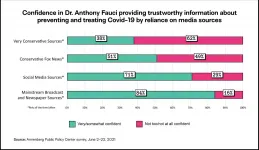
(Press-News.org) With more than two-thirds of American adults vaccinated with at least one dose of an authorized Covid-19 vaccine, the top U.S. health agencies retain the trust of the vast majority of the American public, as does Dr. Anthony Fauci, the public face of U.S. efforts to combat the virus, according to a new survey from the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania.
The survey revealed growing public confidence in both the safety and effectiveness of vaccines to prevent Covid-19.
But after months of attacks on Fauci in conservative and social media, the survey found that people who said they rely on conservative and very conservative media rather than other sources were more likely to have less confidence in Fauci's trustworthiness on Covid-19 and more likely to accept misinformation about him and misinformation and conspiracy theories about the authorized Covid-19 vaccines and the novel coronavirus.
The survey also found that a growing number of Americans - more than 1 in 3 - believes that the coronavirus was created by the Chinese government as a biological weapon.
"Our analysis of the data shows that there is good news and bad news here," said Kathleen Hall Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Public Policy Center. "Those who underestimate the lethality of Covid-19 or the safety of Covid-19 vaccination are less likely to accept a Covid-19 vaccination. The same is true of those who believe Covid-19 conspiracy theories. By contrast, those who trust health authorities are more likely to seek vaccination. Deceptive messages that undermine trust in a health expert such as Dr. Fauci are deeply worrisome."
The latest Annenberg Science Knowledge (ASK) survey was conducted among 1,719 U.S. adult respondents from June 2 - June 22, 2021. Data were weighted to represent the target U.S. adult population. The margin of error is ± 3.2 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. The panel survey is a follow-up to an END
Public trust in CDC, FDA, and Fauci holds steady, survey shows
But heavy users of conservative media have less confidence and are more likely to believe in conspiracy theories
2021-07-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insight into "training" highly reactive chemical compounds
2021-07-20
Led by Dr Jonas Warneke, researchers at the Wilhelm Ostwald Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at Leipzig University have made a decisive advance in the study of one type of highly reactive particles. Based on their research, they now understand the "binding preferences" of these particles.
Their research serves as the basis for the targeted use of these highly reactive molecules, for example, to generate new molecular structures or to bind hazardous chemical "waste" and in this way dispose of it. The researchers have now published their findings in the journal Chemistry - A European Journal, and their research was featured on the cover thanks to the excellent review they received.
What molecules and people have in common
Molecules and people actually have a lot in ...
15,000-year-old viruses discovered in Tibetan glacier ice
2021-07-20
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Scientists who study glacier ice have found viruses nearly 15,000 years old in two ice samples taken from the Tibetan Plateau in China. Most of those viruses, which survived because they had remained frozen, are unlike any viruses that have been cataloged to date.
The findings, published today in the journal Microbiome, could help scientists understand how viruses have evolved over centuries. For this study, the scientists also created a new, ultra-clean method of analyzing microbes and viruses in ice without contaminating it.
"These glaciers were formed gradually, and along with dust and ...
Automobile class society
2021-07-20
In order to correctly separate vehicles into classes, for instance for mobility pricing, one must be able to clearly distinguish mid-sized cars from upper class cars or small cars from compact cars. But this is becoming increasingly difficult: On photos, an Audi A4 looks almost the same as an Audi A6, a Mini One looks similar to a Mini Countryman. To date, there is no independent procedure for doing this.
Thus far, the classes in each country have been determined by experts - to a large extend at their own discretion. Empa researcher Naghmeh Niroomand has now developed a system that can classify cars worldwide based on their dimensions. Purely mathematical and fair. Thanks to it, the current classification ...
Fish friends help in a crisis
2021-07-20
FORT LAUDERDALE/DAVIE, Fla. - It's good to have friends.
Most humans have experienced social anxiety on some level during their lives. We all know the feeling - we show up to a party thinking it is going to be chock full of friends, only to find nearly all total strangers. While we typically attribute the long-lasting bonds of social familiarity to complex thinkers like humans, growing evidence indicates that we underestimate the importance of friendship networks in seemingly "simple" animals, like fish, and its importance for survival in the wild. To better understand how familiarity impacts social fishes, a group of research scientists studied this idea using schooling coral reef fish.
"We studied how the presence of ...
SARS-CoV-2: Achilles' heel of viral RNA
2021-07-20
FRANKFURT, GERMANY. When SARS-CoV-2 infects a cell, it introduces its RNA into it and re-programmes it in such a way that the cell first produces viral proteins and then whole viral particles. In the search for active substances against SARS-CoV-2, researchers have so far mostly concentrated on the viral proteins and on blocking them, since this promises to prevent, or at least slow down, replication. But attacking the viral genome, a long RNA molecule, might also stop or slow down viral replication.
The scientists in the COVID-19-NMR consortium, which is coordinated by Professor Harald Schwalbe from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Goethe University, have now completed an important ...
The environmental toll of disposable masks
2021-07-20
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Since the Covid-19 pandemic began last year, face masks and other personal protective equipment have become essential for health care workers. Disposable N95 masks have been in especially high demand to help prevent the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19.
All of those masks carry both financial and environmental costs. The Covid-19 pandemic is estimated to generate up to 7,200 tons of medical waste every day, much of which is disposable masks. And even as the pandemic slows down in some parts of the world, health care workers are expected to continue wearing masks most of the time.
That toll could be dramatically cut by adopting reusable masks, according to a new study from MIT that has calculated the financial ...
Machine learning models to help photovoltaic systems find their place in the sun
2021-07-20
With the looming threat of climate change, it is high time we embrace renewable energy sources on a larger scale. Photovoltaic systems, which generate electricity from the nearly limitless supply of sunlight energy, are one of the most promising ways of generating clean energy. However, integrating photovoltaic systems into existing power grids is not a straightforward process. Because the power output of photovoltaic systems depends heavily on environmental conditions, power plant and grid managers need estimations of how much power will be injected by photovoltaic systems so as to plan optimal generation and maintenance schedules, among other important operational aspects.
In line with modern trends, if something needs predicting, you can safely ...
Enzyme-based plastics recycling is more energy efficient, better for environment
2021-07-20
Researchers in the BOTTLE Consortium, including from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the University of Portsmouth, have identified using enzymes as a more sustainable approach for recycling polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a common plastic in single-use beverage bottles, clothing, and food packaging that are becoming increasingly relevant in addressing the environmental challenge of plastic pollution. An analysis shows enzyme-recycled PET has potential improvement over conventional, fossil-based methods of PET production across a broad spectrum of energy, carbon, and socioeconomic impacts.
The concept, if further developed and implemented at scale, could lead to ...
Brain 'noise' keeps nerve connections young
2021-07-20
Neurons communicate through rapid electrical signals that regulate the release of neurotransmitters, the brain's chemical messengers. Once transmitted across a neuron, electrical signals cause the juncture with another neuron, known as a synapse, to release droplets filled with neurotransmitters that pass the information on to the next neuron. This type of neuron-to-neuron communication is known as evoked neurotransmission.
However, some neurotransmitter-packed droplets are released at the synapse even in the absence of electrical impulses. These miniature release events -- or ...
"Springing forward" affects early birds less than night owls, study finds
2021-07-20
Every spring, the Daylight Saving Time shift robs people of an hour of sleep - and a new study shows that DNA plays a role in how much the "spring forward" time change affects individuals.
People whose genetic profile makes them more likely to be "early birds" the rest of the year can adjust to the time change in a few days, the study shows. But those who tend to be "night owls" could take more than a week to get back on track with sleep schedule, according to new data published in Scientific Reports by a team from the University of Michigan.
The study uses data from continuous sleep tracking ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Public trust in CDC, FDA, and Fauci holds steady, survey showsBut heavy users of conservative media have less confidence and are more likely to believe in conspiracy theories