(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - Small-scale. Short-lived. All digital. Out of public view. That's how a new form of collective worker resistance is unfolding in China's app-based food delivery economy, new Cornell University research finds.
Though highly fragmented and not always successful, "mini-strikes" by small groups of food couriers - conducted via WeChat - reflect a new form of leverage, suggest Chuxuan "Victoria" Liu and Eli Friedman, associate professor in the ILR School.
Food couriers are able to maintain complete physical invisibility, and each individual worker can 'strike' from anywhere, they write.
The scholars interviewed couriers, in-person and online, who delivered food for Ele.me, an Alibaba-owned company that controlled nearly half the nation's food-delivery market.
Platform-based delivery work has grown exponentially over the past decade. In 2020, Ele.me and Meituan, a slightly larger competitor, together had more than 8 million registered food-delivery couriers, the result of rapid growth achieved in part through exploitative working conditions, according to the researchers.
Friedman said scholars have wondered whether high levels of worker dissatisfaction seen in manufacturing would appear in this new sector. Their research determined it has - if you know where to look.
In addition to crowd sourced freelance couriers who work individually, Ele.me relies on a network of subcontractors that operate "stations" within city districts to provide restaurants with more reliable delivery services.
Like the workers themselves, the app rewards or punishes stations financially based on metrics including numbers of deliveries, worker attendance, on-time performance and customer ratings. That pressure on stations creates bargaining power for couriers who may choose to stay offline during peak lunch and dinner times.
"Simply by refusing to login to the system," they wrote, "a handful of couriers can cause considerable damage to the station's statistics."
Significantly, the government is either unable to monitor such small-scale labor resistance or tolerates it, since it causes minimal social disruption and appears apolitical.
"We've seen in the last few years that any kind of collective, coordinated action in China - for all kinds of activists - is really dangerous," Friedman said. "This refines our understanding of the way public protest can work in light of that new, highly repressive environment, and the role digital media can play in fomenting that kind of action, even on a small scale."
Strikes by food couriers are distinctive for their very small numbers, short duration and concealed nature, the authors wrote, revealing "one of the ways that labor unrest has evolved alongside shifting political, economic and technological conditions."
INFORMATION:
The study "Resistance Under the Radar: Organization of Work and Collective Action in China's Food Delivery Industry," was published in the July issue of The China Journal.
For additional information, see this Cornell Chronicle story.
Tuesday, July 20, 2021, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study demonstrates that adults with obesity lost significantly more weight when they had access to medications for chronic weight management in conjunction with their employer-based weight management program, compared to adults who did not have access to the medications. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Obesity is a complex disease that is caused by multiple factors, including genetic, environmental, and biological. A lifestyle intervention with a focus on nutrition and exercise is often not enough to treat obesity, which is a chronic disease that requires long-term therapy. The U.S. Food and Drug ...
WASHINGTON - A peer-reviewed study by the Environmental Working Group recommends stringent health-based exposure standards for both children and adults for radiofrequency radiation emitted from wireless devices. EWG's children's guideline is the first of its kind and fills a gap left by federal regulators.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Health, relies on the methodology developed by the Environmental Protection Agency to assess human health risks arising from toxic chemical exposures. EWG scientists have applied the same methods to radiofrequency radiation from wireless devices, ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers have found that acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19 resembles sepsis-caused kidney injury, and the immune response triggered by the infection plays a pivotal role.
The findings, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, also suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction -- a loss of function in cellular energy production -- is commonly found in kidney injury related to COVID-19. More than one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients report acute kidney injury, and sudden kidney failure is a risk factor for in-hospital mortality, according to studies published last ...
The remains of microscopic plankton blooms in near-shore ocean environments slowly sink to the seafloor, setting off processes that forever alter an important record of Earth's history, according to research from geoscientists, including David Fike at Washington University in St. Louis.
Fike is co-author of a new study published July 20 in Nature Communications.
"Our previous work identified the role that changing sedimentation rates had on local versus global controls on geochemical signatures that we use to reconstruct environmental change," said Fike, professor of earth and planetary sciences and director of environmental studies in Arts & Sciences.
"In this study, we investigated organic carbon loading, or how much ...
Experts say these unexpected healthcare costs may discourage people from seeking recommended preventive care.
Despite a sharp reduction in out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for preventive care since the Affordable Care Act was enacted in 2010, patients are still receiving unexpected bills for preventive services that should be free, according to a new study co-authored by a Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researcher.
Published in the journal Preventive Medicine, study found that total out-of-pocket costs billed for preventive services to Americans with employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) in 2018 ranged from $75.6 million to $219 million, with 1 in 4 patients who used preventive care incurring these charges.
"The ACA enabled great strides in making preventive care free to ...
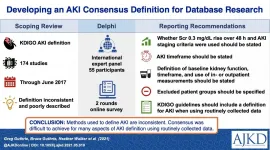
In an article published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), researchers found that among 176 studies on acute kidney injury, the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) definitions of kidney injury were inconsistently applied and 80% of studies did not define recovery of kidney function.
The KDIGO definition of AKI is used in both clinical practice and in research. This scoping review demonstrated that there is a wide variation of practice in how this definition is applied and also a lack of transparency about how researchers applied it. An international panel of experts in AKI was formed in an attempt to achieve consensus on how this definition should be applied. They participated in a Delphi process and while they were able to ...
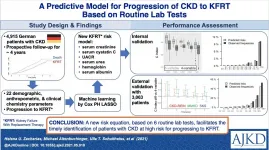
Researchers developed a new risk equation, based on six routinely available patient parameters, that yielded improved performance in estimating the risk of a chronic kidney disease (CKD) patient to progress to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT).
A novel risk equation for the timely identification of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients at risk for progressing to kidney failure requiring kidney replacement therapy was developed in 4,915 patients with CKD stage 1-5 with and without albuminuria, from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) Study. It includes six laboratory tests: ...
TUCSON, Ariz., July 20, 2021 -- The use of digital health technologies across health care and drug development has accelerated. A new paper titled "Digital Progression Biomarkers as Novel Endpoints in Clinical Trials: A Multistakeholder Perspective," co-authored by experts across diverse disciplines, highlights how new remote monitoring technologies present a tremendous opportunity to advance digital medicine in health care even further, specifically in Parkinson's disease. This perspective paper is co-authored by the academic leader of the largest funded project for digital technologies in Europe, Professor Lynn Rochester, University of Newcastle; European Medicines Agency (EMA) ...
Researchers revealed new insights into how acute myeloid leukemia (AML) develops and progresses, according to a study published in END ...
For children with Type 1 diabetes, the risk of experiencing a severe hypoglycemic episode is especially common -- and for parents, the threat of that happening in the middle of the night is especially frightening. Sudden and critical drops in blood sugar can go undetected overnight when the child is asleep, resulting in coma and death -- an event known as "dead in bed syndrome."
"A parent can check their child's glucose levels right before they go to bed and everything looks fine, then around 2 a.m. their blood sugar is dangerously low -- near comatose level," said Matthew Webber, associate professor of chemical and ...