Direct flights save lives! New airline routes can increase kidney sharing by more than 7%
2021-07-12
(Press-News.org) INFORMS Journal Management Science Study Key Takeaways:
Lack of direct airline routes limit the flexibility of organ transplantation policies.
A new airline route can increase the number of kidneys shared between different regions by more than 7% while also decreasing the organ discard rate.
An increase in the quantity of kidneys does not come with a decrease in kidney quality.
CATONSVILLE, MD, July 12, 2021 - It's a supply and demand problem, it's a transportation problem, it's a donor problem - and that just scratches the surface. According to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, every 9 minutes a new patient is added to the organ waiting list. Every day 17 people die waiting for a kidney transplant. New research in the INFORMS journal Management Science tackles the transportation part of this problem.
"Airline transportation limits the flexibility of organ transplantation, but new, more direct airline routes can increase the number of kidneys shared between regions connected by these routes by more than 7%," said Tinglong Dai of Johns Hopkins University. "Operations research and analytics is trying to save lives and allow kidneys to be more readily available to those who need them when they need them. Too often, viable kidneys are wasted because they can't reach a patient in time."
The study, "Does Transportation Mean Transplantation? Impact of New Airline Routes on Sharing of Cadaveric Kidneys," was conducted by Dai alongside Guihua Wang of the University of Texas at Dallas and Ronghuo Zheng of the University of Texas at Austin.
The research identifies how new airline routes can provide the necessary efficient airline transportation needed for the time-sensitive nature of kidney transplantation and reduce the number of viable kidneys being wasted because they didn't reach the patient in time.
The authors analyze U.S. airline transportation and kidney transplantation datasets. They use the data to track the evolution of airline routes connecting all U.S. airports. Then they look at kidney transplants between donors and recipients connected by these airports.
"Transportation plays a major role in providing patients with available donations, if new airline routes can increase the volume of shared kidneys by 7.3%, think of how many lives could be saved," continued Dai, a professor in the Carey Business School at Johns Hopkins. "We also find the post-transplant survival rate remains largely unchanged. It's a step forward in organ donations thanks to O.R. and analytics."
INFORMATION:
About INFORMS and Management Science
Management Science is a premier peer-reviewed scholarly journal focused on research using quantitative approaches to study all aspects of management in companies and organizations. It is published by INFORMS, the leading international association for operations research and analytics professionals. More information is available at http://www.informs.org or @informs.
Contact:
Ashley Smith
443-757-3578
asmith@informs.org
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-12
[Points]
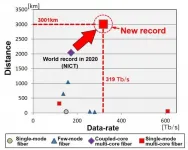
319 Tb/s long-haul transmission of wideband (>120 nm) S, C and L-bands signal using 552 PDM-16QAM, wavelength-division multiplexed channels in a 4-core optical fiber
Long-distance transmission over 3,001 km enabled by adoption of both erbium and thulium doped-fiber amplifiers and distributed Raman amplification
Demonstration shows potential of SDM fibers with standard-cladding diameter and compatibility with existing cabling technologies for near-term adoption of high-throughput SDM fiber systems
[Abstract]
Researchers from the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT, President: TOKUDA ...
2021-07-12
When we think about singularities, we tend to think of massive black holes in faraway galaxies or a distant future with runaway AI, but singularities are all around us. Singularities are simply a place where certain parameters are undefined. The North and South Pole, for example, are what's known as coordinate singularities because they don't have a defined longitude.
Optical singularities typically occur when the phase of light with a specific wavelength, or color, is undefined. These regions appear completely dark. Today, some optical singularities, including ...
2021-07-12
Los Alamos, N.M., July 12, 2021--For the first time, the long-theorized neutron-clustering effect in nuclear reactors has been demonstrated, which could improve reactor safety and create more accurate simulations, according to a new study recently published in the journal Nature Communications Physics.
"The neutron-clustering phenomenon had been theorized for years, but it had never been analyzed in a working reactor," said Nicholas Thompson, an engineer with the Los Alamos Advanced Nuclear Technology Group. "The findings indicate that, as neutrons fission and create more neutrons, some go on to form large lineages of clusters while others quickly die off, resulting in so-called 'power tilts,' ...
2021-07-12
(Boston)--Despite the availability of numerous effective birth control methods, more than 40 percent of pregnancies worldwide are unintended. In addition to contributing significantly to population growth, unintended pregnancies can have pronounced adverse effects on maternal physical, mental and economic wellbeing.
Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and ZabBio (San Diego, CA) have developed an anti-sperm monoclonal antibody, the Human Contraception Antibody (HCA), which they found to be safe and possess potent sperm agglutination (clumping) and immobilization activity in laboratory tests.
"HCA appears to be suitable for contraceptive use and could be administered vaginally in a dissolvable film for a ...
2021-07-12
A research team from the University of Göttingen and the University of British Columbia (Canada) has investigated how people in five different countries react to various usages of genome editing in agriculture. The researchers looked at which uses are accepted and how the risks and benefits of the new breeding technologies are rated by people. The results show only minor differences between the countries studied - Germany, Italy, Canada, Austria and the USA. In all countries, making changes to the genome is more likely to be deemed acceptable when used in crops rather than in livestock. The study was published in Agriculture and Human Values.
Relatively new breeding technologies, such as CRISPR gene editing, have enabled a range of new opportunities for plant and animal breeding. ...
2021-07-12
The sensory cells in the inner ear and the touch receptors in the skin actually have a lot in common, according to a new study from the USC Stem Cell laboratory of Neil Segil published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences (PNAS).
"There are striking similarities in the development of two types of specialized sensory cells: the so-called 'hair cells' that receive sound vibrations in the inner ear, and the Merkel cells that sense light touch at the surface of the skin," said Segil, who is a Professor in the Department of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, and the USC Tina and Rick Caruso Department of Otolaryngology ...
2021-07-12
The Lucinidae family, lucinids for short, comprises approximately 500 living species of bivalves. They are at least 400 million years old, according to fossil records, and have managed to colonize a wide variety of habitats, from beautiful beaches to the abyssal depths untouched by the sun over a kilometer below the sea surface. Their ability to thrive in a wide variety of habitats is made possible by their 'partner in crime', a sulfur-oxidizing bacterial symbiont that utilizes hydrogen sulfide, better known as 'rotten egg gas', as an energy source to power primary production. This process is not unlike photosynthesis used by plants, yet not dependent on sunlight, ...
2021-07-12
BOSTON - By implementing a long-term, prospective approach to the development of celiac disease, a collaborative group of researchers has identified substantial microbial changes in the intestines of at-risk infants before disease onset. Using advanced genomic sequencing techniques, MassGeneral Hospital for Children (MGHfC) researchers, along with colleagues from institutions in Italy and the University of Maryland, College Park, uncovered distinct preclinical alterations in several species, pathways and metabolites in children who developed celiac disease compared to at-risk children who did not develop celiac disease.
As part of the MGHfC Celiac Disease, Genomic, Microbiome and Metabolomic (CDGEMM) Study, researchers ...
2021-07-12
Communities trying to fight sea-level rise could inadvertently make flooding worse for their neighbors, according to a new study from the END ...
2021-07-12
Better treatments of HER2-positive breast cancer are closer at hand, thanks to new research by a team led by Université de Montréal professor Jean-François Côté at the cytoskeleton organization and cell-migration research unit of the UdeM-affiliated Montreal Clinical Research Institute.
Published in PNAS, the journal of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, the new research by Marie-Anne Goyette, a doctoral student in Côté's laboratory, reveals a highly promising therapeutic target to counter the HER2-positive breast cancer.
In HER2-positive breast cancer, a gene called HER2 is expressed that promotes an aggressive form of the disease. Affecting 20 per cent of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Direct flights save lives! New airline routes can increase kidney sharing by more than 7%