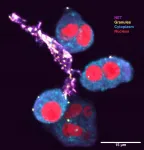
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the Buck Institute and Stanford University have created an inflammatory clock of aging (iAge) which measures inflammatory load and predicts multi-morbidity, frailty, immune health, cardiovascular aging and is also associated with exceptional longevity in centenarians. Utilizing deep learning, a form of AI, in studies of the blood immunome of 1001 people, researchers also identified a modifiable chemokine associated with cardiac aging which can be used for early detection of age-related pathology and provides a target for interventions. Results are published in Nature Aging.
"Standard immune metrics which can be used to identify individuals most at risk for developing single or even multiple chronic diseases of aging have been sorely lacking," said END
First actionable clock that predicts immunological health and chronic diseases of aging
Research highlights the critical role of the immune system in the aging process
2021-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Coastal ecosystems worldwide: Billion-dollar carbon reservoirs
2021-07-12
According to the study, Australia, Indonesia and the USA provide the largest carbon storage potential with their coastal ecosystems. The team also calculated which countries benefit most from the coastal CO2 uptake worldwide. The different ways in which countries are affected by climate change are quantified by using the so-called social costs of carbon.
"If we take into account the differences in marginal climate damages that occur in each country, we find that Australia and Indonesia are clearly the largest donors in terms of globally avoided climate damages originating from coastal CO2 uptake, as they themselves derive comparatively little benefit ...
Haziness of exoplanet atmospheres depends on properties of aerosol particles
2021-07-12
Many exoplanets have opaque atmospheres, obscured by clouds or hazes that make it hard for astronomers to characterize their chemical compositions. A new study shows that haze particles produced under different conditions have a wide range of properties that can determine how clear or hazy a planet's atmosphere is likely to be.
Photochemical reactions in the atmospheres of temperate exoplanets lead to the formation of small organic haze particles. Large amounts of these photochemical hazes form in Earth's atmosphere every day, yet our planet has relatively clear skies. The reason has to do with how ...
A fermented-food diet increases microbiome diversity and lowers inflammation, study finds
2021-07-12
A diet rich in fermented foods enhances the diversity of gut microbes and decreases molecular signs of inflammation, according to researchers at the Stanford School of Medicine.
In a clinical trial, 36 healthy adults were randomly assigned to a 10-week diet that included either fermented or high-fiber foods. The two diets resulted in different effects on the gut microbiome and the immune system.
Eating foods such as yogurt, kefir, fermented cottage cheese, kimchi and other fermented vegetables, vegetable brine drinks, and kombucha tea led to an increase in overall microbial diversity, with stronger effects from larger servings. ...
Immune system 'clock' predicts illness and mortality
2021-07-12
You're as old as your immune system.
Investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine and the Buck Institute for Research on Aging have built an inflammatory-aging clock that's more accurate than the number of candles on your birthday cake in predicting how strong your immune system is, how soon you'll become frail or whether you have unseen cardiovascular problems that could become clinical headaches a few years down the road.
In the process, the scientists fingered a bloodborne substance whose abundance may accelerate cardiovascular aging.
The story of the clock's creation will be published July 12 in Nature Aging.
"Every year, the calendar tells us we're a year older," said David ...
Human environmental genome recovered in the absence of skeletal remains
2021-07-12
The cave of Satsurblia was inhabited by humans in different periods of the Paleolithic: Up to date a single human individual dated from 15,000 years ago has been sequenced from that site. No other human remains have been discovered in the older layers of the cave.
The innovative approach used by the international team led by Prof. Ron Pinhasi and Pere Gelabert with Susanna Sawyer of the University of Vienna in collaboration with Pontus Skoglund and Anders Bergström of the Francis Crick Institute in London permits the identification of DNA in samples of environmental ...
Progress towards new treatments for tuberculosis
2021-07-12
Boosting the body's own disease-fighting immune pathway could provide answers in the desperate search for new treatments for tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis still represents an enormous global disease burden and is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide.
Led by WEHI's Dr Michael Stutz and Professor Marc Pellegrini and published in Immunity, the study uncovered how cells infected with tuberculosis bacteria can die, and that using new medicines to enhance particular forms of cell death decreased the severity of the disease in a preclinical model.
At a glance
Researchers were able to demonstrate that cells infected with tuberculosis bacteria have functional ...
Naturally abundant venom peptide from ants can activate a pseudo allergic pathway unravelling a novel immunomodulatory pathway of MRGPRX2
2021-07-12
Ants are omnipresent, and we often get blisters after an ant bite. But do you know the molecular mechanism behind it? A research team led by Professor Billy K C CHOW from the Research Division for Molecular and Cell Biology, Faculty of Science, the University of Hong Kong (HKU), in collaboration with Dr Jerome LEPRINCE from The Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale (INSERM) and Professor Michel TREILHOU from the Institut National Universitaire Champollion in France, have identified and demonstrated a novel small peptide isolated from the ant venom can initiate an immune pathway via a pseudo-allergic receptor MRGPRX2. The study ...
Sea-level rise may worsen existing Bay Area inequities
2021-07-12
Rather than waiting for certainty in sea-level rise projections, policymakers can plan now for future coastal flooding by addressing existing inequities among the most vulnerable communities in flood zones, according to Stanford research.
Using a methodology that incorporates socioeconomic data on neighborhood groups of about 1,500 people, scientists found that several coastal communities in San Mateo County, California - including half the households in East Palo Alto - are at risk of financial instability from existing social factors or anticipated flooding through 2060. Even with coverage from flood insurance, these residents would not be able to pay for damages from flooding, which could lead to homelessness or bankruptcy ...
People given 'friendly' bacteria in nose drops protected against meningitis
2021-07-12
Led by Professor Robert Read and Dr Jay Laver from the NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre and the University of Southampton, the work is the first of its kind.
Together they inserted a gene into a harmless type of a bacteria, that allows it to remain in the nose and trigger an immune response. They then introduced these bacteria into the noses of healthy volunteers via nose drops.
The results, published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, showed a strong immune response against bacteria that cause meningitis. Published in ...
Hijacked immune activator promotes growth and spread of colorectal cancer
2021-07-12
Through a complex, self-reinforcing feedback mechanism, colorectal cancer cells make room for their own expansion by driving surrounding healthy intestinal cells to death - while simultaneously fueling their own growth. This feedback loop is driven by an activator of the innate immune system. Researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the University of Heidelberg discovered this mechanism in the intestinal tissue of fruit flies.
Maintaining the well-functioning state of an organ or tissue requires a balance of cell growth and differentiation on the one hand, and the elimination of defective cells on the other. The intestinal epithelium is a well-studied example of this balance, termed "tissue homeostasis": Stem cells ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] First actionable clock that predicts immunological health and chronic diseases of agingResearch highlights the critical role of the immune system in the aging process