(Press-News.org) KRAS was one of the first oncogenes to be identified, a few decades ago. It is among the most common drivers of cancer and its mutations can be detected in around 25 per cent of human tumours. The development of KRAS inhibitors is, thus, an extremely active line of research. Effective results have been elusive so far, though - no KRAS inhibitor had been available until a month ago, when the FDA granted approval to Sotorasib.
KRAS encodes two gene products, KRAS4A and KRAS4B, whose levels can vary across organs and embryonic stages. When KRAS mutates, both variants, or isoforms, are activated. Though, some studies have focussed on approaches to target only KRAS4B, since it usually found to be expressed at higher levels in tumours.
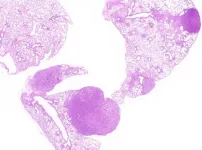
In this study, Matthias Drosten, Marina Salmón and Guillem Paniagua of the Experimental Oncology Programme, headed by Mariano Barbacid at the CNIO, had a more fundamental goal: to understand how the isoforms work separately. As they state in the paper to be published in PNAS, "The biological relevance of the expression of two isoforms has puzzled researchers for decades."
Lung cancer and metastasis
A basic research project in principle, Drosten and Salmón's study produced results that came as "a surprise." Even though KRAS4B is the dominant form in cancer, the KRAS4A mutant is also oncogenic, and it is even more active.
In the words of the authors, "KRAS4AG12V alone, in the absence of KRAS4B, can induce lung cancer and metastasis in 20 percent of individuals. Our results suggest that for therapies to be effective, the two KRAS isoforms should be targeted."
KRAS genes in embryonic development
The researchers at the CNIO created two genetically engineered mouse models that lacked KRAS4B and expressed the KRAS4A variant only, both with and without the G12V mutation (KRAS4AG12V).
In addition, the study explored the role of the two isoforms in embryonic development. One of them, KRAS4B, "is key after birth, since in the absence of this variant, mice cannot grow as a result of heart disease".
The CNIO Experimental Oncology Group is a global reference studying KRAS-related cancers, with notable examples such as the elimination of lung tumors and advanced pancreatic tumors by inactivating the RAF1 kinase in animal models.
INFORMATION:
In this work Sagrario Ortega, head of the Mouse Genomic Editing Core Unit at the CNIO, Javier Muñoz, head of the CNIO Proteomics Core Unit and Eduardo Caleiras of the Histopathology Core Unit at the CNIO, contributed fundamentally. The research was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, the Institute of Health Carlos III, the European Research Council (ERC), the Autonomous Community of Madrid, the Fundación CRIS Cancer and AXA Research Fund.
Evidence shows that early detection and treatment of cancer can significantly improve health outcomes, however women in Mississippi, particularly in underserved populations, experience the worst health outcomes for cervical, breast, and oropharyngeal cancer. ...
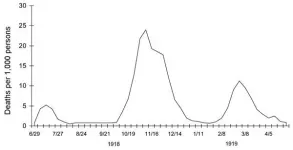
From the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic there have been countless comparisons to the 1918 influenza pandemic in terms of overall medical impact. Many of the comparisons addressed overall cases which, given the lack of a confirmatory lab test in 1918 and no meaningful case definitions for both pandemics, make such comparisons patently invalid. Overall mortality comparisons, although methodologically flawed as well, do offer a reasonably comparative outcome measure and offers a greater degree of validity. This measure is further enhanced when adjusted for population and average life years lost (see accompanying table for mortality comparisons ...
Researchers at Michigan Medicine have discovered yet another functional autoantibody in COVID-19 patients that contributes to the disease's development and the "firestorm" of blood clots and inflammation it induces.
A growing body of studies suggests COVID-19 emulates many aspects of systemic autoimmune disorders, including the release of a flurry of overactive immune cells that produce toxic webs of proteins and DNA called neutrophil extracellular traps, or NETs.
For this study, the team analyzed serum from over 300 hospitalized COVID patients, searching for a novel autoantibody that shields the toxic NETs from being destroyed and produces a lasting ...
The link between on-road traffic and air pollution is well-known, as are the negative health impacts of pollution exposure. However, the many factors that may influence commuters' exposure to pollutants - such as frequency, time, and duration of commute - and the overall impact of commuting remains a matter of on-going scientific discovery.
Dr. Jenna Krall, assistant professor at the George Mason University College of Health and Human Services, is using statistical methods to better understand exposure to air pollution. Krall studies how commuting patterns impact exposure to fine particulate matter ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Tens of millions of patients around the world suffer from persistent and potentially life-threatening wounds. These chronic wounds, which are also a leading cause of amputation, have treatments, but the cost of existing wound dressings can prevent them from reaching people in need.
Now, a Michigan State University researcher is leading an international team of scientists to develop a low-cost, practical biopolymer dressing that helps heal these wounds.
"The existing efficient technologies are far too expensive for most health care systems, ...
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) launched a new online tool that could more quickly advance medical discoveries to reverse progressive hearing loss. The tool enables easy access to genetic and other molecular data from hundreds of technical research studies involving hearing function and the ear. The research portal called gene Expression Analysis Resource (gEAR) was unveiled in a study last month in Nature Methods. It is operated by a group of physician-scientists at the UMSOM Institute for Genome Sciences (IGS) in collaboration with their colleagues at other institutions.
The portal allows researchers to rapidly access data and provides easily interpreted visualizations of datasets. Scientists can also input ...
New Curtin University-led research has called into question existing health advice that mothers wait a minimum of two years after giving birth to become pregnant again, in order to reduce the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as preterm and small-for-gestational age births.
The research found that a World Health Organization (WHO) recommendation to wait at least 24 months to conceive after a previous birth may be unnecessarily long for mothers in high-income countries such as Australia, Finland, Norway and the United States.
Lead researcher ...
Errors in the metabolic processes of mitochondria are responsible for a variety of diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. Scientists needed to find out just how the necessary building blocks are imported into the complex biochemical apparatus of these cell areas. The TOM complex (translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane) is considered the gateway to the mitochondrion, the proverbial powerhouse of the cell. The working group headed by Professor Chris Meisinger at the Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Freiburg has now demonstrated - in human cells - how signaling molecules control this gate. A signaling protein called DYRK1A modifies the molecular machinery of TOM and makes it more permeable ...
Three decades ago, child development researchers found that low-income children heard tens of millions fewer words in their homes than their more affluent peers by the time they reached kindergarten. This "word gap" was and continues to be linked to a socioeconomic disparity in academic achievement.
While parenting deficiencies have long been blamed for the word gap, new research from the University of California, Berkeley, implicates the economic context in which parenting takes place -- in other words, the wealth gap.
The findings, published this month in the journal Developmental Science, provide the first evidence that parents may talk less to their kids when experiencing financial scarcity.
"We were interested in what happens when parents think about or experience financial scarcity ...
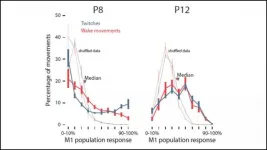
Electrical activity in the motor cortex of rats transforms from redundant to complex over the span of four days shortly after birth. Sleep twitches guide this metamorphosis, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Despite its name, the motor cortex doesn't control movement right off the bat. Early in development, this part of the brain is solely a sensory structure. Feedback from self-generated movements -- sleep twitches in particular -- may build representations of the body that will later orchestrate movement.
To characterize this transition, Glanz et al. recorded electrical activity from the motor cortex of rat pups eight and 12 days after birth while monitoring their behavior. ...