Noninvasive, label-free optical method visualizes deep, cellular brain disease in vivo
2021-07-16
(Press-News.org) Central nervous system (CNS) diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) manifest early at the microscopic (i.e. cellular) level, deep in the brain. Yet, optical microscopes that can see cells in the living brain are superficial or invasive. Whole brain imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging are deep and non-invasive, but lack cellular resolution.
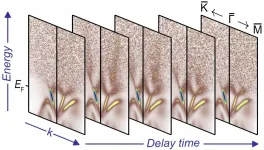
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Vivek J. Srinivasan from the Departments of Ophthalmology and Radiology and Tech4Health Institute, NYU Langone Health, USA, and co-workers have developed a label-free optical microscopy approach that has a unique ability to image deep, with high resolution and minimal invasiveness. Specifically, they demonstrated an in vivo high numerical aperture optical coherence microscopy (OCM) approach that utilizes the 1700 nm water absorption window, where attenuation of light by scattering and absorption is minimized.
The 1700 nm water absorption window, also known as the third near-infrared (NIR) window, boasts a local water absorption minimum and relatively low scattering. In OCM, a broader spectrum provides a finer axial resolution, and with it, a stronger ability to reject multiply scattered light that causes image blur. Yet the entire 1700 nm window, which spans from 1560 to 1820 nm, is often not used:
"The transition from standard wavelengths to 1700 nm OCM, while optimally using the entire water absorption window (not just a portion of the window), has been very difficult to date due to the numerous optical engineering challenges." the scientists mentioned.
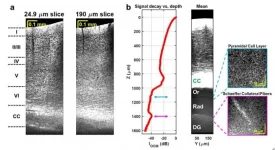
These challenges include noisy detectors and light sources, severe chromatic dispersion, and lack of standardized optical components. The scientists addressed these issues through the choice of a low noise supercontinuum light source, a custom numerical dispersion compensation method, and optical system design. With these technical advances, neuronal cell and myelin architecture across the entire depth of the mouse neocortex, and some sub-cortical regions, can be imaged through a thinned-skull preparation that preserves intracranial space.
"The results represent unprecedented depths for cellular-scale brain imaging through a minimally invasive preparation. We next investigated the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), which is expected to show a gradation of pathology with cortical depth. The imaging results confirmed the appearance of severe pathology in deep but not superficial cortex, which would be missed by more superficial imaging techniques."
Another important feature of the method is that the image contrast arises from intrinsic properties of the brain itself. OCM does not require transgenic mice or administration of compounds. Neuronal cell body loss, demyelination of axons, plaques, and local tissue changes can all be imaged.
"Now disease can be visualized deep in the mouse brain with a simple surgical preparation, without exogenous labeling. The 1700 nm optical window can also quantify tissue water and lipid content in vivo, which may provide further insights into disease progression." the scientists forecast.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-16
Shizuoka, Japan - At Shikine Island, Japan, kelp forests and abalone fisheries were once common, but over the last twenty years they have disappeared. Now, researchers from Japan have discovered that these temperate coastal marine ecosystems are becoming more "simple", losing biodiversity, complexity and their aesthetic values.
In a study published this month, researchers from the University of Tsukuba and international collaborators explored how the combined effects of ocean warming and acidification are changing temperate coastal marine ecosystems.
Tropical coastal seas are synonymous with coral reefs. As ocean temperatures cool toward the poles, corals give way to kelp as the main habitat-forming species. The shift from coral to kelp can clearly be seen along the 2000 km ...
2021-07-16
The laws of quantum physics rule the microcosm. They determine, for example, how easily electrons move through a crystal and thus whether the material is a metal, a semiconductor or an insulator. Quantum physics may lead to exotic properties in certain materials: In so-called topological insulators, only the electrons that can occupy some specific quantum states are free to move like massless particles on the surface, while this mobility is completely absent for electrons in the bulk. What's more, the conduction electrons in the "skin" of the material are necessarily spin polarized, and form robust, metallic surface states that could be utilized as channels in which to drive pure spin currents on femtosecond ...
2021-07-16
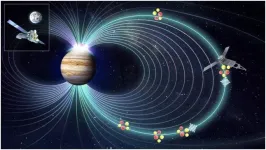
An international research team led by YAO Zhonghua from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS) has explained the cause of Jupiter's X-ray aurorae, a mystery that has puzzled scientists for 40 years.
The findings were published in Science Advances on July 9.
It is the first time planetary researchers have described the entire causality chain for Jupiter's X-ray auroral flares. The mechanism in producing X-ray auroral flares at Jupiter may have potential applications in X-ray astronomy.
The X-ray auroral spectra tell us these aurorae are produced by heavy ions with energies in the ...
2021-07-16
From the vocal cords that produce our voice, to our heartbeat, our body's cells are constantly subjected to mechanical forces that steadily change their response to these stimuli, regulating vital processes, in healthy individuals and in diseases such as cancer alike. Nevertheless, despite their importance, we remain largely ignorant of how cells sense and respond to these forces.
Now, an international team co-led by the researcher Pere Roca-Cusachs, from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), and Isaac Almendros, a researcher at the Respiratory Diseases Networking Biomedical Research Centre (CIBERES) and IDIBAPS, both professors at the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences of the University of Barcelona (UB), has proved that what determines mechanical ...
2021-07-16
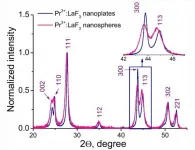
The article represents the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and flow cytometry study of A-549 (human lung carcinoma) cellular uptake of Pr3+:LaF3 nanoparticles. The Pr3+:LaF3 nanoparticles are promising platforms for cell nano-sensors.
The objective of the work was to study the influence of nanoparticle morphology (nanoplates and nanospheres) on cytotoxicity and the dynamic of cellular uptake.
In the flow cytometry method, the cells go through a small tube (as a flow) and are irradiated by a laser. Cells scatter the laser light, and this scattering ...
2021-07-16
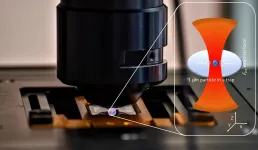
Measurements of biomechanical properties inside living cells require minimally invasive methods. Optical tweezers are particularly attractive as a tool. It uses the momentum of light to trap and manipulate micro- or nanoscale particles. A team of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Cornelia Denz from the University of Münster (Germany) has now developed a simplified method to perform the necessary calibration of the optical tweezers in the system under investigation. Scientists from the University of Pavia in Italy were also involved. The results of the study have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The calibration ensures that measurements of different samples and with different devices are comparable. ...
2021-07-16
The ability to predict and interpret modifications of ribonucleic acid (RNA) has been a welcome advance in biochemistry research.
However, existing predictive approaches have a key drawback--they can only predict a single type of RNA modification without supporting multiple types or providing insightful interpretation of their prediction results.
Researchers from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University, led by Dr Jia Meng, have addressed this issue by developing a model that supports 12 RNA modification types, greatly expanding RNA research prediction and interpretation.
"To the best of our knowledge, ...
2021-07-16
While tropical forests remain threatened and their future is uncertain, the importance of understanding how well individual protected areas avoid deforestation increases. Researchers from the University of Turku and University of Helsinki, Finland, have investigated this question in a newly published study that focuses on the State of Acre in Brazilian Amazonia.
Tropical forests are unique environments that have huge species diversity and also act as important reservoirs of organic carbon, thereby counteracting climate change. However, their area is diminishing due to deforestation, ...
2021-07-16
Tsukuba, Japan - A team of scientists led by Associate Professor Haruka Ozaki of the Center for Artificial Intelligence Research at the University of Tsukuba in collaboration with Dr. Koichi Takahashi from RIKEN used mathematical algorithms to optimize the schedule of automated biology laboratory robots. By analyzing the needs of time-sensitive samples that require investigation using multiple instruments, the researchers were able to maximize the number of experiments that can be performed within time and laboratory resource constraints. This work may help in the design of future automated biology labs and other workspaces.
Biology laboratories have seen increasing automation because many tasks, like pipetting solutions or moving cells from one ...
2021-07-16
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Most of the tests that doctors use to diagnose cancer -- such as mammography, colonoscopy, and CT scans -- are based on imaging. More recently, researchers have also developed molecular diagnostics that can detect specific cancer-associated molecules that circulate in bodily fluids like blood or urine.
MIT engineers have now created a new diagnostic nanoparticle that combines both of these features: It can reveal the presence of cancerous proteins through a urine test, and it functions as an imaging agent, pinpointing the tumor location. In principle, this diagnostic could be used to detect cancer anywhere in the body, including tumors that have metastasized from their original locations.
"This is a really broad sensor intended to respond to both primary tumors and their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Noninvasive, label-free optical method visualizes deep, cellular brain disease in vivo