(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON - A peer-reviewed study by the Environmental Working Group recommends stringent health-based exposure standards for both children and adults for radiofrequency radiation emitted from wireless devices. EWG's children's guideline is the first of its kind and fills a gap left by federal regulators.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Health, relies on the methodology developed by the Environmental Protection Agency to assess human health risks arising from toxic chemical exposures. EWG scientists have applied the same methods to radiofrequency radiation from wireless devices, including cellphones and tablets.
EWG recommends the Federal Communications Commission, or FCC, adjust its woefully outdated health standards for wireless radiation, last revised a quarter-century ago, well before wireless devices became ubiquitous, heavily used appliances synonymous with modern life. The recommendation draws on data from a landmark 2018 study from the National Toxicology Program, or NTP, one of the largest long-term studies on the health effects of radiofrequency radiation exposure.
EWG's new guidelines, the first developed in the U.S. to focus on children's health, recommend that children's exposure overall be 200 to 400 lower than the whole-body exposure limit set by the FCC in 1996.
The EWG recommended limit for so-called whole-body Specific Absorption Rate, or SAR, for children is 0.2 to 0.4 milliwatts per kilogram, or mW/kg. For adults, EWG recommends a whole-body SAR limit of 2 to 4 mW/kg, which is 20 to 40 times lower than the federal limit.
The FCC has not set a separate standard for children. Its standards for radiofrequency radiation set a maximum SAR of 0.08 watts per kilogram, or W/kg, for whole-body exposure and an SAR for localized spatial peak - the highest exposure level for a specific part of the body, such as the brain - of 1.6 W/kg for the general population.
The NTP studies examined the health effects of 2G and 3G wireless radiation and found there is "clear evidence" of a link between exposure to radiofrequency radiation and heart tumors in laboratory animals. Similar results were reported by a team of Italian scientists from the Ramazzini Institute.
Cellphone radiation was classified a "possible carcinogen" in 2011 by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, part of the World Health Organization, a conclusion based on human epidemiological studies that found an increased risk of glioma, a malignant brain cancer, associated with cellphone use.
EWG scientists say that more research is needed on the health impacts of the latest generation of communication technologies, such as 5G. In the meantime, EWG's recommendation for strict, lower exposure limits for all radiofrequency sources, especially for children.
When the FCC established its radiofrequency radiation limits, following the passage of the 1996 Telecommunications Act, relatively few Americans, and likely no children, owned and used cellphones.
Much has changed since the federal limits were set, including technology and how these devices are used. A survey completed by the nonprofit Common Sense Media in March 2020, just before the start of the Covid-19 spread in the U.S., found that 46 percent of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 67 percent of 5- to 8-year-olds, had their own mobile devices, such as a tablet or smartphone.
With remote learning, a necessity during the Covid-19 pandemic, phones, tablets and other wireless devices became a part of life for young children, tweens and teens nationwide.
"The FCC must consider the latest scientific research, which shows that radiation from these devices can affect health, especially for children," said Uloma Uche, Ph.D., EWG environmental health science fellow and lead author of the study.
"It has been 25 years since the FCC set its limits for radiofrequency radiation. With multiple sources of radiofrequency radiation in the everyday environment, including Wi-Fi, wireless devices and cell towers, protecting children's health from wireless radiation exposures should be a priority for the FCC," she added.
"We have grave concerns over the outdated approach the federal government has relied on to study the health effects of cellphone radiation and set its current safety limit and advice for consumers," said EWG President Ken Cook. "Government guidelines are a quarter-century old and were established at a time when wireless devices were not a constant feature of the lives of nearly every American, including children."
Reviewing 5G and other aspects of wireless technology should be the focus of public health agencies, noted Cook. "It is long past time the federal government made exposure to 5G wireless devices safe. We strongly believe those exposures deserve far more investigation and scientific rigor than has been applied to date."
"The evidence shows that children absorb more radiofrequency radiation than adults, and the developing body of a child is more vulnerable to such effects," said Olga Naidenko, Ph.D., EWG's vice president for science investigations and co-author of the study.
"More research on the safety and sustainability of wireless technology is essential," added Naidenko. "Meanwhile, there are simple steps everyone can take to protect their health, such as keeping wireless devices farther from their bodies."
There are a number of easy, precautionary steps consumers can take until the government conducts the rigorous scientific assessment the issue deserves, which should have occurred years ago.
"Based on our review of the health risks and the inadequacy of current standards to protect children, while the science evolves, it is perfectly reasonable for parents to consider minimizing or eliminating radiofrequency radiation sources at home by relying more on wired internet access, and to urge schools to take comparable steps to reduce classroom and campus exposure," said Cook.
Other health-protective tips for consumers who want to reduce radiofrequency radiation from wireless devices include using a headset or speaker, texting instead of talking, and limiting the time children spend on smart phones.
Find all of EWG's tips to reduce exposure to wireless radiation here.
EWG's recommendation for limits for radiofrequency radiation exposure is its latest effort to advance the public dialogue about science-based standards that protect public health.
INFORMATION:
The Environmental Working Group is a nonprofit, non-partisan organization that empowers people to live healthier lives in a healthier environment. Through research, advocacy and unique education tools, EWG drives consumer choice and civic action.
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers have found that acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19 resembles sepsis-caused kidney injury, and the immune response triggered by the infection plays a pivotal role.
The findings, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, also suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction -- a loss of function in cellular energy production -- is commonly found in kidney injury related to COVID-19. More than one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients report acute kidney injury, and sudden kidney failure is a risk factor for in-hospital mortality, according to studies published last ...
The remains of microscopic plankton blooms in near-shore ocean environments slowly sink to the seafloor, setting off processes that forever alter an important record of Earth's history, according to research from geoscientists, including David Fike at Washington University in St. Louis.
Fike is co-author of a new study published July 20 in Nature Communications.
"Our previous work identified the role that changing sedimentation rates had on local versus global controls on geochemical signatures that we use to reconstruct environmental change," said Fike, professor of earth and planetary sciences and director of environmental studies in Arts & Sciences.
"In this study, we investigated organic carbon loading, or how much ...
Experts say these unexpected healthcare costs may discourage people from seeking recommended preventive care.
Despite a sharp reduction in out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for preventive care since the Affordable Care Act was enacted in 2010, patients are still receiving unexpected bills for preventive services that should be free, according to a new study co-authored by a Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researcher.
Published in the journal Preventive Medicine, study found that total out-of-pocket costs billed for preventive services to Americans with employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) in 2018 ranged from $75.6 million to $219 million, with 1 in 4 patients who used preventive care incurring these charges.
"The ACA enabled great strides in making preventive care free to ...
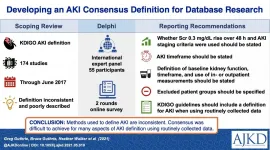
In an article published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), researchers found that among 176 studies on acute kidney injury, the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) definitions of kidney injury were inconsistently applied and 80% of studies did not define recovery of kidney function.
The KDIGO definition of AKI is used in both clinical practice and in research. This scoping review demonstrated that there is a wide variation of practice in how this definition is applied and also a lack of transparency about how researchers applied it. An international panel of experts in AKI was formed in an attempt to achieve consensus on how this definition should be applied. They participated in a Delphi process and while they were able to ...
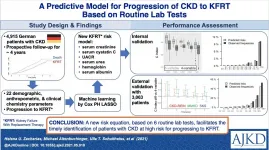
Researchers developed a new risk equation, based on six routinely available patient parameters, that yielded improved performance in estimating the risk of a chronic kidney disease (CKD) patient to progress to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT).
A novel risk equation for the timely identification of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients at risk for progressing to kidney failure requiring kidney replacement therapy was developed in 4,915 patients with CKD stage 1-5 with and without albuminuria, from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) Study. It includes six laboratory tests: ...
TUCSON, Ariz., July 20, 2021 -- The use of digital health technologies across health care and drug development has accelerated. A new paper titled "Digital Progression Biomarkers as Novel Endpoints in Clinical Trials: A Multistakeholder Perspective," co-authored by experts across diverse disciplines, highlights how new remote monitoring technologies present a tremendous opportunity to advance digital medicine in health care even further, specifically in Parkinson's disease. This perspective paper is co-authored by the academic leader of the largest funded project for digital technologies in Europe, Professor Lynn Rochester, University of Newcastle; European Medicines Agency (EMA) ...
Researchers revealed new insights into how acute myeloid leukemia (AML) develops and progresses, according to a study published in END ...
For children with Type 1 diabetes, the risk of experiencing a severe hypoglycemic episode is especially common -- and for parents, the threat of that happening in the middle of the night is especially frightening. Sudden and critical drops in blood sugar can go undetected overnight when the child is asleep, resulting in coma and death -- an event known as "dead in bed syndrome."
"A parent can check their child's glucose levels right before they go to bed and everything looks fine, then around 2 a.m. their blood sugar is dangerously low -- near comatose level," said Matthew Webber, associate professor of chemical and ...
WASHINGTON (July 20, 2021)--A new study of COVID-19 shutdowns in the United States reveals pronounced disparities in air pollution -- with disenfranchised, minority neighborhoods still experiencing more exposure to a harmful air pollutant compared to wealthier, white communities. This first-of-a-kind study published today by researchers at the George Washington University looks at how air pollution changed after schools and businesses shut down in March 2020 in attempts to curb the spread of COVID-19.
"New York and other major urban areas had cleaner air as many commuters and others stayed off the roads," Gaige Kerr, the lead researcher on the study and a research scientist at the GW Milken ...
Researchers want sexual assault survivors to know that it's normal to feel awful right after the assault, but that many will feel better within three months.
In a meta-analysis published in Trauma, Violence & Abuse, researchers found that 81% of sexual assault survivors had significant symptoms of post-traumatic stress (PTSD) one week after the assault. One month afterward - the first point in time that PTSD can be diagnosed - 75% of sexual assault survivors met criteria for the disorder. That figure dropped to 54% after three months and 41% after one year.
"One of the main takeaways is that the majority of recovery from post-traumatic stress happens in first three months," ...