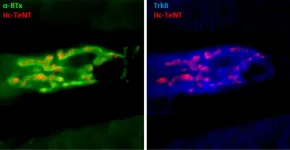
Discovery of a mechanism for efficient autophagosome formation
Revealing the molecular role of the most famous autophagy factor
2021-07-09
(Press-News.org) Drs. Nobuo Noda (Director) and Tatsuro Maruyama (Researcher) et al. at the Institute of Microbial Chemistry (BIKAKEN, Tokyo, Japan) discovered that lipidated Atg8(1), the most famous factor that mediates autophagy, has membrane perturbation activity and elucidated that this activity is responsible for efficient autophagosome formation.
Autophagosome formation is an essential step in determining the target of degradation in autophagy, which is one of the mechanisms of intracellular protein degradation. It is known that lipidated Atg8 plays a primary role in autophagy processes; however, the molecular function of lipidated Atg8 on the autophagy-related membranes remains unknown.
The research group demonstrated through in vitro experiments that yeast Atg8 exhibits membrane transforming activity. Moreover, on examining the three-dimensional structure of lipidated Atg8 by solution NMR spectroscopy(2), they found that lipidated Atg8 interacts with the membrane via two aromatic amino acids(3). In addition, they found that mutant aromatic amino acids resulted in the loss of the membrane transforming activity of lipidated Atg8 in vitro, inhibited the autophagosome formation in yeast, and attenuated autophagy in mammalian cells. Consequently, they revealed a novel mechanism wherein lipidated Atg8 perturbs and transforms membranes through direct interaction, thereby promoting autophagosome formation.
The elucidation of the molecular role of the main autophagy factor, Atg8, which has been a long-standing issue in the field of autophagy, holds promise in accelerating research that will contribute to a complete understanding of the molecular mechanisms of autophagosome formation. Furthermore, it is expected to promote research and development for treating and preventing various diseases through the artificial control of autophagy by deepening our understanding of autophagosome formation mechanisms.
The present research was conducted in collaboration with the group of Drs. Hitoshi Nakatogawa (Associate Professor, Tokyo Institute of Technology), Yoshinori Ohsumi (Honorary Professor), Tomotake Kanki (Professor, Niigata University), Masaaki Komatsu (Professor, Juntendo University), and Ichio Shimada (Team Leader, RIKEN) in JST Strategic Basic Research Programs (CREST).
(1) Lipidated Atg8
The functional state of Atg8 involves its covalent conjugation with a phospholipid via enzymatic reactions. Since lipidated Atg8 is abundant in the membranes of autophagosomes and their precursors, it is widely utilized as the main autophagy marker protein in autophagy research.
(2) NMR spectroscopy
Atomic nuclei in a strong magnetic field interact with electromagnetic waves having a specific frequency (named resonance frequency), which reflects the nuclear property and chemical environment. NMR spectroscopy is a technique used for obtaining information regarding the structure and property of compounds by detecting the electromagnetic waves as NMR signals. NMR is an abbreviation for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance.
(3) Aromatic amino acids
Aromatic amino acids, such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine, have an aromatic side chain. It is known that buried aromatic amino acids contribute to the stabilization of protein folding, whereas exposed aromatic amino acids mediate interactions with other proteins and membranes.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-09
A new study from Queen Mary University of London has demonstrated that immune cells can be stimulated to assemble into special structures within pancreatic cancer such that, at least in a pre-clinical model, researchers can demonstrate an improvement in the efficacy of chemotherapy.
The body's immune system is a critical defence against illness such as infections, as has been highlighted by the recent COVID-19 pandemic. The same immune system can also help us fight cancer. However, pancreatic cancer is different; a key feature of this cancer type is that the pancreatic cancer cells are surrounded by a dense, impenetrable barrier known as the stroma, which often blocks the access of immune cells to ...
2021-07-09
Coral reefs are a favorite spot for scuba divers and are among the world's most diverse ecosystems. For example, the Hawaiian coral reefs, known as the "rainforests of the sea," host over 7,000 species of marine animals, fishes, birds and plants. But coral reefs are facing serious threats, including a number of diseases that have been linked to human activity.
To understand the connection between human activity and a type of tumorlike disease called growth anomalies (GAs), researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have collaborated with the U.S Geological Survey (USGS) and the National ...
2021-07-09
ATLANTA--The American College of Rheumatology (ACR), in partnership with the Vasculitis Foundation (VF), released three new guidelines for the treatment and management of systemic vasculitis. Vasculitis is a group of about 20 rare diseases that have inflammation of blood vessels in common, which can restrict blood flow and damage vital organs. The three guidelines cover six forms of vasculitis, and a fourth guideline on Kawasaki disease will be released in the coming weeks.
"Many rheumatologists may have limited experience caring for patients with these diseases," ...
2021-07-09
Strokes, which occur when the blood supply to part of our brain is interrupted or reduced, are the leading cause of death and disability in the adult population. Among the patients who survive, 75% will experience difficulties carrying out daily activities independently and need long-term functional exercises and rehabilitation. But the outcomes using traditional rehabilitation equipment are poor. In addition, the motivation of patients to train is often low.
The Department of Neurology in Tongji Hospital, which is affiliated to Tongji Medical College at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, is recognised in China for the quality of its scientific research and clinical strength. Similarly, Zhejiang BrainCo, Ltd., incubated by the Harvard Innovation Lab, is a market ...
2021-07-09
Contrary to conventional thought, songbirds can taste sugar--even though songbirds are the descendants of meat-eating dinosaurs and are missing a key protein that allows humans and many other animals to taste sweetness. An international team investigated how many bird species can taste sweet and how far back that ability evolved. Their work was published today in the journal Science.
The researchers offered two species of songbirds a choice between sugar water and plain water--nectar-taking honeyeaters, as well as canaries, a grain-eating bird not known for consuming sweet foods. They also examined taste receptor responses sampled from a variety of other species. Regardless of whether their main ...
2021-07-09
A team of physicists from the Harvard-MIT Center for Ultracold Atoms and other universities has developed a special type of quantum computer known as a programmable quantum simulator capable of operating with 256 quantum bits, or "qubits."
The system marks a major step toward building large-scale quantum machines that could be used to shed light on a host of complex quantum processes and eventually help bring about real-world breakthroughs in material science, communication technologies, finance, and many other fields, overcoming research hurdles that are beyond the capabilities of even the fastest supercomputers today. Qubits are the fundamental building blocks on which quantum computers ...
2021-07-09
How does unicellular life transition to multicellular life? The research team of Professor Lutz Becks at the Limnological Institute of the University of Konstanz has taken a major step forward in explaining this very complex process. They were able to demonstrate - in collaboration with a colleague from the Alfred Wegner Institute (AWI) - that the unicellular green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, over only 500 generations, develops mutations that provide the first step towards multicellular life. This experimentally confirmed a theory on the origin of multicellular life, which says that the evolution of cell groups and the subsequent steps towards multicellularity can only take place when cell groups are both better at reproduction and more likely to survive than single cells. ...
2021-07-09
Although the giant panda is in practice a herbivore, its masticatory system functions differently from the other herbivores. Through the processes of natural selection, the giant panda's dietary preference has strongly impacted the evolution of its teeth and jaws. Researchers from the Institute of Dentistry at the University of Turku and the Biodiversity unit of the University of Turku together with researchers from the China Conservation and Research Center for Giant Panda (CCRCGP) have been the first in the world to solve the mystery of how the giant panda's special stomatognathic system functions.
The bamboo diet of the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) has long been a ...
2021-07-09
Pichia pastoris (syn. Komagataella phaffii), a model methylotrophic yeast, can easily achieve high density fermentation, and thus is considered as a promising chassis cell for efficient methanol biotransformation. However, inefficient gene editing and lack of synthetic biology tools hinder its metabolic engineering toward industrial application.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. ZHOU Yongjin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences established an efficient genetic engineering platform in Pichia pastoris.
The study was published in Nucleic Acids Research on July 1.
The researchers developed ...
2021-07-09
Depression has been treated traditionally with inhibitors of serotonin reuptake in the central nervous system. These drugs do not come without side effects, such as lack of immediate therapeutic action, the need for daily doses and the danger of becoming addicted to some of these drugs. That is why scientists continue to work on new therapies to treat depression.
In 2019, an international group of researchers co-led by Dr Yousef Tizabe from the Howard University College of Medicine in Washington, D.C., and Professor José Aguilera from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and the Institut de Neurociències ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Discovery of a mechanism for efficient autophagosome formation
Revealing the molecular role of the most famous autophagy factor