Sea-level rise solutions
Stanford researchers map how sea-level rise adaptation strategies impact economies and floodwaters
2021-07-12
(Press-News.org) Communities trying to fight sea-level rise could inadvertently make flooding worse for their neighbors, according to a new study from the END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promising new research on aggressive breast cancer
2021-07-12
Better treatments of HER2-positive breast cancer are closer at hand, thanks to new research by a team led by Université de Montréal professor Jean-François Côté at the cytoskeleton organization and cell-migration research unit of the UdeM-affiliated Montreal Clinical Research Institute.
Published in PNAS, the journal of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, the new research by Marie-Anne Goyette, a doctoral student in Côté's laboratory, reveals a highly promising therapeutic target to counter the HER2-positive breast cancer.
In HER2-positive breast cancer, a gene called HER2 is expressed that promotes an aggressive form of the disease. Affecting 20 per cent of ...
New research suggests explosive volcanic activity on Venus
2021-07-12
ITHACA, N.Y. - Traces of the gas phosphine point to volcanic activity on Venus, according to new research from Cornell University.
Last autumn, scientists revealed that phosphine was found in trace amounts in the planet's upper atmosphere. That discovery promised the slim possibility that phosphine serves as a biological signature for the hot, toxic planet.
Now Cornell scientists say the chemical fingerprint support a different and important scientific find: a geological signature, showing evidence of explosive volcanoes on the mysterious planet.
"The phosphine is not telling us about the biology ...
Childhood lead exposure may adversely affect adults' personalities
2021-07-12
AUSTIN, Texas -- Lead exposure in childhood may lead to less mature and less healthy personalities in adulthood, according to a new study lead by psychology researchers at The University of Texas at Austin.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, sampled more than 1.5 million people in 269 U.S. counties and 37 European nations. Researchers found that those who grew up in areas with higher levels of atmospheric lead had less adaptive personalities in adulthood -- lower levels of conscientiousness and agreeableness and higher levels of neuroticism.
"Links between lead exposure and personality traits are quite impactful, because we take our personalities with us everywhere," ...
Sweet success: CABBI demonstrates first precision breeding of sugarcane with CRISPR-Cas9
2021-07-12
Sugarcane is one of the most productive plants on Earth, providing 80 percent of the sugar and 30 percent of the bioethanol produced worldwide. Its size and efficient use of water and light give it tremendous potential for the production of renewable value-added bioproducts and biofuels.
But the highly complex sugarcane genome poses challenges for conventional breeding, requiring more than a decade of trials for the development of an improved cultivar.
Two recently published innovations by University of Florida researchers at the Department of Energy's Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) demonstrated the ...
Crystal clear: Lepidopterans have many ways of being transparent
2021-07-12
Butterflies and moths have beautiful wings: the bright flare of an orange monarch, the vivid stripes of a swallowtail, the luminous green of a Luna moth. But some butterflies flutter on even more dramatic wings: parts of their wing, or sometimes the entire wing itself, are actually transparent.
Many aquatic organisms, including jellies and fish, are transparent. But transparent butterfly and moth wings are so arresting that merely catching a glimpse of one typically causes a human to lunge for a camera or at least point it out to their friends. These enigmatic, transparent butterfly wings have not been studied comprehensively.
Doris Gomez and Marianne Elias (French National Center for Scientific Research) set out to change that. Last week, along with a multidisciplinary ...
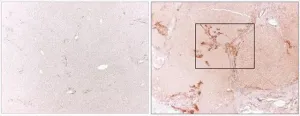
Selective, toxin-bearing antibodies could help treat liver fibrosis
2021-07-12
Chronic alcohol abuse and hepatitis can injure the liver and lead to fibrosis, the buildup of collagen and scar tissue. As a potential approach to treating liver fibrosis, University of California San Diego School of Medicine researchers and their collaborators are looking for ways to stop liver cells from producing collagen.
"So we thought...what if we take immunotoxins and try to get them to kill collagen-producing cells in the liver," said team lead Tatiana Kisseleva, MD, PhD, associate professor of surgery at UC San Diego School of Medicine. "If these antibodies carrying toxic molecules can find and bind the cells, the cells will eat up the 'gift' and die."
In a study published July 12, 2021 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Kisseleva ...
Shape-memory alloys might help airplanes land without a peep
2021-07-12
Having a home near a busy airport certainly has its perks. It is close to many establishments and alleviates the problem of wading through endless traffic to catch flights. But it does come at a cost -- tolerating the jarring sounds of commercial airplanes during landing and takeoff.
Researchers at Texas A&M University have conducted a computational study that validates using a shape-memory alloy to reduce the unpleasant plane noise produced during landing. They noted that these materials could be inserted as passive, seamless fillers within airplane wings ...
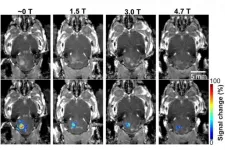
Magnetic field from MRI affects focused-ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier
2021-07-12
MRI-guided focused ultrasound combined with microbubbles can open the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and allow therapeutic drugs to reach the diseased brain location under the guidance of MRI. It is a promising technique that has been shown safe in patients with various brain diseases, such as Alzheimer's diseases, Parkinson's disease, ALS, and glioblastoma. While MRI has been commonly used for treatment guidance and assessment in preclinical research and clinical studies, until now, researchers did not know the impact of the static magnetic field generated by the MRI scanner on the BBB opening size and ...
Gene therapy offers long-awaited hope for children with rare, incurable disorder
2021-07-12
Children with a devastating genetic disorder characterized by severe motor disability and developmental delay have experienced sometimes dramatic improvements in a gene therapy trial launched at UCSF Benioff Children's Hospitals.
The trial includes seven children aged 4 to 9 born with deficiency of AADC, an enzyme involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine, that leaves them unable to speak, feed themselves or hold up their head. Six of the children were treated at UCSF and one at Ohio State Wexner Medical Center.
Children in the study experienced improved motor function, better mood, and longer sleep, and were able to interact more fully with their ...
The promise of inclusive sustainability
2021-07-12
Historically, shared resources such as forests, fishery stocks, and pasture lands have often been managed with an aim toward averting "tragedies of the commons," which are thought to result from selfish overuse. Writing in BioScience, Drs. Senay Yitbarek (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill), Karen Bailey (University of Colorado Boulder), Nyeema Harris (Yale University), and colleagues critique this model, arguing that, all too often, such conservation has failed to acknowledge the complex socioecological interactions that undergird the health of resource ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Sea-level rise solutionsStanford researchers map how sea-level rise adaptation strategies impact economies and floodwaters