Watching the ultrafast dance moves of a laser plasma
2021-07-16
(Press-News.org) Great leaps in science and technology have been propelled by recent advances in seeing fast evolving physical phenomena, as they happen. Femtosecond lasers from the infrared to the X-ray region have enabled us to 'watch', in real time, atoms dance in molecules and solids on femtosecond and picosecond timescales. Watching such fascinating motions not just in real time but at the spatial locations where they happen, is a bigger challenge.
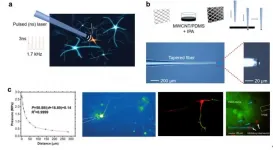
It is precisely this advance that has been made by a team of researchers at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, York University and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratories, UK [1]. They exploded a solid surface with an ultrahigh intensity (10^19 W/sq.cm), 25 femtosecond laser pulse (pump) creating a hot, dense plasma and monitored its ultra-rapid motion by reflecting a weak second femtosecond pulse (probe). The Doppler shifts in the wavelength imposed on the reflected probe pulse by the fast evolving plasma give away the outward (blue shift) and inward (red shift) motions of the plasma.
No previous study captured the motion on the entire plasma surface -- the 'dance floor' -- in a single experiment. This team coupled femtosecond time resolution with micrometre space resolution, thereby capturing the ultra-rapid twists and turns of the plasma at different transverse locations.
The experiments devised a novel 2-D Doppler monitor with sixteen independent, single shot, high resolution spectrometers all triggered by the pump laser pulse and capturing the instantaneous velocity of the plasma at different spatial locations. They show that different portions of the plasma move in and out at different times, contrary to the usual expectation of a somewhat uniform motion. This new method can prove very useful for tracking the flow of heat and energy along the surface and watching the growth of plasma instabilities, very important for understanding laser plasma science and pushing forward applications of high intensity, femtosecond laser driven laser plasmas in imaging and laser fusion.
INFORMATION:
[1] Femtosecond, two-dimensional spatial Doppler mapping of ultraintense laser-solid target interaction, PHYSICAL REVIEW RESEARCH 3, 033034 (2021)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-16
Fear is an important reaction that warns and protects us from danger. But when fear responses are out of control, this can lead to persistent fears and anxiety disorders. In Europe, about 15 percent of the population is affected by anxiety disorders. Existing therapies remain largely unspecific or are not generally effective, because the detailed neurobiological understanding of these disorders is lacking.
What was known so far is that distinct nerve cells interact together to regulate fear responses by promoting or suppressing them. Different circuits of nerve cells are involved in this process. A kind of "tug-of-war" takes place, with one brain circuit ...
2021-07-16
A new way of producing coherent light in the ultra-violet spectral region, which points the way to developing brilliant table-top x-ray sources, has been produced in research led at the University of Strathclyde.
The scientists have developed a type of ultra-short wavelength coherent light source that does not require laser action to produce coherence. Common electron-beam based light sources, known as fourth-generation light sources, are based on the free-electron laser (FEL), which uses an undulator to convert electron beam energy into X-rays.
Coherent light sources are powerful tools that enable research in many areas of medicine, biology, material sciences, chemistry and physics.
This new way of producing coherent radiation could revolutionise light sources, as it would ...
2021-07-16
In the field of industrial engineering, using simulations to model, predict and even optimise the response of a system or device is widespread, as it is less expensive and less complex -and, sometimes, less dangerous- than fabricating and testing several prototypes.
This type of simulation studies uses numerical methods that, depending on the problem to be addressed -for example, reducing the aerodynamic forces of an aircraft by changing its shape or using the minimum possible amount of material on elements under loading without breaking- require the simulation of a wide variety of possible combinational cases, which entails high computational costs.
The researchers from the School of Industrial Engineering of the University of Malaga Francisco Javier Granados Ortiz ...
2021-07-16
Neuro-evolutionary robotics is an attractive approach to realize collective behaviors for swarms of robots. Despite the large number of studies that have been devoted to it and although many methods and ideas have been proposed, empirical evaluations and comparative analyses are rare.
A publication in the journal Nature Communications, led by Mauro Birattari and his team at the research center IRIDIA, École Polytechnique de Bruxelles, Université Libre de Bruxelles, compares some of the most popular and advanced neuro-evolutionary methods for offline design of robot swarms.
"Concretely, these ...
2021-07-16
RUDN University biologists discovered the way how macrophages (the cells of the "first line" immune response) respond to inflammation and identified how the immune response depends on their origin. It turned out that when exposed to an inflammatory stimulus, two opposing mechanisms are activated in macrophages simultaneously -- inducing and inhibiting inflammation. These data can potentially be useful in the treatment of cancer, as targeted activation of macrophages will strengthen the immune response of the organism in the fight against a tumor. The results were published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
Macrophages are the cells responsible for phagocytosis -- they capture bacteria, the dead cells remains ...
2021-07-16
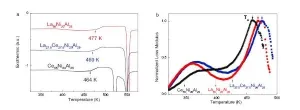
A collaborative group from Tohoku University and Johns Hopkins University have provided valuable insights into the glass transition.
When a liquid is cooled rapidly, it gains viscosity and eventually becomes a rigid solid glass. The point at which it does so is known as the glass transition.
But the exact physics behind the glass transition, and the nature of glass in general, still pose many questions for scientists.
Metallic Glasses (MGs) are highly sought after since they combine the flexibility of plastic with the strength of steel. They are amorphous materials with a disordered atomic structure and exhibit unique and divergent thermodynamic ...
2021-07-16
Neuromodulation at high spatial resolution has been an invaluable approach for treating neurological diseases and advancing fundamental knowledge in the field of neuroscience, as firing of a small population or even single neurons can specifically alter animal behavior or brain state. Optogenetics is a powerful method capable of modulating population neural activity in rodents, yet its requirement for viral transfection limits its applications in nonhuman primates and humans. As a rapidly growing modality, focused ultrasound has been harnessed in a myriad of brain neuromodulation applications. However, conventional piezo-based transducers offer a spatial resolution of several millimeters. It is also challenging ...
2021-07-16
JULY 15, 2021, NEW YORK - A Ludwig Cancer Research study has found that inducing random chromosome instability (CIN) events in mice for as little as one week is enough to trigger harmful chromosomal patterns in cells that spur the formation of tumors.
"We show that you don't need chronic, lifelong chromosomal mistakes to produce tumorigenesis at a quite respectable frequency," said Don Cleveland, Member of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, San Diego, who led the study with Floris Foijer of the University of Groningen, in The Netherlands. "A very transient exposure would likely be sufficient to drive a very substantial increase in tumorigenesis."
The finding, detailed this week in the journal END ...
2021-07-16
Washington, DC / New Delhi, India - Researchers at CDDEP recently published 'Improving vaccination coverage and timeliness through periodic intensification of routine immunization: evidence from Mission Indradhanush' where they evaluated the performance of India's Mission Indradhanush (MI) child vaccination campaign -- a periodic intensification of the routine immunization program.
Each year, 1.2 million Indian children die, accounting for a fifth of global under-5 deaths. Over 400,000 of these deaths are from vaccine-preventable diseases. An estimated 38% of Indian children under the age of two years were not-fully-immunized in 2016. Additionally, vaccinated children received 23%-35% of the doses of polio, diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus ...
2021-07-16
Main points
Strong evidence that patients with pre-existent mental disorders are twice as likely to die or be hospitalised after SARS-CoV-2 infection
Psychotic and mood disorders are linked with COVID-19-associated mortality, as are exposure to antipsychotic and anxiolytic treatments.
Patients with substance use disorders are at increased risk of hospitalisation.
In the largest systematic review and meta-analysis to date on COVID-19 outcomes in individuals with psychiatric disorders, the odds of dying or being hospitalized following COVID-19 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Watching the ultrafast dance moves of a laser plasma