RUDN University biologists prove the anticancer potential of macrophages
2021-07-16
(Press-News.org) RUDN University biologists discovered the way how macrophages (the cells of the "first line" immune response) respond to inflammation and identified how the immune response depends on their origin. It turned out that when exposed to an inflammatory stimulus, two opposing mechanisms are activated in macrophages simultaneously -- inducing and inhibiting inflammation. These data can potentially be useful in the treatment of cancer, as targeted activation of macrophages will strengthen the immune response of the organism in the fight against a tumor. The results were published in the journal Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
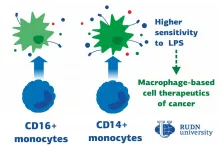
Macrophages are the cells responsible for phagocytosis -- they capture bacteria, the dead cells remains and other foreign particles. This is the first line of defense of immune system. Most macrophages are formed from blood monocytes, which in turn differ in the level of two proteins on their surface: CD14 and CD16. Until now, it was not known how macrophages derived from the two most polar types of monocytes -- called CD14+monocytes and CD16+monocytes-respond to inflammation. RUDN University biologists have identified these differences.
"Surprisingly, among the published data, there is practically no information about the activation of macrophages obtained from CD14+monocytes and CD16+monocytes. There have only been several published works devoted to the pro-inflammatory polarization of human macrophages with varying monocytic origin. Most data derived from mouse models. We decided to fill this gap and discover how macrophages obtained from CD14+ and CD16+monocytes are activated", said Polina Vishnyakova, PhD, researcher at Medical Biotechnology Laboratory at RUDN University.
The receptors on the surface of macrophages react, for example, to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) -- the main component of bacterial membranes. RUDN University biologists used blood samples from six healthy women aged 26 to 34 years and isolated CD14+monocytes and CD16+monocytes from the blood using magnetic separation. Then the monocytes were "turned" into macrophages - by cultivation with special differentiation factors. Macrophages obtained from different types of monocytes were subjected to LPS and analyzed using flow cytometry, secretome, transcriptomic and proteomic analysis.
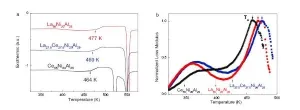
The results demonstrated that, firstly, the traditional division of macrophages into pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory is not quite correct -- they switch their functions depending on the surrounding conditions. RUDN University biologists also found out that macrophages derived from CD14+monocytes are more prone to a pro-inflammatory response. Flow cytometry showed that these macrophages synthesize more CD86 protein, which is responsible for the activation of T-lymphocytes -- other cells of the immune response. At the same time, secretome analysis showed that macrophages derived from CD14+monocytes secrete more pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine molecules.
These results can be used in the future for the treatment of oncological diseases. The fact is that pro-inflammatory macrophages are able to fight tumors. Picking the most suitable monocytes of the patient (CD14 or CD16), turning them into pro-inflammatory macrophages and transplanting them back to the tumor, one can stimulate the organism's fight against cancer cells.
"The key issue is the choice of monocyte subset for further therapeutic application of macrophages. Thus, macrophages obtained from different populations of human monocytes are potentially relevant for cell therapy in case of malignant oncological diseases", said Polina Vishnyakova, PhD, researcher at Medical Biotechnology Laboratory at RUDN University.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-16
A collaborative group from Tohoku University and Johns Hopkins University have provided valuable insights into the glass transition.
When a liquid is cooled rapidly, it gains viscosity and eventually becomes a rigid solid glass. The point at which it does so is known as the glass transition.
But the exact physics behind the glass transition, and the nature of glass in general, still pose many questions for scientists.
Metallic Glasses (MGs) are highly sought after since they combine the flexibility of plastic with the strength of steel. They are amorphous materials with a disordered atomic structure and exhibit unique and divergent thermodynamic ...
2021-07-16
Neuromodulation at high spatial resolution has been an invaluable approach for treating neurological diseases and advancing fundamental knowledge in the field of neuroscience, as firing of a small population or even single neurons can specifically alter animal behavior or brain state. Optogenetics is a powerful method capable of modulating population neural activity in rodents, yet its requirement for viral transfection limits its applications in nonhuman primates and humans. As a rapidly growing modality, focused ultrasound has been harnessed in a myriad of brain neuromodulation applications. However, conventional piezo-based transducers offer a spatial resolution of several millimeters. It is also challenging ...
2021-07-16
JULY 15, 2021, NEW YORK - A Ludwig Cancer Research study has found that inducing random chromosome instability (CIN) events in mice for as little as one week is enough to trigger harmful chromosomal patterns in cells that spur the formation of tumors.
"We show that you don't need chronic, lifelong chromosomal mistakes to produce tumorigenesis at a quite respectable frequency," said Don Cleveland, Member of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, San Diego, who led the study with Floris Foijer of the University of Groningen, in The Netherlands. "A very transient exposure would likely be sufficient to drive a very substantial increase in tumorigenesis."
The finding, detailed this week in the journal END ...
2021-07-16
Washington, DC / New Delhi, India - Researchers at CDDEP recently published 'Improving vaccination coverage and timeliness through periodic intensification of routine immunization: evidence from Mission Indradhanush' where they evaluated the performance of India's Mission Indradhanush (MI) child vaccination campaign -- a periodic intensification of the routine immunization program.
Each year, 1.2 million Indian children die, accounting for a fifth of global under-5 deaths. Over 400,000 of these deaths are from vaccine-preventable diseases. An estimated 38% of Indian children under the age of two years were not-fully-immunized in 2016. Additionally, vaccinated children received 23%-35% of the doses of polio, diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus ...
2021-07-16
Main points
Strong evidence that patients with pre-existent mental disorders are twice as likely to die or be hospitalised after SARS-CoV-2 infection
Psychotic and mood disorders are linked with COVID-19-associated mortality, as are exposure to antipsychotic and anxiolytic treatments.
Patients with substance use disorders are at increased risk of hospitalisation.
In the largest systematic review and meta-analysis to date on COVID-19 outcomes in individuals with psychiatric disorders, the odds of dying or being hospitalized following COVID-19 ...
2021-07-16
The team's findings, with important implications for ocean biogeochemistry and climate science, have been published by Nature Communications in a paper by Associate Professor Mark Holzer from UNSW Science's School of Mathematics & Statistics, with co-authors Tim DeVries (UCSB) and Casimir de Lavergne (LOCEAN).
"The deep North Pacific is a vast reservoir of remineralized nutrients and respired carbon that have accumulated over centuries," says A/Prof. Holzer. "When these deep waters are returned to the surface, their nutrients support biological production and their dissolved CO2 can be released into the atmosphere. As such, the deep Pacific plays a key ...
2021-07-16
Central nervous system (CNS) diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) manifest early at the microscopic (i.e. cellular) level, deep in the brain. Yet, optical microscopes that can see cells in the living brain are superficial or invasive. Whole brain imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging are deep and non-invasive, but lack cellular resolution.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Vivek J. Srinivasan from the Departments of Ophthalmology and Radiology and Tech4Health Institute, ...
2021-07-16
Shizuoka, Japan - At Shikine Island, Japan, kelp forests and abalone fisheries were once common, but over the last twenty years they have disappeared. Now, researchers from Japan have discovered that these temperate coastal marine ecosystems are becoming more "simple", losing biodiversity, complexity and their aesthetic values.
In a study published this month, researchers from the University of Tsukuba and international collaborators explored how the combined effects of ocean warming and acidification are changing temperate coastal marine ecosystems.
Tropical coastal seas are synonymous with coral reefs. As ocean temperatures cool toward the poles, corals give way to kelp as the main habitat-forming species. The shift from coral to kelp can clearly be seen along the 2000 km ...
2021-07-16
The laws of quantum physics rule the microcosm. They determine, for example, how easily electrons move through a crystal and thus whether the material is a metal, a semiconductor or an insulator. Quantum physics may lead to exotic properties in certain materials: In so-called topological insulators, only the electrons that can occupy some specific quantum states are free to move like massless particles on the surface, while this mobility is completely absent for electrons in the bulk. What's more, the conduction electrons in the "skin" of the material are necessarily spin polarized, and form robust, metallic surface states that could be utilized as channels in which to drive pure spin currents on femtosecond ...
2021-07-16
An international research team led by YAO Zhonghua from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS) has explained the cause of Jupiter's X-ray aurorae, a mystery that has puzzled scientists for 40 years.
The findings were published in Science Advances on July 9.
It is the first time planetary researchers have described the entire causality chain for Jupiter's X-ray auroral flares. The mechanism in producing X-ray auroral flares at Jupiter may have potential applications in X-ray astronomy.
The X-ray auroral spectra tell us these aurorae are produced by heavy ions with energies in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RUDN University biologists prove the anticancer potential of macrophages