(Press-News.org) The link between on-road traffic and air pollution is well-known, as are the negative health impacts of pollution exposure. However, the many factors that may influence commuters' exposure to pollutants - such as frequency, time, and duration of commute - and the overall impact of commuting remains a matter of on-going scientific discovery.
Dr. Jenna Krall, assistant professor at the George Mason University College of Health and Human Services, is using statistical methods to better understand exposure to air pollution. Krall studies how commuting patterns impact exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) from various traffic-related sources such as tailpipe emissions, road salts, and brake wear.
New study examines commuter characteristics and traffic pollution exposure among commuters
George Mason University faculty Jenna Krall studies commuter habits, such as departure time and commute length, and their associations with air pollution exposure
2021-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new, inexpensive way to heal chronic wounds
2021-07-19
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Tens of millions of patients around the world suffer from persistent and potentially life-threatening wounds. These chronic wounds, which are also a leading cause of amputation, have treatments, but the cost of existing wound dressings can prevent them from reaching people in need.
Now, a Michigan State University researcher is leading an international team of scientists to develop a low-cost, practical biopolymer dressing that helps heal these wounds.
"The existing efficient technologies are far too expensive for most health care systems, ...
New high-tech portal launched to speed hearing loss innovations
2021-07-19
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) launched a new online tool that could more quickly advance medical discoveries to reverse progressive hearing loss. The tool enables easy access to genetic and other molecular data from hundreds of technical research studies involving hearing function and the ear. The research portal called gene Expression Analysis Resource (gEAR) was unveiled in a study last month in Nature Methods. It is operated by a group of physician-scientists at the UMSOM Institute for Genome Sciences (IGS) in collaboration with their colleagues at other institutions.
The portal allows researchers to rapidly access data and provides easily interpreted visualizations of datasets. Scientists can also input ...
Curtin study challenges recommended wait time between pregnancies
2021-07-19
New Curtin University-led research has called into question existing health advice that mothers wait a minimum of two years after giving birth to become pregnant again, in order to reduce the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as preterm and small-for-gestational age births.
The research found that a World Health Organization (WHO) recommendation to wait at least 24 months to conceive after a previous birth may be unnecessarily long for mothers in high-income countries such as Australia, Finland, Norway and the United States.
Lead researcher ...
How cells control mitochondria
2021-07-19
Errors in the metabolic processes of mitochondria are responsible for a variety of diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. Scientists needed to find out just how the necessary building blocks are imported into the complex biochemical apparatus of these cell areas. The TOM complex (translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane) is considered the gateway to the mitochondrion, the proverbial powerhouse of the cell. The working group headed by Professor Chris Meisinger at the Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Freiburg has now demonstrated - in human cells - how signaling molecules control this gate. A signaling protein called DYRK1A modifies the molecular machinery of TOM and makes it more permeable ...
When money's tight, parents talk less to kids; could this explain the word gap?
2021-07-19
Three decades ago, child development researchers found that low-income children heard tens of millions fewer words in their homes than their more affluent peers by the time they reached kindergarten. This "word gap" was and continues to be linked to a socioeconomic disparity in academic achievement.
While parenting deficiencies have long been blamed for the word gap, new research from the University of California, Berkeley, implicates the economic context in which parenting takes place -- in other words, the wealth gap.
The findings, published this month in the journal Developmental Science, provide the first evidence that parents may talk less to their kids when experiencing financial scarcity.
"We were interested in what happens when parents think about or experience financial scarcity ...
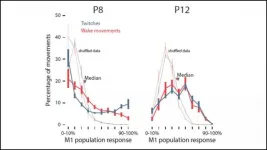
Sleep twitches facilitate motor cortex development in rats
2021-07-19
Electrical activity in the motor cortex of rats transforms from redundant to complex over the span of four days shortly after birth. Sleep twitches guide this metamorphosis, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Despite its name, the motor cortex doesn't control movement right off the bat. Early in development, this part of the brain is solely a sensory structure. Feedback from self-generated movements -- sleep twitches in particular -- may build representations of the body that will later orchestrate movement.
To characterize this transition, Glanz et al. recorded electrical activity from the motor cortex of rat pups eight and 12 days after birth while monitoring their behavior. ...
Angry politicians make angry voters, new study finds
2021-07-19
Politicians may have good reason to turn to angry rhetoric, according to research led by political scientists from Colorado--the strategy seems to work, at least in the short term.
In a new study, Carey Stapleton at the University of Colorado Boulder and Ryan Dawkins at the U.S. Air Force Academy discovered that political furor may spread easily: Ordinary citizens can start to mirror the angry emotions of the politicians they read about in the news. Such "emotional contagion" might even drive some voters who would otherwise tune out of politics to head to the polls.
"Politicians want to get reelected, and anger is a powerful tool that they can use to make that happen," said Stapleton, who recently earned his PhD in political science at ...
Study may show why MS patients develop progressive disability
2021-07-19
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Did you know multiple sclerosis (MS) means multiple scars? New research shows that the brain and spinal cord scars in people with MS may offer clues to why they developprogressive disability but those with related diseases where the immune system attacks the central nervous system do not.
In a study published in Neurology, Mayo Clinic researchers and colleagues assessed if inflammation leads to permanent scarring in these three diseases:
MS.
Aquaporin-4 antibody positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (AQP4-NMOSD).
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody associated disorder (MOGAD).
They also studied whether scarring may be a reason for ...
Making clean hydrogen is hard, but researchers just solved a major hurdle
2021-07-19
For decades, researchers around the world have searched for ways to use solar power to generate the key reaction for producing hydrogen as a clean energy source -- splitting water molecules to form hydrogen and oxygen. However, such efforts have mostly failed because doing it well was too costly, and trying to do it at a low cost led to poor performance.
Now, researchers from The University of Texas at Austin have found a low-cost way to solve one half of the equation, using sunlight to efficiently split off oxygen molecules from water. The finding, published recently in Nature Communications, represents a step forward toward greater adoption ...
DNA duplication linked to the origin and evolution of pine trees and their relatives
2021-07-19
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Plants are DNA hoarders. Adhering to the maxim of never throwing anything out that might be useful later, they often duplicate their entire genome and hang on to the added genetic baggage. All those extra genes are then free to mutate and produce new physical traits, hastening the tempo of evolution.
A new study shows that such duplication events have been vitally important throughout the evolutionary history of gymnosperms, a diverse group of seed plants that includes pines, cypresses, sequoias, ginkgos and cycads. Published today in Nature Plants, the research indicates that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] New study examines commuter characteristics and traffic pollution exposure among commutersGeorge Mason University faculty Jenna Krall studies commuter habits, such as departure time and commute length, and their associations with air pollution exposure