Engineered protein inspired by nature may help plastic plague
2021-07-07
(Press-News.org) Cheap to produce and long to degrade, plastic was once a manufacturing miracle. Now, plastic is an environmental plague, clogging landfills and choking waterways. A Japan-based research team has turned back to nature to develop an approach to degrading the stubborn substance. Similar to how a protein binds to cellulose in plants or to chitin in crustaceans to initiate decomposition, an engineered protein is on its way to binding to plastic particles in an effort to more efficiently break them down.
They published their results on June 29 in ACS Catalysis, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
"Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is produced and used in large quantities in modern society due to its low cost and ease of processing," said paper author Ryota Iino, professor of the Institute for Molecular Science (IMS) in the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS). "However, in recent years, from the perspective of realizing a sustainable society, the complete recycling of PET in industry and the removal of PET from the natural environment have become global issues. To resolve these issues, it is very important to understand how to degrade PET efficiently."
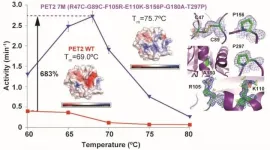
The researchers investigated and engineered an enzyme cloned from a library of genetic materials collected from nature. This enzyme -- called PET2 -- was found to facilitate the degradation of PET by accelerating the reaction between PET's chemical components and water.
Using single-molecule imaging analysis, the team found that the way the enzyme binds to the surface of PET actually limited the rate of degradation.
"We also revealed that by introducing positive charges on the surface of PET-degrading enzyme, the binding rate to the PET surface can be increased," Iino said.
The positive charges react favorably to the PET surface, so more of the enzyme can bind and more effectively degrade the PET. The researchers also found that while engineered PET2 showed high thermal stability and highest activity at 68 degrees Celsius -- slightly lower than most residential kitchen ovens can go -- it may be more effective at higher temperatures where PET's molecular bonds become more flexible and breakable.
"Our ultimate goal is to create a bacterium that can sense PET in the environment, move toward it, and degrade it," Iino said. Such a bacterium would then be able to turn the degraded PET into energy useful for other organisms, effectively acting as an automated recycling center for plastic. "In nature, chitin and cellulose are recycled in this way."
Iino is also affiliated with the School of Physical Sciences at The Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI). Other contributors include Akihiko Nakamura, Department of Applied Life Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, Shizuoka University, and the Shizuoka Institute for the Study of Marine Biology and Chemistry; and Naoya Kobayashi and Nobuyasu Koga, Exploratory Research Center on Life and Living Systems (ExCELLS), NINS. Koga is also affiliated with IMS, NINS, and SOKENDAI.
The Leading Initiative for Excellent Young Researchers, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan, the Sumitomo Foundation, and the ExCELLS Special Collaboration Program supported this research.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-07
In two recent articles published in Schizophrenia Bulletin, Sharon Hunter, PhD, an associate professor in the University of Colorado School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry, and M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, an associate professor in the University of Colorado School of Medicine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, along with their research group, have uncovered a potential link between choline deficiency in Black pregnant women in the United States and increased risk of developmental and behavioral issues that can evolve into mental illness later in their children's lives.
The first article, published in November 2020, is a study, titled, "Black American Maternal Prenatal Choline, Offspring Gestational Age at Birth, and Developmental Predisposition to Mental Illness." The ...
2021-07-07
Scientists at KAIST have fabricated a laser system that generates highly interactive quantum particles at room temperature. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics, could lead to a single microcavity laser system that requires lower threshold energy as its energy loss increases.
The system, developed by KAIST physicist Yong-Hoon Cho and colleagues, involves shining light through a single hexagonal-shaped microcavity treated with a loss-modulated silicon nitride substrate. The system design leads to the generation of a polariton laser at room temperature, which is exciting because this usually requires cryogenic temperatures.
The researchers found another unique and counter-intuitive feature of this design. Normally, energy is lost during laser operation. ...
2021-07-07
Australian scientists researching how our immune system responds to COVID-19 have revealed that those infected by early variants in 2020 produced sustained antibodies, however, these antibodies are not as effective against contemporary variants of the virus.
The research is one of the world's most comprehensive studies of the immune response against COVID-19 infection. It suggests vaccination is more effective than the body's natural immune response following infection and shows the need to invest in new vaccine designs to keep pace with emerging COVID variants.
Published today in PLOS ...
2021-07-07
Polymer composite materials that combine magnetic and electrical properties are the subjects of particular attention for modern-day researchers. Their basic property is the ability to convert electric polarization into a magnetic field and vice versa. Although some materials exhibit a much better magnetoelectric effect, polymer-based composites are easier not only to produce but also to modify.
Such composites have great potential in a variety of different fields. For example, using them as a basis, scientists can develop surfaces that help cultivate various cells. In this case, polymer composites serve as a substrate through which it is possible to affect the culture using a non-contact and controlled electric charge and morphological properties ...
2021-07-07
DANVILLE, Pa. - Having multiple chronic health conditions and living in a rural area were the top two factors affecting increased healthcare system contact among older patients with bladder cancer, a research team has found.
The Geisinger-led team evaluated 73,395 Medicare beneficiaries age 66 and older who had been diagnosed with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer to assess their treatment burden, defined as the number of days the patients had contact with a health system in the year following diagnosis.
Nearly two-thirds of the patients had multiple co-existing chronic conditions at the time of bladder cancer diagnosis, as well as other aging-related conditions, including a history of falls, ...
2021-07-07
Opioid prescribing preferences and practices among surgical residents and faculty differ, according to a new study published in the journal Surgery.
The study, titled "Evaluation of opioid prescribing preferences among surgical residents and faculty," was based on a survey of 56 residents and 57 faculty within the University of Colorado School of Medicine Department of Surgery. In the survey, participants were asked how many oxycodone tablets they would prescribe for 14 common surgical procedures.
Answers were compared between residents and faculty, as well as against the Opioid Prescribing Engagement Network (OPEN) guidelines and actual opioids ...
2021-07-07
A new screening method that can test the effectiveness of therapeutic molecules designed to 'glue' proteins together in the body has been developed by researchers at the University of Birmingham and the University of Leicester.
The research paves the way for drug developers to screen large numbers of potential new drug compounds to discover new treatments for diseases such as breast cancer and Parkinson's disease.
The ways in which proteins interact with each other are fundamental to all cell functions. These interactions underpin every function of a healthy body, with any slight change in these interactions resulting in disease.
A handful ...
2021-07-07
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have identified rare genetic variants - carried by one in 3,000 people - that have a larger impact on the risk of developing type 2 diabetes than any previously identified genetic effect.
Type 2 diabetes is thought to be driven in part by inherited genetic factors, but many of these genes are yet unknown. Previous large-scale studies have depended on efficient 'array genotyping' methods to measure genetic variations across the whole genome. This approach typically does a good job at capturing the common genetic differences between people, though individually these each confer only small increases in diabetes ...
2021-07-07
DALLAS, July 7, 2021 -- Myocarditis in children is a rare yet challenging condition to treat. Diagnosis and treatment includes multiple options, and many cases of myocarditis resolve on their own, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association, "Diagnosis and Management of Myocarditis in Children," published today in Circulation, the Association's flagship journal. The scientific statement writing group reviewed the latest research to develop guidance in diagnosis and treatment for myocarditis in children.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the middle layer of the wall of the heart muscle, the myocardium, and it ...
2021-07-07
The newly developed method lets researchers rapidly and accurately measure stress hormones in snow leopards without the need for bulky equipment or specialised knowledge. It uses widely available equipment that can be carried into the field, allowing hormone extraction from faecal samples and analysis to be done on site.
This differs from existing approaches to hormone monitoring in wild animals, where faecal samples must be taken to laboratories for hormone extraction and analysis. These approaches are particularly limiting in remote locations, such as the Himalayas.
"Because conventional hormone monitoring methods require frozen and refrigerated chemical reagents, and laboratory equipment, it is almost impossible to use them on-site." explained ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Engineered protein inspired by nature may help plastic plague


