(Press-News.org) By uprooting carbon trapped in soil, wild pigs are releasing around 4.9 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide annually across the globe, the equivalent of 1.1 million cars.
An international team led by researchers from The University of Queensland and The University of Canterbury have used predictive population models, coupled with advanced mapping techniques to pinpoint the climate damage wild pigs are causing across five continents.
UQ's Dr Christopher O'Bryan said the globe's ever-expanding population of feral pigs could be a significant threat to the climate.
"Wild pigs are just like tractors ploughing through fields, turning over soil to find food," Dr O'Bryan said.
"When soils are disturbed from humans ploughing a field or, in this case, from wild animals uprooting, carbon is released into the atmosphere.
"Since soil contains nearly three times as much carbon than in the atmosphere, even a small fraction of carbon emitted from soil has the potential to accelerate climate change.
"Our models show a wide range of outcomes, but they indicate that wild pigs are most likely currently uprooting an area of around 36,000 to 124,000 square kilometres, in environments where they're not native.
"This is an enormous amount of land, and this not only affects soil health and carbon emissions, but it also threatens biodiversity and food security that are crucial for sustainable development."
Using existing models on wild pig numbers and locations, the team simulated 10,000 maps of potential global wild pig density.
They then modelled the amount of soil area disturbed from a long-term study of wild pig damage across a range of climatic conditions, vegetation types and elevations spanning lowland grasslands to sub-alpine woodlands.
The researchers then simulated the global carbon emissions from wild pig soil damage based on previous research in the Americas, Europe, and China.
University of Canterbury PhD candidate Nicholas Patton said the research would have ramifications for curbing the effects of climate change into the future.
"Invasive species are a human-caused problem, so we need to acknowledge and take responsibility for their environmental and ecological implications," Mr Patton said.
"If invasive pigs are allowed to expand into areas with abundant soil carbon, there may be an even greater risk of greenhouse gas emissions in the future.
"Because wild pigs are prolific and cause widespread damage, they're both costly and challenging to manage.
"Wild pig control will definitely require cooperation and collaboration across multiple jurisdictions, and our work is but one piece of the puzzle, helping managers better understand their impacts.
"It's clear that more work still needs to be done, but in the interim, we should continue to protect and monitor ecosystems and their soil which are susceptible to invasive species via loss of carbon."
INFORMATION:
The research has been published in Global Change Biology (DOI: 10.1111/gcb.15769).
Research conducted at the Sharon Eccles Steele Center for Translational Medicine (SCTM) at the University of Utah's John A. Moran Eye Center explains why people carrying a block of genetic variants strongly associated with the development of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) may develop the disease and identifies a potential therapeutic pathway for slowing or even reversing disease progression.
AMD is a major cause of irreversible blindness worldwide and the leading cause of blindness for Americans aged 55 and over. Following more than 15 years of research that has employed an extensive repository of donated human ocular ...
A new approach to analyse satellite measurements of Earth's cloud cover reveals that clouds are very likely to enhance global heating.
The research, by scientists at Imperial College London and the University of East Anglia, is the strongest evidence yet that clouds will amplify global heating over the long term, further exacerbating climate change.
The results, published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, also suggest that at double atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations above pre-industrial levels, the climate is unlikely to warm below 2°C, and is more likely on average to warm more than 3°C.
Pre-industrial CO2 levels were around 280 ppm (parts per million), ...
Throughout history, people of different cultures and stages of evolution have found ways to adapt, with varying success, to the gradual warming of the environment they live in. But can the past inform the future, now that climate change is happening faster than ever before?
Yes, say an international team of anthropologists, geographers and earth scientists in Canada, the U.S. and France led by Université de Montréal anthropologist Ariane Burke.
In a paper published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Professor Burke and her colleagues ...
A major drought and forest fires in the Amazon rainforest killed billions of trees and plants and turned one of the world's largest carbon sinks into one of its biggest polluters.
Triggered by the 2015-16 El Niño, extreme drought and associated mega-wildfires caused the death of around 2.5 billion trees and plants and emitted 495 million tonnes of CO2 from an area that makes up just 1.2 per cent of the entire Brazilian Amazon rainforest, and 1 per cent of the whole biome.
The stark findings, discovered by an international team of scientists working for more than eight years on a long-term study in the Amazon before, during and after the El Niño, have significant implications for global efforts to control the atmospheric ...
The oil industry, pharmaceutical companies and bioreactor manufacturers all face one common enemy: bubbles. Bubbles can form during the manufacturing or transport of various liquids, and their formation and rupture can cause significant issues in product quality.
Inspired by these issues and the puzzling physics behind bubbles, an international scientific collaboration was born. Stanford University chemical engineer Gerald Fuller along with his PhD students Aadithya Kannan and Vinny Chandran Suja, as well as visiting PhD student Daniele Tammaro from the University of Naples, teamed up to study how different kinds of bubbles pop.
The researchers were particularly interested in bubbles with proteins embedded on their surfaces, which is a common occurrence in the pharmaceutical industry ...
New research has found marine seismic surveys used in oil and gas exploration are not impacting the abundance or behaviour of commercially valuable fishes in the tropical shelf environment in north-western Australia.
The research is the first of its kind to use dedicated seismic vessels to measure the impacts of the survey's noise in an ocean environment, with the eight-month experiment conducted within a 2500 square kilometre fishery management zone near the Pilbara coast.
It involved using multiple acoustic sensors, tagging 387 red emperor fish and deploying more than ...
KRAS was one of the first oncogenes to be identified, a few decades ago. It is among the most common drivers of cancer and its mutations can be detected in around 25 per cent of human tumours. The development of KRAS inhibitors is, thus, an extremely active line of research. Effective results have been elusive so far, though - no KRAS inhibitor had been available until a month ago, when the FDA granted approval to Sotorasib.
KRAS encodes two gene products, KRAS4A and KRAS4B, whose levels can vary across organs and embryonic stages. When KRAS mutates, both variants, or isoforms, are activated. Though, some studies have focussed on approaches to target only KRAS4B, since it usually found to be expressed at ...
Evidence shows that early detection and treatment of cancer can significantly improve health outcomes, however women in Mississippi, particularly in underserved populations, experience the worst health outcomes for cervical, breast, and oropharyngeal cancer. ...
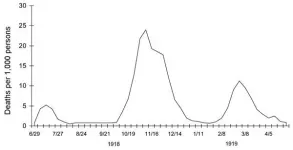
From the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic there have been countless comparisons to the 1918 influenza pandemic in terms of overall medical impact. Many of the comparisons addressed overall cases which, given the lack of a confirmatory lab test in 1918 and no meaningful case definitions for both pandemics, make such comparisons patently invalid. Overall mortality comparisons, although methodologically flawed as well, do offer a reasonably comparative outcome measure and offers a greater degree of validity. This measure is further enhanced when adjusted for population and average life years lost (see accompanying table for mortality comparisons ...
Researchers at Michigan Medicine have discovered yet another functional autoantibody in COVID-19 patients that contributes to the disease's development and the "firestorm" of blood clots and inflammation it induces.
A growing body of studies suggests COVID-19 emulates many aspects of systemic autoimmune disorders, including the release of a flurry of overactive immune cells that produce toxic webs of proteins and DNA called neutrophil extracellular traps, or NETs.
For this study, the team analyzed serum from over 300 hospitalized COVID patients, searching for a novel autoantibody that shields the toxic NETs from being destroyed and produces a lasting ...