days.
The research team found that the presence of multiple co-existing conditions had the largest effect on treatment burden, with each additional condition increasing the average number of health system contact days by 13%. Regardless of the number of chronic conditions reported, rural patients consistently had higher treatment burden than their urban counterparts.
The results were published in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
"These findings highlight the need for interventions that reduce treatment burden among the growing population of older adults with cancer, particularly in rural areas," said Tullika Garg, M.D., M.P.H., a urologic oncologist at Geisinger and lead author of the study. "Cancer care, and care for other chronic conditions, goes beyond a single-disease approach and needs to account for the whole person."
Geisinger is making better health easier for patients age 65 and older and those with chronic conditions through innovative programs like 65 Forward Health Centers, offering personalized primary care and wellness services for Geisinger Gold members, and Geisinger at Home, bringing care into the home for Geisinger Gold members with certain chronic conditions.
INFORMATION:
About Geisinger
Geisinger is committed to making better health easier for the more than 1 million people it serves. Founded more than 100 years ago by Abigail Geisinger, the system now includes nine hospital campuses, a health plan with more than half a million members, a Research Institute, and the Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. With nearly 24,000 employees and more than 1,600 employed physicians, Geisinger boosts its hometown economies in Pennsylvania by billions of dollars annually. Learn more at geisinger.org or connect with us on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn and Twitter.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-07
Opioid prescribing preferences and practices among surgical residents and faculty differ, according to a new study published in the journal Surgery.
The study, titled "Evaluation of opioid prescribing preferences among surgical residents and faculty," was based on a survey of 56 residents and 57 faculty within the University of Colorado School of Medicine Department of Surgery. In the survey, participants were asked how many oxycodone tablets they would prescribe for 14 common surgical procedures.
Answers were compared between residents and faculty, as well as against the Opioid Prescribing Engagement Network (OPEN) guidelines and actual opioids ...
2021-07-07
A new screening method that can test the effectiveness of therapeutic molecules designed to 'glue' proteins together in the body has been developed by researchers at the University of Birmingham and the University of Leicester.
The research paves the way for drug developers to screen large numbers of potential new drug compounds to discover new treatments for diseases such as breast cancer and Parkinson's disease.
The ways in which proteins interact with each other are fundamental to all cell functions. These interactions underpin every function of a healthy body, with any slight change in these interactions resulting in disease.
A handful ...
2021-07-07
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have identified rare genetic variants - carried by one in 3,000 people - that have a larger impact on the risk of developing type 2 diabetes than any previously identified genetic effect.
Type 2 diabetes is thought to be driven in part by inherited genetic factors, but many of these genes are yet unknown. Previous large-scale studies have depended on efficient 'array genotyping' methods to measure genetic variations across the whole genome. This approach typically does a good job at capturing the common genetic differences between people, though individually these each confer only small increases in diabetes ...
2021-07-07
DALLAS, July 7, 2021 -- Myocarditis in children is a rare yet challenging condition to treat. Diagnosis and treatment includes multiple options, and many cases of myocarditis resolve on their own, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association, "Diagnosis and Management of Myocarditis in Children," published today in Circulation, the Association's flagship journal. The scientific statement writing group reviewed the latest research to develop guidance in diagnosis and treatment for myocarditis in children.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the middle layer of the wall of the heart muscle, the myocardium, and it ...
2021-07-07
The newly developed method lets researchers rapidly and accurately measure stress hormones in snow leopards without the need for bulky equipment or specialised knowledge. It uses widely available equipment that can be carried into the field, allowing hormone extraction from faecal samples and analysis to be done on site.
This differs from existing approaches to hormone monitoring in wild animals, where faecal samples must be taken to laboratories for hormone extraction and analysis. These approaches are particularly limiting in remote locations, such as the Himalayas.
"Because conventional hormone monitoring methods require frozen and refrigerated chemical reagents, and laboratory equipment, it is almost impossible to use them on-site." explained ...
2021-07-07
CLEVELAND, Ohio (July 7, 2021)--Estrogen has been thought to play a role in a woman's risk of developing Alzheimer disease (AD). A new study has taken a different approach to identifying risk factors for AD by examining the association between a woman's reproductive life span as an indicator of endogenous estrogen exposure and levels of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Alzheimer disease represents 60% to 70% of all dementia diagnoses, making it the most common form of dementia. Approximately ...
2021-07-07
A new study in the Journal of the European Economic Association, published by Oxford University Press, finds that electoral districts with a larger gender pay gaps show favoritism toward male political candidates in Parliamentary elections, with fewer female candidates on the ballot.
The researchers here gathered data for seven parliamentary elections in France between 1988 and 2017. Researchers studied candidates from the Left and Right political coalitions, which account for 80% of elected members of Parliament. The researchers consulted administrative and web data on candidates and electoral outcomes, survey data on ...
2021-07-07
Oncotarget published "Association between miRNA signatures in serum samples from epidermal growth factor inhibitor treated patients and skin toxicity" which reported that on average 70% of patients treated with EGFRIs suffer from skin toxicity.
Studies showed a correlation between overall survival and the appearance of a skin rash, which is used as a biomarker for therapy efficacy.
In this study, the authors searched for associations of miRNA expression profiles in serum, with the severity of skin rash, in order to identify tentative therapy predictive biomarkers.
In this cohort of patients treated with EGFR inhibiting monoclonal antibodies, miR-21 and miR-520e serum concentrations were negatively correlated with severity of skin rash whereas for miR-31, a positive correlation was ...
2021-07-07
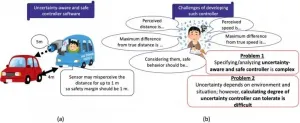
A research team consisting of Tsutomu Kobayashi, Ichiro Hasuo, Fuyuki Ishikawa, and Shinya Katsumata at the National Institute of Informatics (NII, Japan) and Rick Salay and Krzysztof Czarnecki at University of Waterloo (Canada) developed a method that automatically transforms models of controller software into models that satisfy safety requirements even when there is uncertainty in sensing the state of the environment. In addition to the transformation, the method generates formulas that represent the degree of uncertainty that the controller software can tolerate. The method can be applied to various controller systems that interact with the external environment, ...
2021-07-07
In the line-up of wild African fruits, the marula is the best known. For thousands of years, people have depended on the trees for food, medicines, and more. It is also exported globally as the rockstar ingredient of a cream liqueur. The fruit is a success story far beyond the savannas and bushveld where the trees grow.
But there is a whole choir of other wild, indigenous fruits in Southern Africa. And some exceed daily nutritional values recommended by the WHO and others.
Research from the University of Johannesburg uncovers a variety of building blocks for protein in the fruit of 14 species. Several are analyzed for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Aging-related conditions increase treatment burden in older cancer patients
Research finds multiple chronic conditions, rural residence main contributors to increased healthcare visits