Most studies of acute kidney injury are flawed due to non-use of standard definitions
2021-07-20
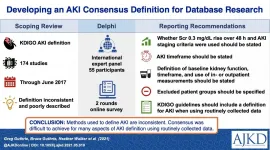
(Press-News.org) In an article published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), researchers found that among 176 studies on acute kidney injury, the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) definitions of kidney injury were inconsistently applied and 80% of studies did not define recovery of kidney function.
The KDIGO definition of AKI is used in both clinical practice and in research. This scoping review demonstrated that there is a wide variation of practice in how this definition is applied and also a lack of transparency about how researchers applied it. An international panel of experts in AKI was formed in an attempt to achieve consensus on how this definition should be applied. They participated in a Delphi process and while they were able to agree on some aspects of how the definition should be implemented, there were many areas in which no agreement could be reached. Dr Guthrie and his coauthors recommend that researchers clearly state how they applied the KDIGO definition for AKI when basing it absence or presence on healthcare data.
INFORMATION:
ARTICLE TITLE: Developing an AKI Consensus Definition for Database Research: Findings From a Scoping Review and Expert Opinion Using a Delphi Process
AUTHORS: Greg Guthrie, MB, ChB, Bruce Guthrie, PhD, Heather Walker, MB, ChB, Matthew T James, MD, PhD, Nicholas M Selby, MD, Marcello Tonelli, MD, SM, and Samira Bell, MD
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.05.019
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-20
Researchers developed a new risk equation, based on six routinely available patient parameters, that yielded improved performance in estimating the risk of a chronic kidney disease (CKD) patient to progress to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT).
A novel risk equation for the timely identification of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients at risk for progressing to kidney failure requiring kidney replacement therapy was developed in 4,915 patients with CKD stage 1-5 with and without albuminuria, from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) Study. It includes six laboratory tests: ...
2021-07-20
TUCSON, Ariz., July 20, 2021 -- The use of digital health technologies across health care and drug development has accelerated. A new paper titled "Digital Progression Biomarkers as Novel Endpoints in Clinical Trials: A Multistakeholder Perspective," co-authored by experts across diverse disciplines, highlights how new remote monitoring technologies present a tremendous opportunity to advance digital medicine in health care even further, specifically in Parkinson's disease. This perspective paper is co-authored by the academic leader of the largest funded project for digital technologies in Europe, Professor Lynn Rochester, University of Newcastle; European Medicines Agency (EMA) ...
2021-07-20
Researchers revealed new insights into how acute myeloid leukemia (AML) develops and progresses, according to a study published in END ...
2021-07-20
For children with Type 1 diabetes, the risk of experiencing a severe hypoglycemic episode is especially common -- and for parents, the threat of that happening in the middle of the night is especially frightening. Sudden and critical drops in blood sugar can go undetected overnight when the child is asleep, resulting in coma and death -- an event known as "dead in bed syndrome."
"A parent can check their child's glucose levels right before they go to bed and everything looks fine, then around 2 a.m. their blood sugar is dangerously low -- near comatose level," said Matthew Webber, associate professor of chemical and ...
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON (July 20, 2021)--A new study of COVID-19 shutdowns in the United States reveals pronounced disparities in air pollution -- with disenfranchised, minority neighborhoods still experiencing more exposure to a harmful air pollutant compared to wealthier, white communities. This first-of-a-kind study published today by researchers at the George Washington University looks at how air pollution changed after schools and businesses shut down in March 2020 in attempts to curb the spread of COVID-19.
"New York and other major urban areas had cleaner air as many commuters and others stayed off the roads," Gaige Kerr, the lead researcher on the study and a research scientist at the GW Milken ...
2021-07-20
Researchers want sexual assault survivors to know that it's normal to feel awful right after the assault, but that many will feel better within three months.
In a meta-analysis published in Trauma, Violence & Abuse, researchers found that 81% of sexual assault survivors had significant symptoms of post-traumatic stress (PTSD) one week after the assault. One month afterward - the first point in time that PTSD can be diagnosed - 75% of sexual assault survivors met criteria for the disorder. That figure dropped to 54% after three months and 41% after one year.
"One of the main takeaways is that the majority of recovery from post-traumatic stress happens in first three months," ...
2021-07-20
LAWRENCE -- A new paper appearing the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences gives new detail and understanding to the cultivation of corn, one of the United States' biggest cash crops.
The research by a team at the University of Kansas centers on "hybrid vigor," also known as "heterosis," a well-known phenomenon where crosses between inbred lines of corn and other crops produce offspring that outperform their parents in yield, drought resistance and other desirable qualities. Yet, the mechanisms underpinning heterosis are little understood despite over a century of intensive research.
The new PNAS research examines the relationship between heterosis and soil microbes, showing, ...
2021-07-20
Ten years after one of the largest nuclear accidents in history spewed radioactive contamination over the landscape in Fukushima, Japan, a University of Georgia study has shown that radioactive contamination in the Fukushima Exclusion Zone can be measured through its resident snakes.
The team's findings, published in the recent journal of Ichthyology & Herpetology, report that rat snakes are an effective bioindicator of residual radioactivity. Like canaries in a coal mine, bioindicators are organisms that can signal an ecosystem's health.
An abundant species in Japan, rat snakes travel short distances and can accumulate high levels of radionuclides. According ...
2021-07-20
A recent study led by Geoff Burns, an elite runner and postdoctoral researcher at the University of Michigan Exercise & Sport Science Initiative, compared the "bouncing behavior"--the underlying spring-like physics of running--in elite-level male runners (sub-four-minute milers) vs. highly trained but not elite runners.
Subjects ran on a treadmill instrumented with a pressure plate beneath the belt, so Burns and colleagues could see how much time they spent in the air and in contact with the ground. When running, muscles and limbs coordinate to act like a giant pogo stick, and those muscles, tendons and ligaments interact to recycle energy from step to step, Burns says.
The researchers looked at the basic physics of the runners ...
2021-07-20
Routine adolescent preventive visits provide important opportunities for promoting sexual and reproductive health and for preventing unintended pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections.
A new study END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Most studies of acute kidney injury are flawed due to non-use of standard definitions